









Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
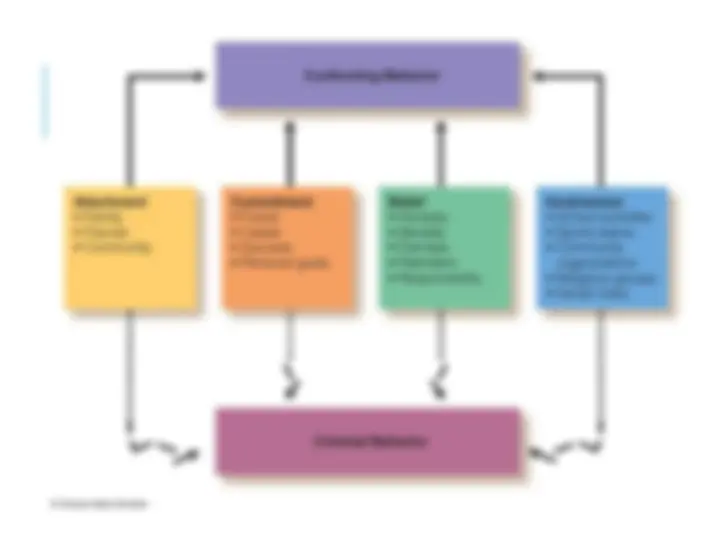
Hirschi control theory or bond theory have 4 key components: attachment, commitment, involvement, and belief.
Typology: Slides
1 / 14

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!









Travis Hirschi’s social bonding theory may be the most popular criminological theory today. First presented in 1969, Hirschi questioned why people do not commit crime. Hirschi theorized that crime is more common among individuals with weakened bonds to societal institutions.
Developed by Travis Hirschi The Theory: Assumes that all people have the capacity to be delinquent Preventing most people from engaging in delinquency is a “bonding” to conventional society Hirschi identifies 4 elements to the social bond Travis Hirschi
Social Bond Theory Travis Hirschi Commitment involves the time, energy, and effort expended in conventional lines of action, such as getting an education and saving money for the future. Commitment : to conventional lines of action.
Social Bond Theory Travis Hirschi Heavy involvement in conventional activities leaves little time for illegal behavior. Involvement : with activities that promote the interests of society
Testing Social Bond Theory Hirschi’s Supporting Research Youths who were strongly attached to their parents were less likely to commit criminal acts. Commitment to conventional values, such as striving to get a good education and refusing to drink alcohol and “cruise around,” was indicative of conventional behavior. Youths involved in conventional activity, such as homework, were less likely to engage in criminal behavior. Youths involved in unconventional behavior, such as smoking and drinking, were more delinquency prone. Youths who maintained weak and distant relationships with people tended toward delinquency. Those who shunned unconventional acts were attached to their peers. Delinquents and nondelinquents shared similar beliefs about society.
Physical and sexual abuse are thought to contribute to delinquency Children of teen mothers at higher risk Poor grades and negative attitudes about teachers more likely to be delinquent Religiosity helps prevent delinquency/criminal behavior?
Social Bonding Theory Evaluation of the theory Relationship between social bonding and delinquency pretty weak Explains minor offending more so than serious offending Causal order Difficult to distinguish between commitment and involvement
Testing Social Bond Theory Opposing Views Friendship Not all elements of the bond are equal Deviant peers and parents Restricted in scope Changing bonds Crime and social bonds