

























Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Material Type: Lab; Professor: Gotel; Class: Computer Programming I; Subject: Computer Science; University: Pace University-New York; Term: Unknown 1989;
Typology: Lab Reports
1 / 35

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




























Object Reference Variables
Dr Olly Gotel
ogotel@pace.edu
http://csis.pace.edu/~ogotel
Having problems?
-- Come see me or call me in my office hours
-- Use the CSIS programming tutors
shopping questions in lab 2
object things anyway?
not the same as passing primitives
Finish Lab 2 after this week
Car myCar = new Car();
1 - Declare a reference variable , of class type Car, called myCar
2 - Create a new Car object
3 - Link the new object to the named reference variable
What is going on here? 3 distinct things…
Need to step back a moment…
(Called an object reference variable)
(1)
(3) (2)
stack; reference variable is called myCar; it is of type Car
memory (where to find an object); we know how much
memory we need to hold an address
heap
not know how big it will be
think of the reference variable as a locator for the object
variable - to know the values it can take and
permissible operations
be used - so it can allocate space in memory
most efficient
letter
Java, others are
represented using
called object reference
types
Integer data types – no fractions
Floating point data
types –fractions
types (like a bank account, an address, etc)
to represent a sequence of characters (char)
strings, so strings are actually objects, which requires
a bit of extra code to use
“This is a string”
directly in the container
objects in the container (these are called object
reference variables), the objects are elsewhere
In Java, we are VERY
concerned with references
Your object reference variable
actually points to the object!
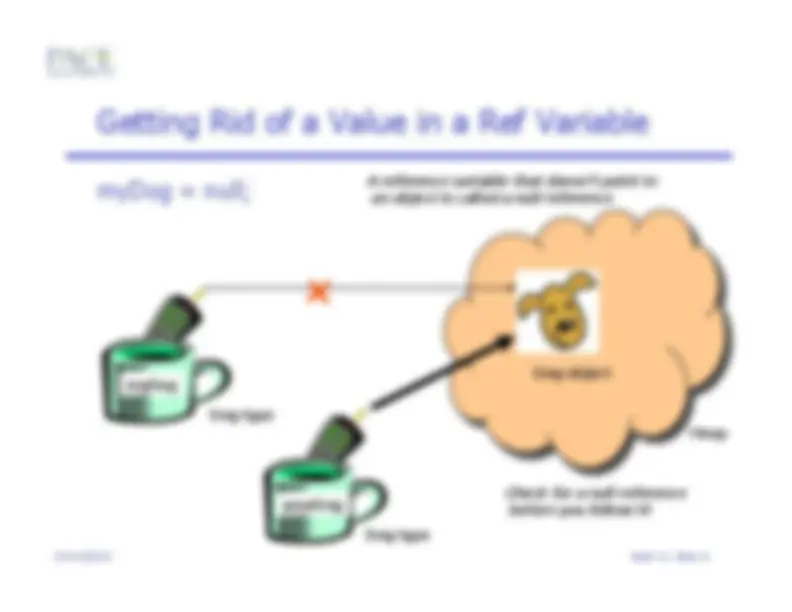
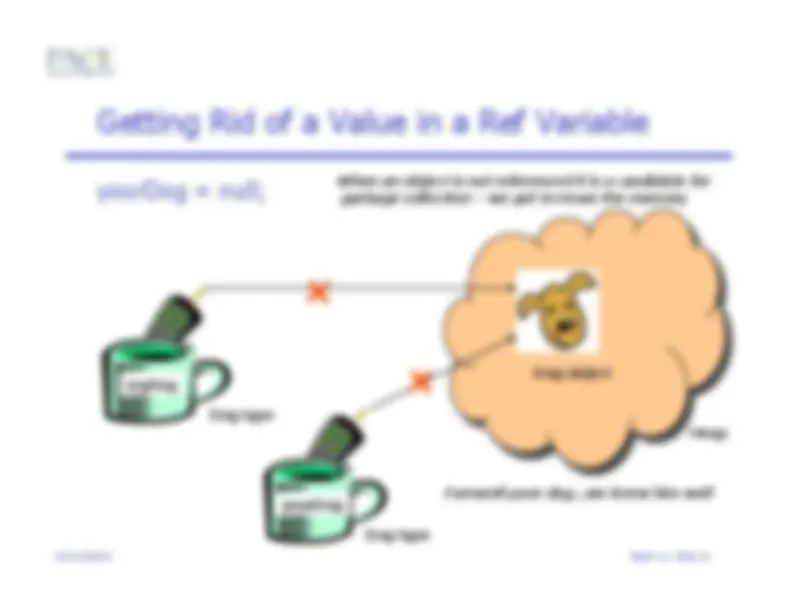
Dog myDog = new Dog();
Dog myDog = new Dog();
Dog myDog = new Dog();
Dog myDog = new Dog();
Example from [Sierra & Bates 2003] - best ever!
Dog type
Dog type
myDog
myDog
Dog object
Dog object
Index cards
Can’t do:
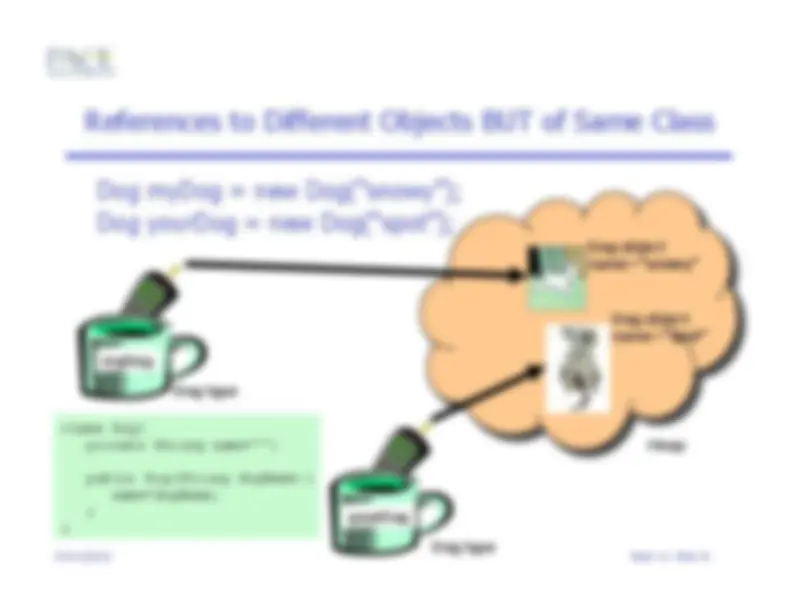
Dog myDog = new Cat();
myDog can only point to a Dog object!
But we could do:
Animal myDog = new Dog();
If Dog is defined as a type of Animal. Later!
Ouch!
CS121/IS223 Week 12, Slide 20
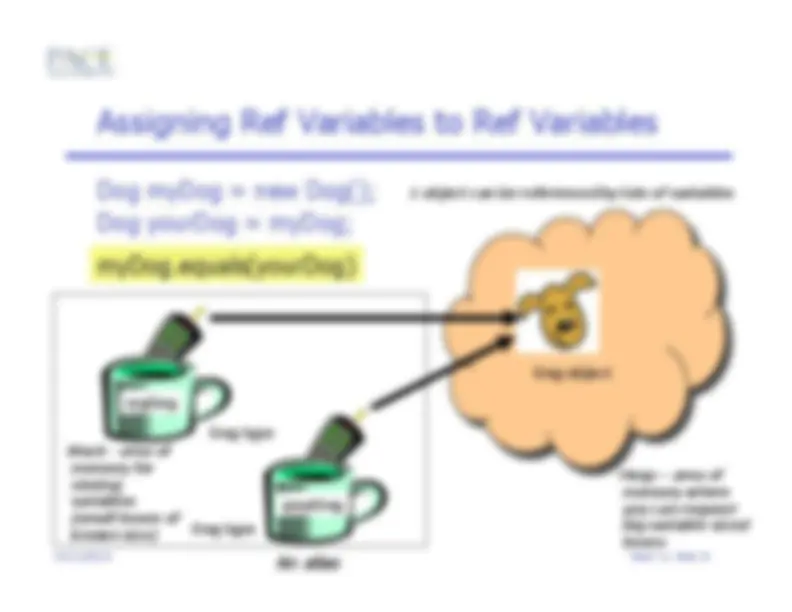
Dog myDog = new Dog();
Dog yourDog = myDog;
Dog type
myDog
Dog object
Heap – area of
memory where
you can request
big variable-sized
boxes
Dog type
yourDog
Stack - area of
memory for
storing
variables
(small boxes of
known size)
An alias
myDog.equals(yourDog)
1 object can be referenced by lots of variables