


Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Solved worksheet on acids bases and salts
Typology: Exercises
1 / 2

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!


in aqueous solution to form 1-l ro -e ions.
HN0 3 (aq) ➔ H. (aq) + N03- (aq)
HCI (aq) ➔ H + l°'-i\ +- t L- ( °' 1,.-)
in aqueous solution to form ro^ ì^ e.ions.
KOH (aq) ➔ K• (aq) + OH- (aq)
NaOH (aq) ➔ N CJ+ f OdÌ,_ + Q H - l °'-q,._ \
8� d
-R V, ions nor hycJ ro ')l ìo\Rws.
KCI (aq) ➔ K• (aq) +^ ci- (aq)
NaCl(aq) ➔ J\l0t-.
/C<._Q \ t C.,L-L°'l-'\
V-
HBr A
:i
{\
Ez
t-�,- KCI
���l�: nB^ -^
l<._-1- (^) �D�- Al(OHh
--1-- (^) ro y^
o._ t J Df\ - NaCI
o
1-\�
s
A
A
J-l_
C,l -
-s
,-I- 1-t-- K--t- (^) p Q y
dt- t11J
Acids and bases can a/so be identified using an operational definition. Operational
definitions are simply a /ist of properties.
solution.
♦ Acids react with some metals to produce ,._,
,
_:μ.
♦ Because aqueous acid solutions conduct electricity, t are identified as
,
with
b 9
I
♦ Bases react
_
with ci\
♦ Bases turn I '{_ I � o__f(ijiff'fyent colors.
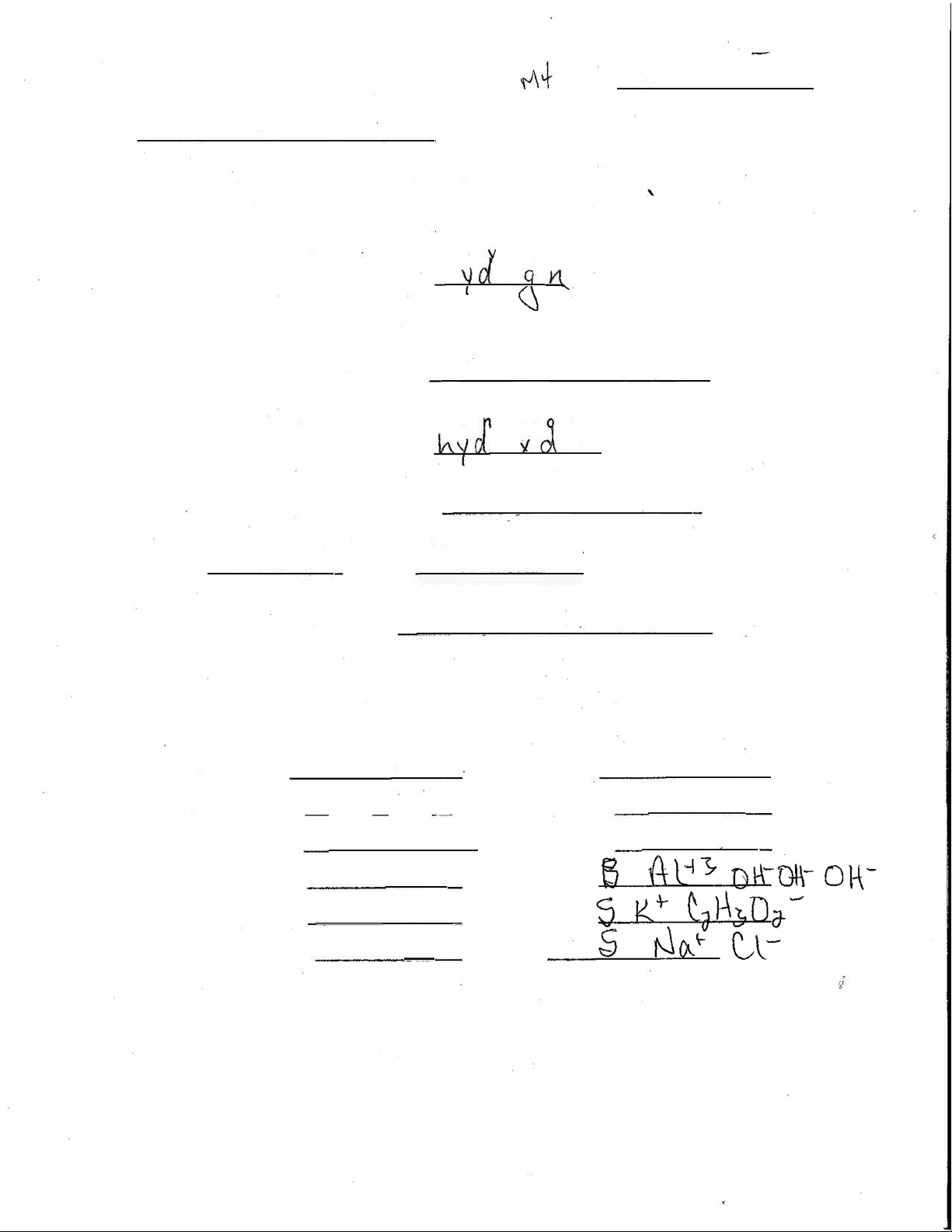
Naminq Acids. Bases. and Salts
Since bases and salts are ·:CON \ C compounds, they are named in the us �
KN0 3 'p-c,,ss·,v..tM.. \l);-.ro__--�NH.oH IJiM(Y,ti\l\ V-.VV. r- �
d..vO',( Ì
► Binary acids cons,st of (^) J----. elements, the first being r _tV_
Binary acids are named using the format:
hydro{root word of second element)ic acid
change the ending of the polyatomic ion's nome and add the word "acid":
Nome the following acids:
HF .l. �
�vot\J-..orì e;__ o.s..:\d.__H2s
�(&, .\ rl,o\ov'OVV..', e_ (}.1:_',J.ç