
































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
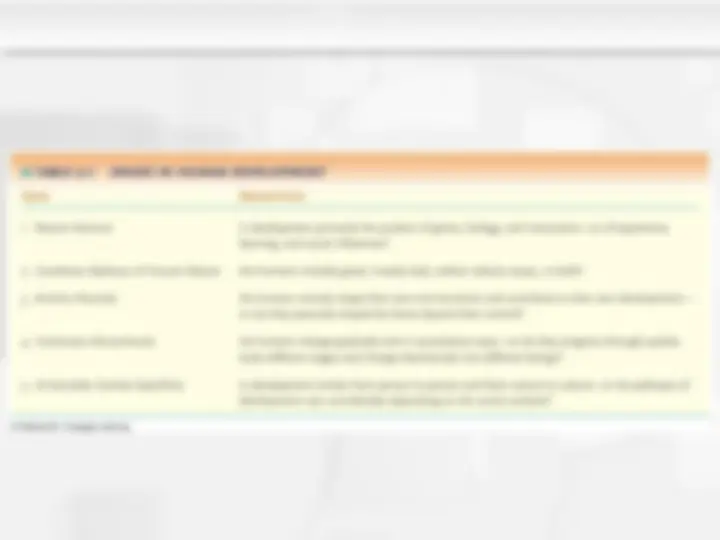
An overview of various theories of human development, including the works of Freud, Erikson, Piaget, and others. It covers the key issues in human development, the theories' distinct features, and their strengths and weaknesses. Students will learn about the role of instincts, unconscious motivation, stages of development, and the interaction of nature and nurture.
What you will learn
Typology: Slides
1 / 39

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
































Learning Objectives
development?
Erikson, Skinner, Bandura, Piaget, and Gottlieb – stand on each of these issues?
Other Assumptions About Human Nature
influential?
determination or by others
change
transformation
Freud: Psychoanalytic Theory
energy ( Libido )
Freud’s Psychosexual Development
mechanisms
personality
Learning Objectives
compare to Freud’s theory?
psychosocial stages?
Erik Erikson
Learning Objectives
theories covered in this chapter: Watson’s classical conditioning, Skinner’s operant conditioning, and Bandura’s social-cognitive theory?
the learning theories?
Learning Theories: Classical Conditioning
on observable behavior only
Learning Theories: Operant Conditioning
environmental consequences