













Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
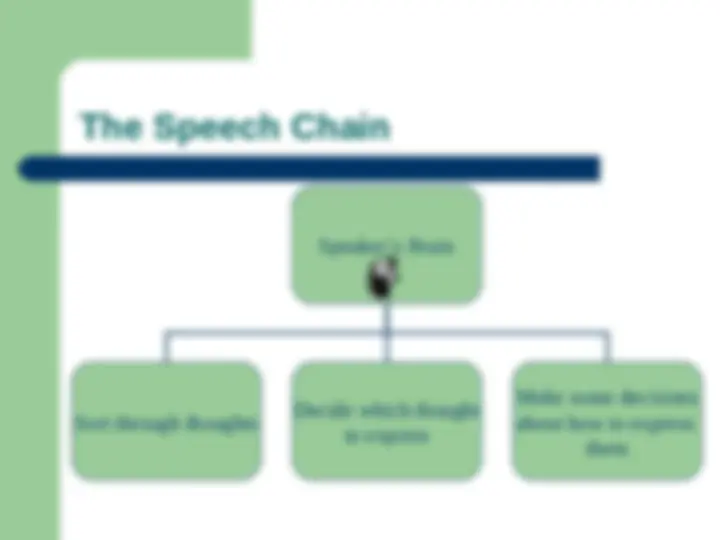
The speech chain theory by denes and pinson, focusing on the speaker's brain to listener's brain process. It also introduces charles f. Hockett's essay 'the origin of speech' and his thirteen design features that distinguish human speech from other animal communication. These features include the vocal-auditory channel, broadcast transmission and directional reception, rapid fading, interchangeability, total feedback, specialization, semanticity, arbitrariness, discreteness, displacement, productivity, duality of patterning, and traditional transmission.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 20

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!













Finish movie/Lecture In-class project
He wrote an essay entitled “The Origin of Speech”. He describes the “ thirteen-design-features ” of language. These features SEPARATE human speech form other forms of animal communication.
2. Broadcast Transmission and Directional Reception Sending and Receiving Signals When speech is produced, it radiates in all directions and can be received by any listener who is in range. The listener that can hear well can compare the loudness and timing of the signals in each ear and can determine the direction from which the sound is coming.
2. Broadcast Transmission and Directional Reception Sending and Receiving Signals When speech is produced, it radiates in all directions and can be received by any listener who is in range. The listener that can hear well can compare the loudness and timing of the signals in each ear and can determine the direction from which the sound is coming.
If you can say it, I can say it Any human being can say anything that is said by any other human being. Males and females can produce the same speech forms.
Did I Say That?...Did I Mean That? We monitor what we say and how we say it. We get feedback from our senses.
Sending Messages Loud and Clear Humans convey very specific messages with words having relatively stable relationships with the people, things, events and concepts they represent.
Because we say so! We use words to refer to people, things, events and concepts in human experiences that do not directly reflect their referents.
Back to the Future Humans can talk about things that are distant in time and space.
The Creativity of the Mind and Mouth This in one of the most important design-features of human speech. We have the ability to be creative in our communication efforts.
Born to Talk Speech is instinctive to humans. We have a genetic or biological capacity for language so powerful that few environmental factors can stop the acquisition of speech.
Semanticity Displacement Productivity Traditional Transmission