


























































































Estude fácil! Tem muito documento disponível na Docsity

Ganhe pontos ajudando outros esrudantes ou compre um plano Premium


Prepare-se para as provas
Estude fácil! Tem muito documento disponível na Docsity
Prepare-se para as provas com trabalhos de outros alunos como você, aqui na Docsity
Os melhores documentos à venda: Trabalhos de alunos formados
Prepare-se com as videoaulas e exercícios resolvidos criados a partir da grade da sua Universidade
Responda perguntas de provas passadas e avalie sua preparação.

Ganhe pontos para baixar
Ganhe pontos ajudando outros esrudantes ou compre um plano Premium
Comunidade
Peça ajuda à comunidade e tire suas dúvidas relacionadas ao estudo
Descubra as melhores universidades em seu país de acordo com os usuários da Docsity
Guias grátis
Baixe gratuitamente nossos guias de estudo, métodos para diminuir a ansiedade, dicas de TCC preparadas pelos professores da Docsity
Esta é a Resolução Cap 10- Método dos Trabalhos Virtuais Mecânica Beer
Tipologia: Exercícios

Oferta por tempo limitado
Compartilhado em 10/09/2020
4.9
(8)13 documentos
1 / 134

Esta página não é visível na pré-visualização
Não perca as partes importantes!






























































































Em oferta
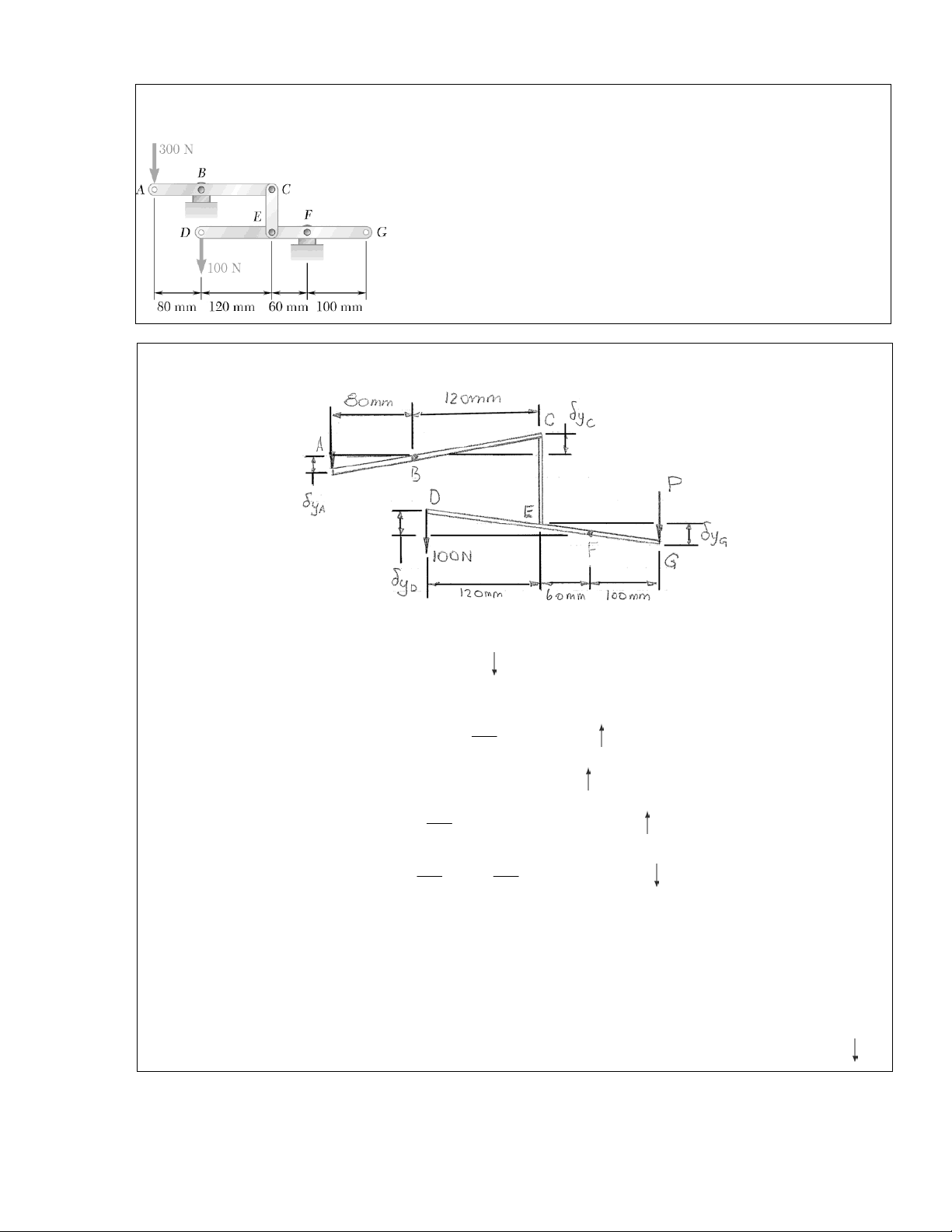
Determine the vertical force P which must be applied at G to maintain the equilibrium of the linkage.
Assuming
δ y A
it follows
120
C (^) 80 A A δ y = δ y = δ y
δ y (^) E = δ yC = 1.5δ yA
δ y = δ y = δ y = δ y
δ y = δ y = δ y = δ y
Then, by Virtual Work
Determine the vertical force P which must be applied at G to maintain the equilibrium of the linkage.
Link ABC
Link DEFG
Assume
δθclockwise Then for point C
and for point D
And for link DEFG
δ xD = 15 δφ
∴ 5 δ θ = 15 δφ
or
δφ = δθ
Then
4 2 2 in. G 3 δ δφ δθ
Now δ yG = δ G cos 45°
2 cos 45 3
δθ
in. 3
δθ
Then, by Virtual Work.
δθ δθ P δθ
or P =40 lb W
Determine the couple M which must be applied to member DEFG to maintain the equilibrium of the linkage.
Assuming
δ y A
it follows
120
C (^) 80 A A δ y = δ y = δ y
δ y (^) E = δ yC = 1.5δ yA
δ y = δ y = δ y = δ y
E A A
y y y δ δ δφ= = = δ
Then, by Virtual Work:
δ y (^) A δ y (^) A M δ yA
M = + 6000 N mm⋅ M = 6.00 N m⋅ W
An unstretched spring of constant 4 lb/in. is attached to pins at points C and I as shown. The pin at B is attached to member BDE and can slide freely along the slot in the fixed plate. Determine the force in the spring and the horizontal displacement of point H when a 20-lb horizontal force directed to the right is applied ( a ) at point G , ( b ) at points G and H.
First note:
xG = 3 xD ⇒ δ xG = 3 δ xD
xH = 4 xD ⇒ δ xH = 4 δ xD
xI = 5 xD ⇒ δ xI = 5 δ xD
( a ) Virtual Work δ U = 0: FG δ xG − FSP δ xI = 0
thus, FSP = 12.00 lb T W
Now FSP = k ∆ xI
Thus, ∆ x (^) I =3 in.
and
δ x D = δ xH = δ xI
∴ ∆ xH = ∆ xI
3 in. 5
= or ∆ x (^) H = 2.40 in. W
( b ) Virtual Work: δ U = 0: FG δ xG + FH δ xH − FSP δ xI = 0
thus, FSP = 28.0 lb T W
Now FSP = k ∆ xI
Thus, ∆ x (^) I =7 in.
From part ( a )
∆ x (^) H = ∆ xI
7 in. 5
= or ∆ x (^) H = 5.60 in. W
Now FSP = k ∆ xI
Thus, ∆ x (^) I =3 in.
From part ( a )
∆ x (^) H = ∆ xI
3 in. 5
= or ∆ x (^) H = 2.40 in. W
Knowing that the maximum friction force exerted by the bottle on the cork is 300 N, determine ( a ) the force P which must be applied to the corkscrew to open the bottle, ( b ) the maximum force exerted by the base of the corkscrew on the top of the bottle.
From sketch
yA = 4 yC
Thus, δ yA = 4 δ yC
( a ) Virtual Work:
δ U = 0: P δ y (^) A − F δ yC = 0
( b ) Free body: Corkscrew
Σ F (^) y = 0: R + P − F = 0
The mechanism shown is acted upon by the force P ; derive an expression for the magnitude of the force Q required for equilibrium.
Virtual Work:
Have x (^) A =2 sin l θ
δ x (^) A = 2 cos l θ δθ
and yF =3 cos l θ
δ yF = − 3 sin l θ δθ
Virtual Work: δ U = 0: Q δ x (^) A + P δ yF = 0
tan 2
Q = P θW
Knowing that the line of action of the force Q passes through point C , derive an expression for the magnitude of Q required to maintain equilibrium
Have yA = 2 cos l θ ; δ y (^) A = −2 sin l θ δθ
CD l CD l θ θ = δ = δθ
Virtual Work:
P l Q l θ θ δθ δθ
sin 2 cos /
θ θ
The slender rod AB is attached to a collar A and rests on a small wheel at C. Neglecting the radius of the wheel and the effect of friction, derive an expression for the magnitude of the force Q required to maintain the equilibrium of the rod.
For ∆ AA C ′ :
A C ′^ = a tan θ
A cos 2
a δ y δθ θ
For ∆ CC B ′ :
BC ′^ = l sin θ− A C ′
= l sin θ − a tan θ
yB = BC ′= l sin θ− a tan θ
B cos^ cos 2
a δ y l θδθ δθ θ
Virtual Work:
δ U = 0: Q δ y (^) A − P δ yB = 0
cos^2 cos^ cos^20
a a Q δθ P l θ δθ θ θ
cos 2 cos cos^2
a a Q P l θ θ θ
Q P l cos^3 a
θ
A double scissor lift table is used to raise a 1000-lb machine component. The table consists of a platform and two identical linkages on which hydraulic cylinders exert equal forces. (Only one linkage and one cylinder are shown.) Each member of the linkage is of length 24 in., and pins C and G are at the midpoints of their respective members. The hydraulic cylinder is pinned at A to the base of the table and at F which is 6 in. from E. If the component is placed on the table so that half of its weight is supported by the system shown, determine the force exerted by each cylinder when θ = 30 .°
First note y (^) H = 2 L sin θ L =24 in. (length of link)
Then δ yH = 2 L cos θδθ
Now
2 2 3 5 cos sin 4 4
d (^) AF L θ L θ
(^1 9) 16sin 2 4
= L + θ
Then
2
2 16sin cos (^4 2 9) 16sin AF
d
θ θ δ δθ θ
2
sin cos 4 9 16sin
L θ θ δθ θ
=
Virtual Work:
cyl
δ U F δ d (^) AF W δ yH
2
sin cos 4 500 lb 2 cos 0 9 16sin
θ θ δθ θδθ θ
and (^) cyl 2
sin 250 lb 9 16sin
F θ θ
=
Finally, (^) cyl 2
sin 30 250 lb 9 16sin 30
F ° =
or F cyl (^) = 1803 lbW
Derive an expression for the magnitude of the couple M required to maintain the equilibrium of the linkage shown.
ABC : y (^) B = a sin θ ⇒ δ yB = a cosθδθ
yC = 2 a sin θ ⇒ δ yC = 2 a cosθδθ
CDE : Note that as ABC rotates counterclockwise, CDE rotates clockwise while it moves to the left.
Then δ yC = a δφ
or 2 a cos θδθ = a δφ
or δφ=2 cosθδθ
Virtual Work:
δ U = 0: − P δ yB − P δ yC + M δφ= 0
or
M = Pa W
Derive an expression for the magnitude of the couple M required to maintain the equilibrium of the linkage shown.
Have
xB = l cos θ
δ xB = − l sin θδθ (1)
yC = l sin θ
δ yC = l cos θδθ
Now
δ x B = l δθ
Substituting from Equation (1)
1 sin 2
− l θδθ = l δφ
or δφ = −2sinθδθ
Virtual Work:
δ U = 0: M δϕ + P δ yC = 0
or 1 cos 2 sin
M Pl θ θ
2 tan
Pl M θ
The pin at C is attached to member BCD and can slide along a slot cut in the fixed plate shown. Neglecting the effect of friction, derive an expression for the magnitude of the couple M required to maintain equilibrium when the force P which acts at D is directed ( a ) as shown, ( b ) vertically downward, ( c ) horizontally to the right.
Have xD = l cos θ
δ xD = − l sin θδθ
yD = 3 sin l θ
δ y (^) D = 3 cos l θδθ
( a ) For P directed along BCD , β =θ
( b ) For P directed , β = 90 °
M = 3 Pl cos θW
( c ) For P directed , β = 180 °
M = Pl sin θW
A 1-kip force P is applied as shown to the piston of the engine system. Knowing that AB = 2.5 in.and BC = 10 in., determine the couple M required to maintain the equilibrium of the system when ( a ) θ = 30 ,° ( b ) θ = 150 .°
Analysis of the geometry:
Law of Sines
sin sin AB BC
sin sin
φ = θ (1)
Now
xC = AB (^) cos θ+ BC cos φ
δ xC = − AB sin θδθ− BC sinφδφ (2)
Now, from Equation (1) cos cos
φδφ= θδθ
or cos cos
θ δφ δθ φ
From Equation (2)
cos sin sin cos C
x AB BC BC
θ δ θδθ φ δθ φ
cos C
δ x θ φ φ θ δθ φ
Then
cos C
AB x
θ φ δ δθ φ
= −