




Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Solutions to test 2 in the elements of electrical engineering ii (ece207) course. The test covers various topics such as three-phase power systems, transformers, and coils. Students are required to determine the 1φ equivalent diagram, line current, total power, and power factor for a transmission line supplying two loads. They also need to determine the approximate equivalent circuit of a transformer based on open-circuit and short-circuit test results. Additionally, students are asked to calculate the voltage regulation, coil loss, core loss, and efficiency for a transformer, as well as the voltage and inductance of a coil. Lastly, they are required to determine the rated output torque, rated efficiency, rated air-gap power, electrical losses in the rotor, mechanical rotational losses at rated speed, and motor speed for a three-phase induction motor.
Typology: Exams
1 / 6

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




-
A very short 230 kV, three-phase transmission line has negligible impedance and supplies power to two three-phase loads. Load 1 is Δ-connected and draws 75 MW @ 0. lag pf. Load 2 is Y-connected and draws 150 MVA @ 0.8 lead pf. The voltage at both loads is 230 kV. Determine: a) The 1φ, Y-equivalent diagram (do not combine the loads into one; take Van as your reference voltage). b) Line current flowing in the “A” phase of the transmission line. c) Total real and reactive power drawn from the supply. d) Supply power factor.
a) The 1φ equivalent is:
b) S 1 = 25 + j25tan(cos-1^ 0.9) = 25 + j12.1 MVA/ph S 2 = 50 x 0.8 – j50sin(cos -1^ 0.8) = 40 – j30 MVA/ph Ssource = 65 – j17.89 = 67.42/–15.4 MVA/ph
6 0
c) Total power drawn from the source = 3 Ssource = 195 – j53.68 = 202.3/–15.4 MVA
d) Supply pf = cos(–15.4) = 0.9641 lead
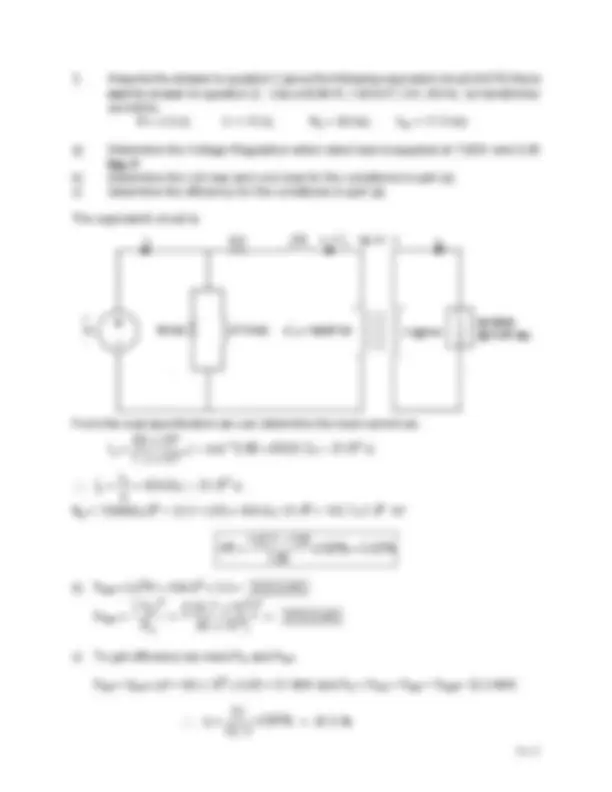
a) Determine the Voltage Regulation when rated load is supplied at 7200V and 0. lag pf. b) Determine the coil loss and core loss for the conditions in part (a). c) determine the efficiency for the conditions in part (a).
The equivalent circuit is:
From the load specification we can determine the load current as:
1 0 3
6
' 2 0
Vp = 138000∠ 00 + (3.3 + j15) x 434.8∠-31.8^0 = 142.7∠1.9^0 kV
b) Pcoil = |I 1 |^2 R = 434.8^2 x 3.3 = 623.9 kW.
Pcore =
3
3 2
c
2 p
c) To get efficiency we need Pin and Pout.
Pout = Sout x pf = 60 x 10^6 x 0.85 = 51 MW and Pin = Pout + Pcoil + Pcore = 52.3 MW
A toroid is made from material that has a relative permeability of 1000. It has a square cross-section of 3 cm and an internal diameter of 27 cm, with an air-gap of 1 mm. The coil has 200 turns, a resistance of 4.37 Ω and is fed from a dc supply. a) Determine the voltage (V) needed to produce a flux of 2 mWb in the air-gap. b) Determine the inductance of the coil.
Rg = g g
g μ A
l = (^73)
3
− −
−
= 884.2 x 10^3 H-
Rc = (^7 ) 1000 x 4 x 10 x 0. 9 x 10
π − −
= 832.4 x 10^3 H-
R = Rc + Rg = 1.717 x 10^6 H-
b) (^6)
2