









































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Instructions for project 2 of the cs245-2009s data structures and algorithms course at the university of san francisco. The project focuses on huffman codes, a method for compressing data by assigning variable-length codes to characters based on their frequency. Topics such as ascii codes, representing codes as trees, prefix codes, variable length codes, file length, decoding files, file compression, and huffman coding. Students are expected to use this information to complete the project.
Typology: Study Guides, Projects, Research
1 / 56

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!

















































Department of Computer Science
University of San Francisco
ASCII – American Standard Code forInformation Interchange Text file is a sequence of binary digits whichrepresent the codes for each character.
We need 8 bits to represent all possiblecharacter combinations
(including control characters, and unprintablecharacters) Breaking up file into individual characters iseasy Finding the kth character in a file is easy
All characters require 8 bits Frequently used characters require the samenumber of bits as infrequently used characters We could be more efficient if frequently usedcharacters required fewer than 8 bits, and lessfrequently used characters required more bits
How many bits are required for each code, ifeach code has the same length? 2 bits are required, since there are 4 possibleoptions to distinguish
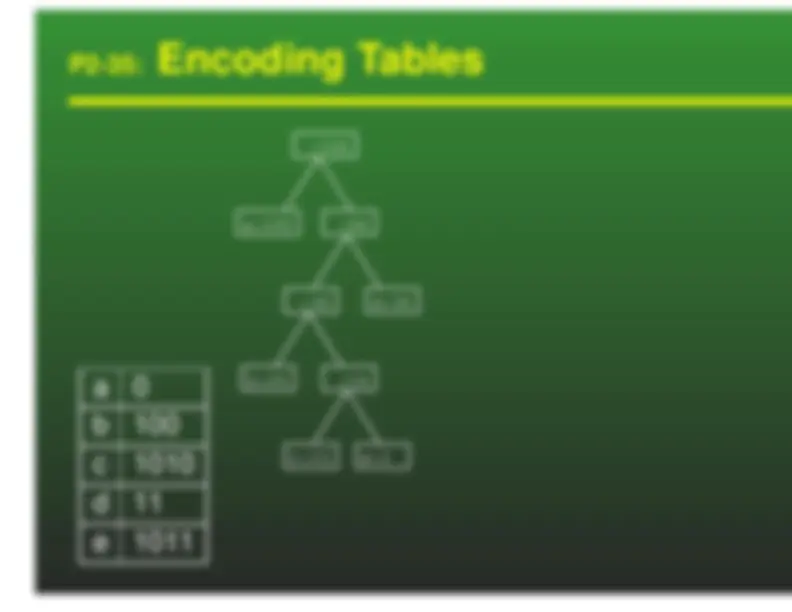
a: 00 b: 01 c: 10 d: 11 We can represent these codes as a tree
Characters are stored at the leaves of the tree Code is represented by path to leaf
a
b^
c
d
0
1
0
0
1
1
Any prefix code can be represented as a tree a: 0, b: 100, c: 101, d: 11
c
d
0
1 0
(^01)
1
a
b
If we use the code:
a:00, b:01, c:10, d: How many bits are required to encode a file of 20characters?
If we use the code:
a:0, b:100, c:101, d: How many bits are required to encode a file of 20characters?
If we use the code:
a:0, b:100, c:101, d: How many bits are required to encode a file of 20characters? It depends upon the number of a’s, b’s, c’s and d’sin the file
If we use the code:
a:0, b:100, c:101, d: How many bits are required to encode a file of:
11 a’s, 2 b’s, 2 c’s, and 5 d’s? 111 + 23 + 23 + 52 = 33 < 40
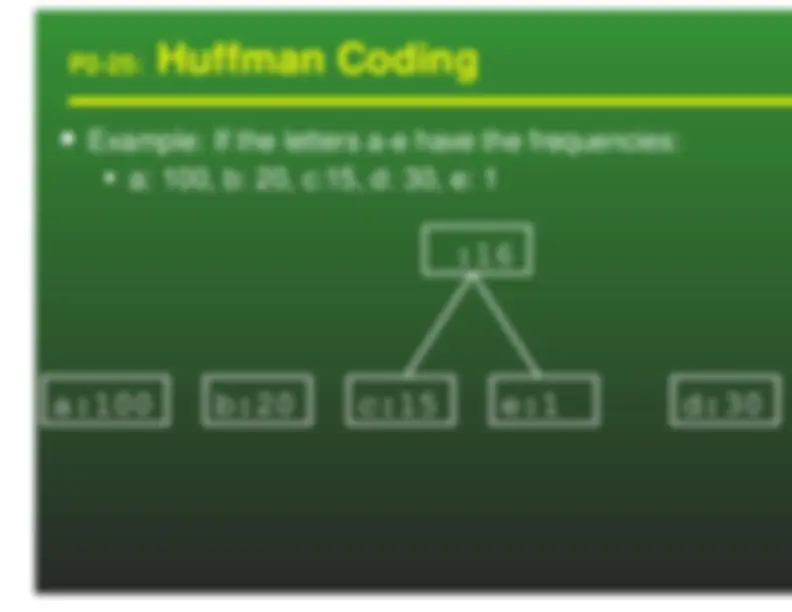
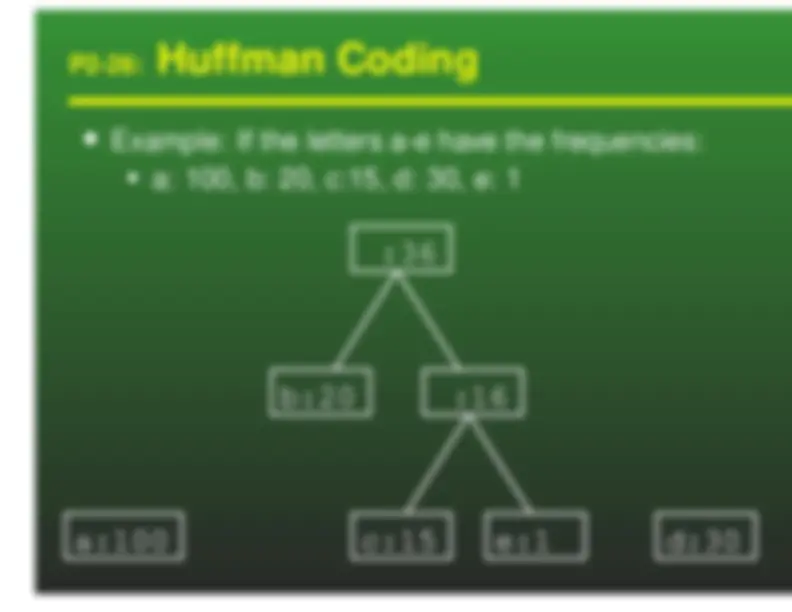
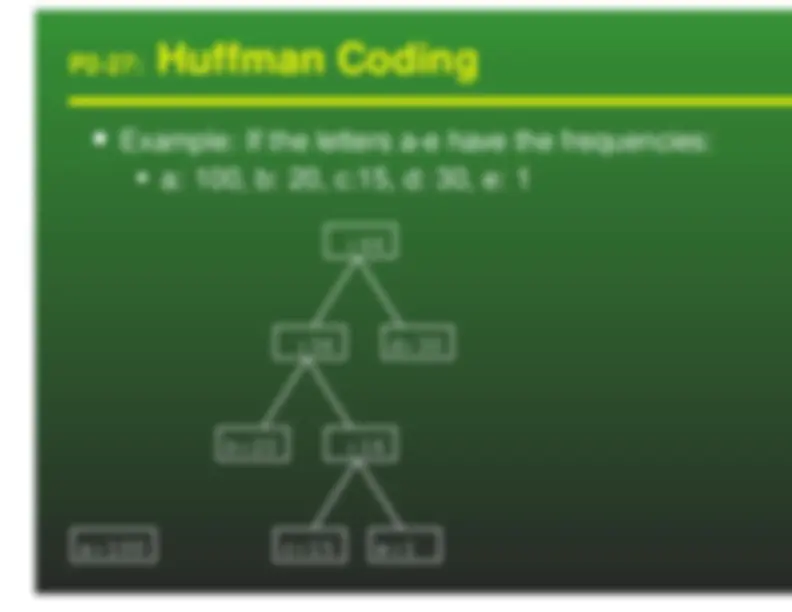
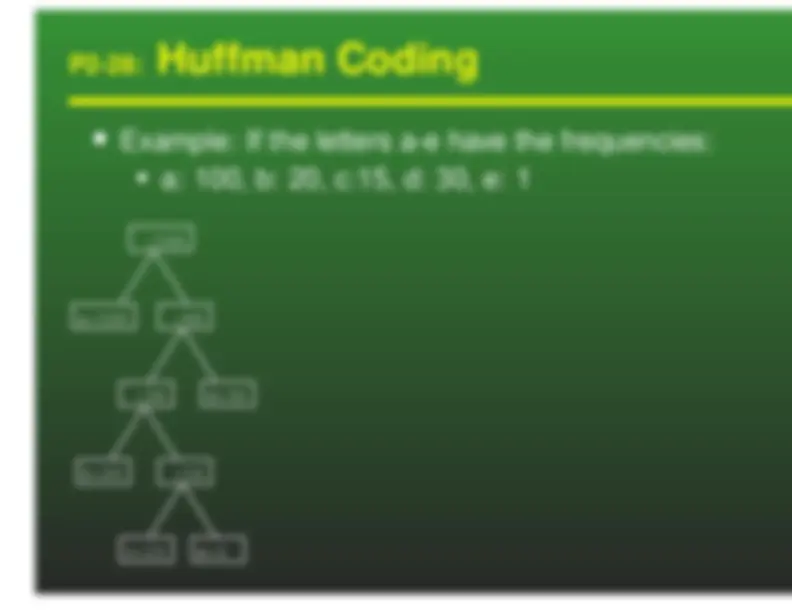
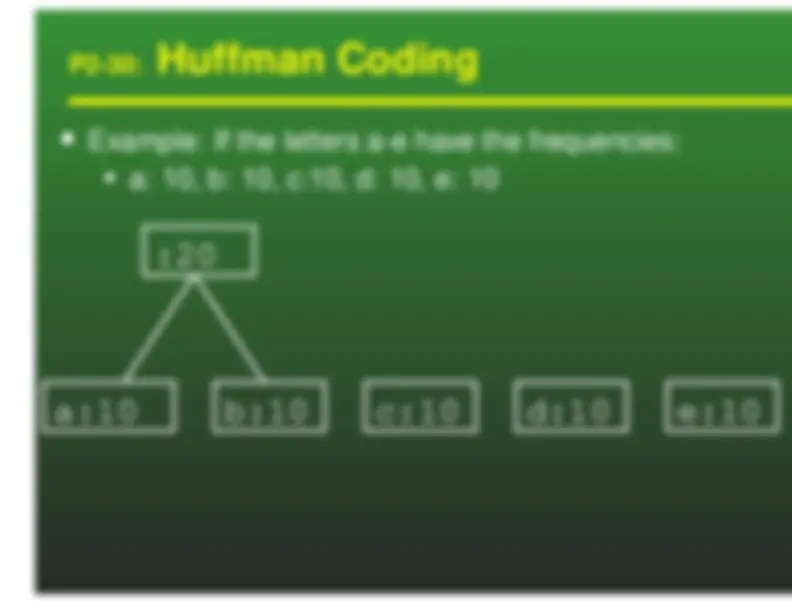
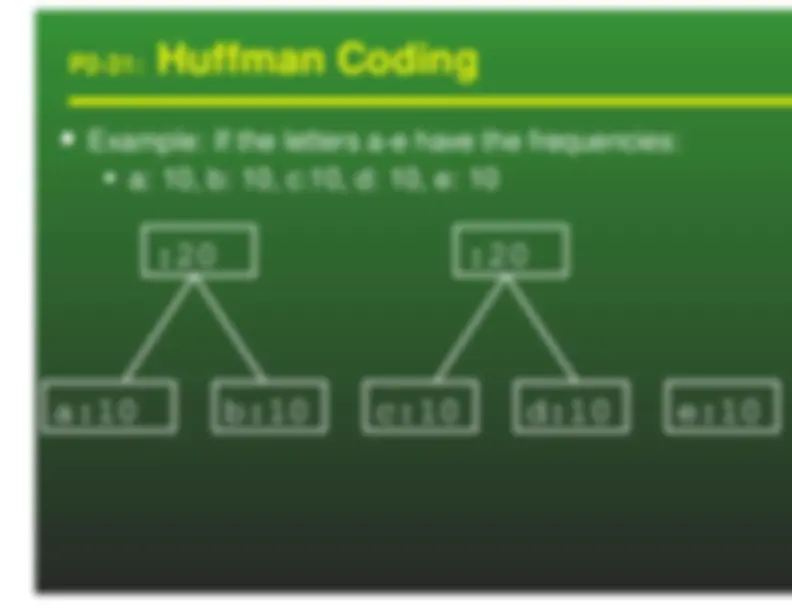
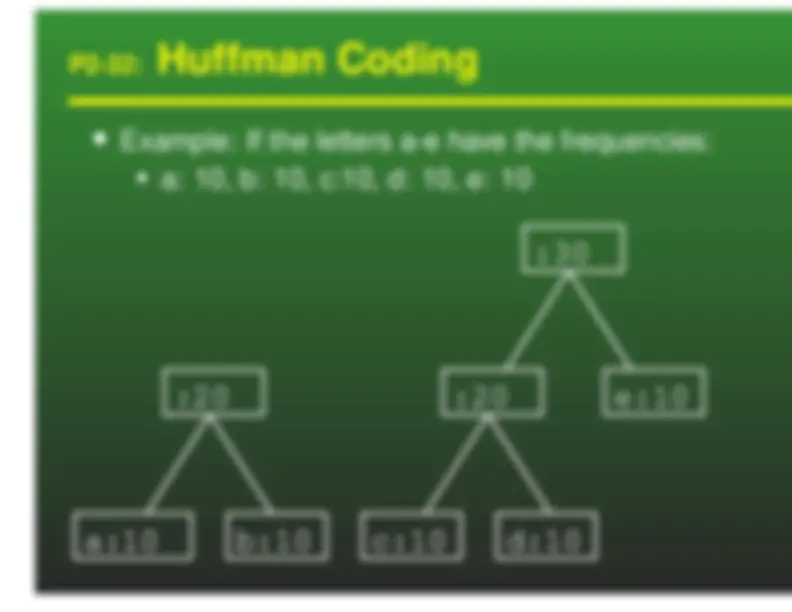
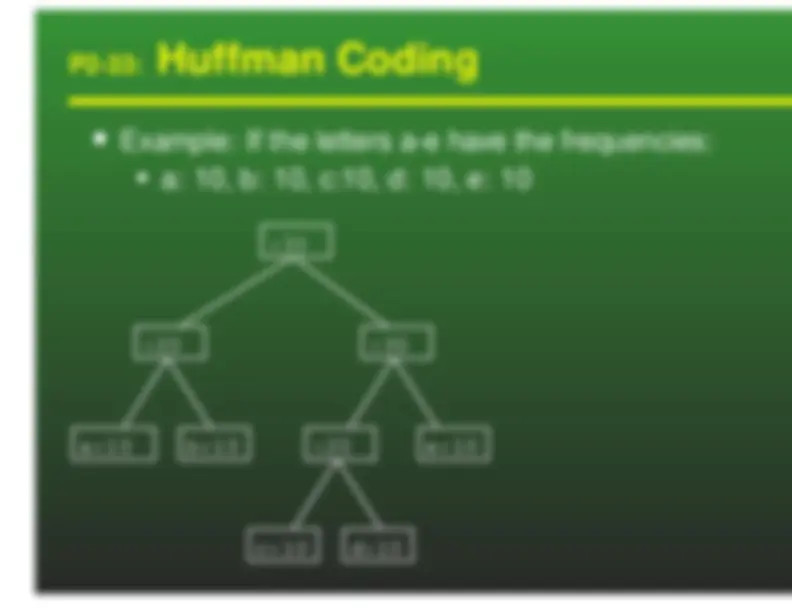
We can use variable length keys to encode a textfile Given the encoded file, and the tree representationof the codes, it is easy to decode the file
c
d
0
(^10)
(^01)
1
a
b 0111001010011