









Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An introduction to the Method of Sections, a technique used in engineering analysis to determine forces in truss members. The method involves dividing a truss into two parts by making an imaginary cut, and then applying the principles of equilibrium to find the internal forces. examples and quiz questions to help students understand the concept.
Typology: Study Guides, Projects, Research
1 / 18

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!











In-Class Activities :
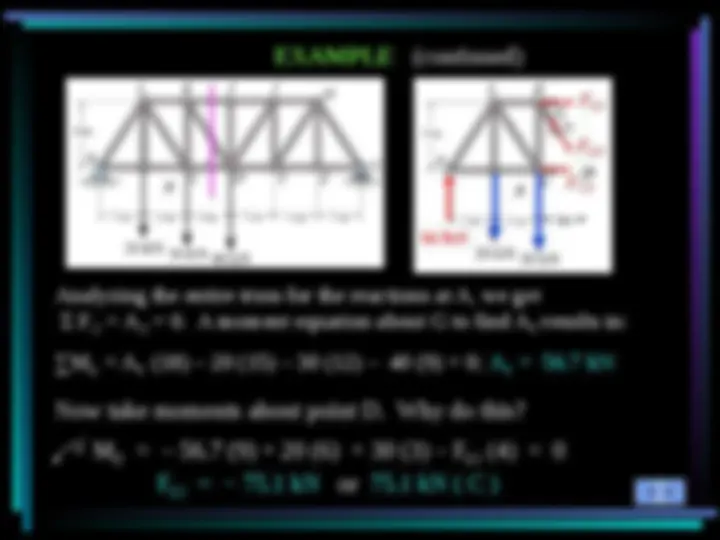
In the method of sections, a truss is divided into two parts by taking an imaginary “cut” (shown here as a-a) through the truss. Since truss members are subjected to only tensile or compressive forces along their length, the internal forces at the cut members will also be either tensile or compressive with the same magnitude as the forces at the joint. This result is based on the equilibrium principle and Newton’s third law.
a) Take a cut through members KJ, KD and CD. b) Work with the left part of the cut section. Why? c) Determine the support reactions at A. What are they? d) Apply the E-of-E to find the forces in KJ, KD and CD. Given : Loads as shown on the truss. Find : The force in members KJ, KD, and CD. Plan:
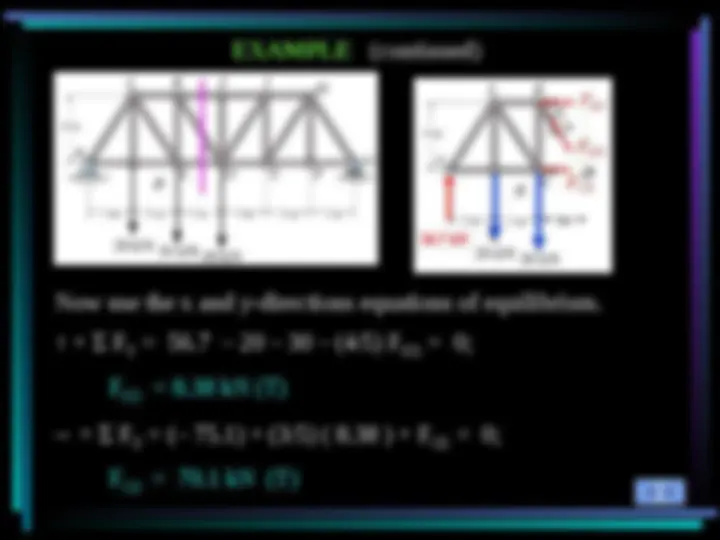
EXAMPLE (continued) Now use the x and y-directions equations of equilibrium. ↑ + F Y
KD
KD = 8.38 kN (T) → + F X
CD
CD = 70.1 kN (T) 56.7 kN
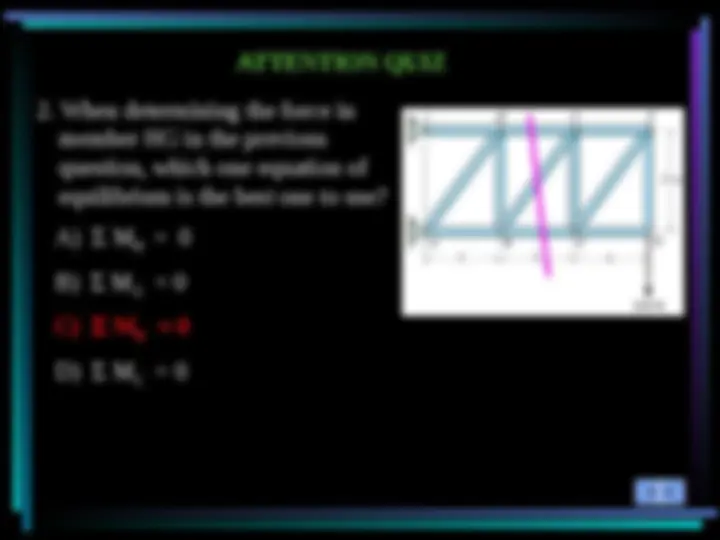
CONCEPT QUIZ (continued)
A) By taking section b-b and using M E
B) By taking section b-b, and using F X = 0 and F Y
C) By taking section a-a and using M B
D) By taking section a-a and using M D
a) Take the cut through members GF, GB and AB. b) Analyze the left section. Determine the support reactions at A. Why? c) Draw the FBD of the left section. d) Apply the equations of equilibrium (if possible, try to do it so that every equation yields an answer to one unknown. Given : Loads as shown on the truss. Find : The force in members GB and GF. Plan:
GROUP PROBLEM SOLVING (continued)
X
D
Y
Y = 671.4 lb Why is A x equal zero by inspection?