













Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An overview of the evolution of animal diversity, starting from the simplest multicellular organisms, sponges, and progressing through various phyla, including flatworms, roundworms, and mollusks, to more complex organisms like crabs, insects, and mammals. The defining characteristics of animals, the stages of animal development, and the origins of animals from choanoflagellate ancestors.
Typology: Quizzes
1 / 27

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




















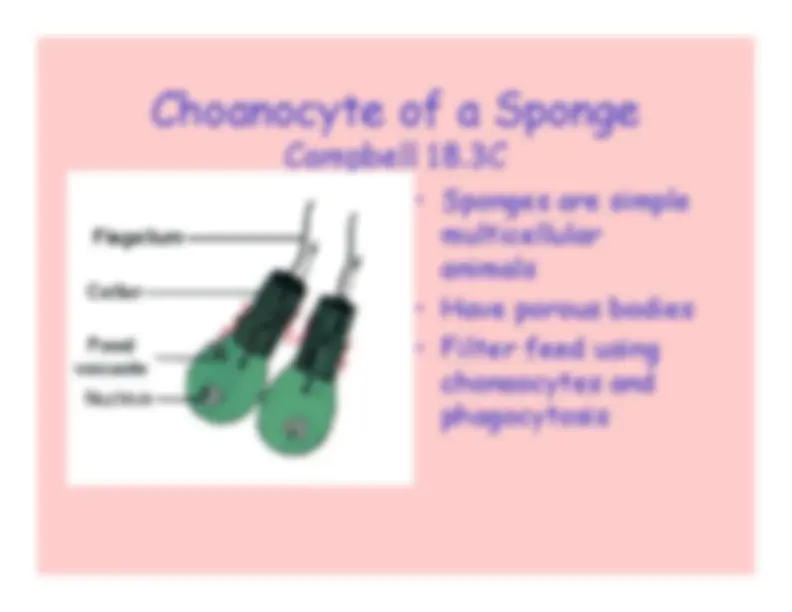
Sponges
-^
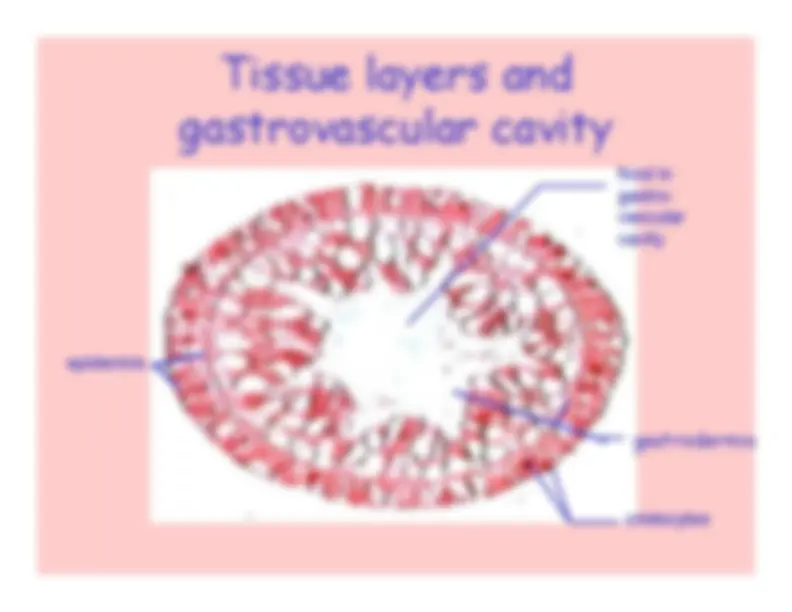
Jellyfish
-^
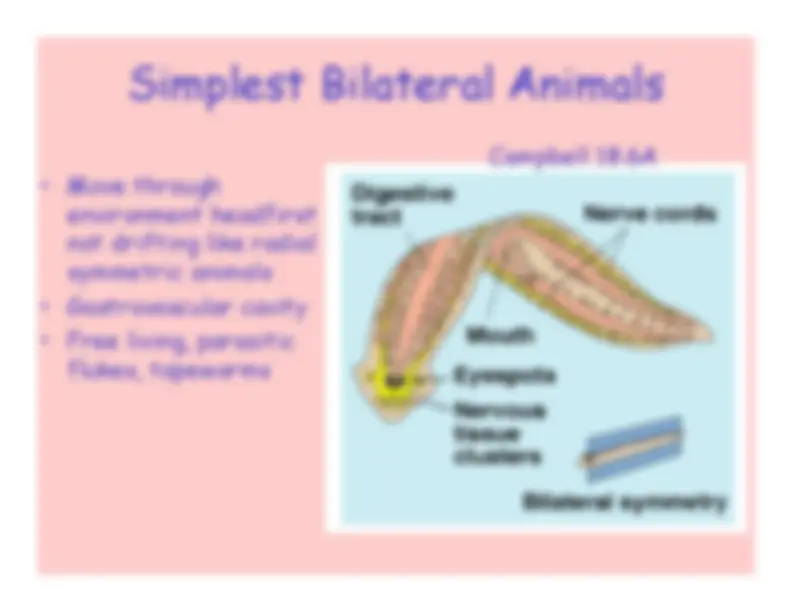
Flatworms
-^
Roundworms
-^
Segmented worms
-^
Crabs, insects
-^
Snails, squid, clams
-^
Starfish, sand dollars
-^
Mammals, birds etc.
Porifora
-^
Cnidaria
-^
Platyhelminthes
-^
Nematoda
-^
Annelida
-^
Arthropoda
-^
Mollusca
-^
Echinodermata
-^
Chordata
Campbell 18.
small choanoflagellate colony
or silica (glass)
defense
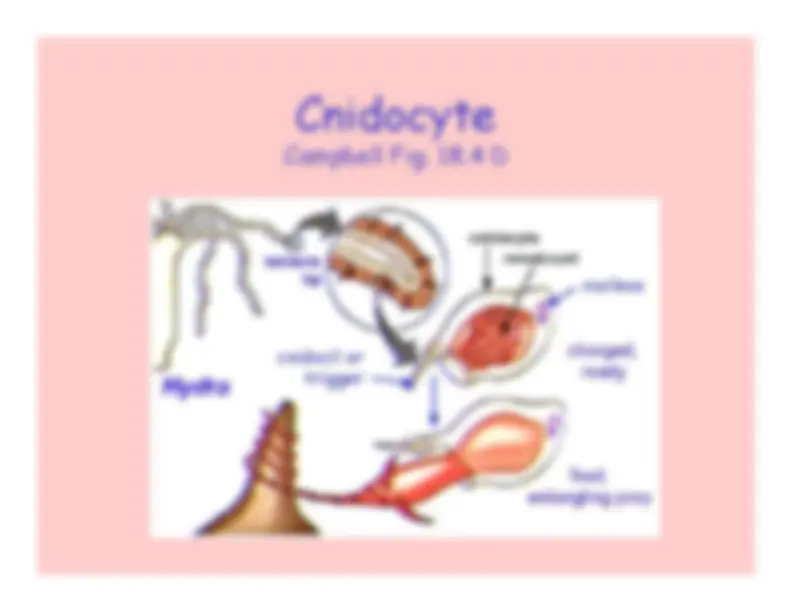
Campbell Fig. 18.4 A-C
polyp
(attached, mouth-up)
medusa(free-drifting, mouth-down)
cnidocil or
trigger
nucleus