




Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Exploring and producing data, Probability and Sampling Distributions, Inference about Means etc concepts are part of this cheat sheet.
Typology: Cheat Sheet
1 / 6

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
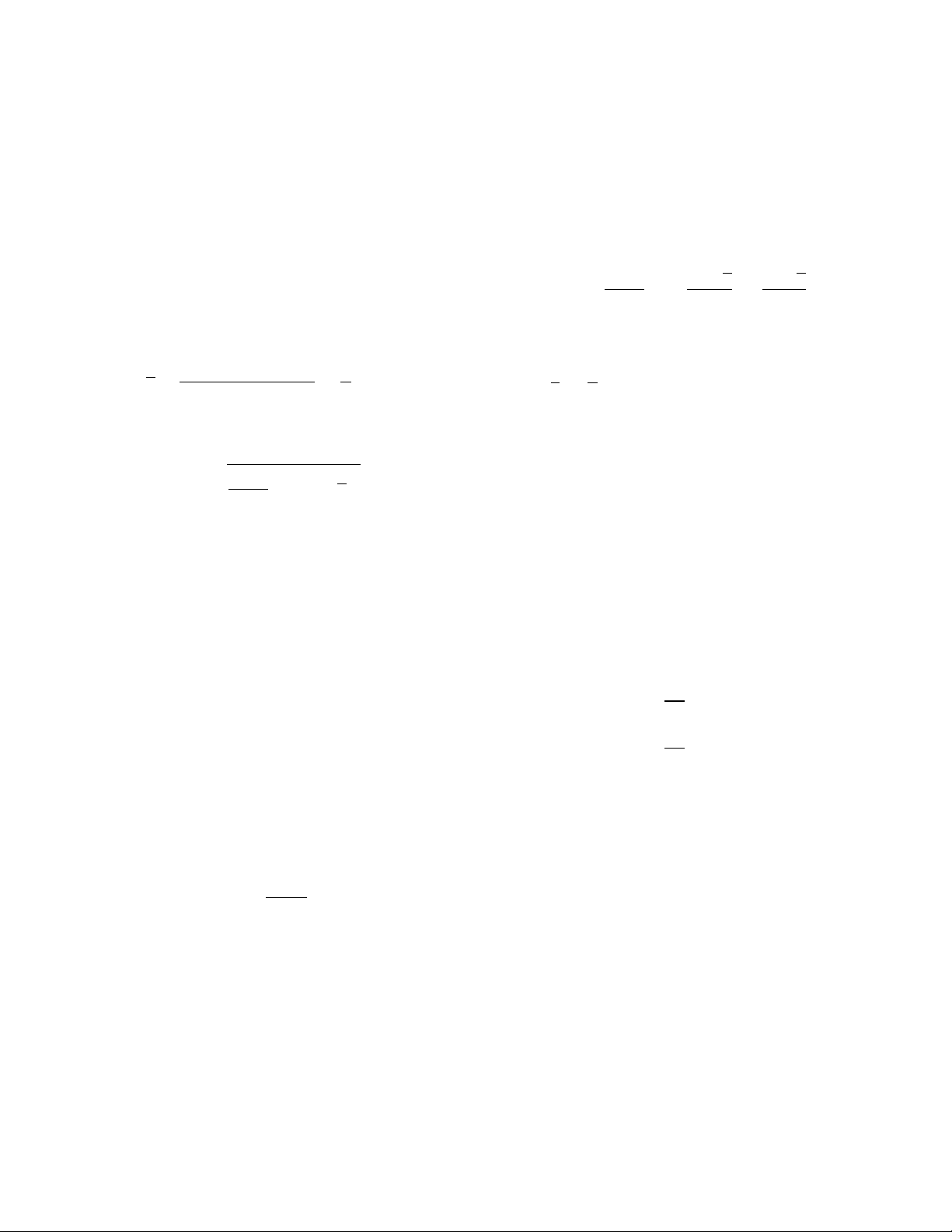



√ n.
Basics of Inference
(σ known, SRS from Normal population):
x ± z ∗^
σ √ n
z ∗^ from N (0, 1)
n =
z ∗^ σ
m
from Normal population):
z =
x − μ 0
σ/
√ n
P -values from N (0, 1)
Inference About Means
from Normal population):
x ± t
∗ (^) √s n
t
from t(n − 1)
population):
t =
x − μ 0
s/
√ n
P -values from t(n − 1)
two treatments, apply the one-sample t proce-
dures to the observed differences.
dependent SRSs from Normal populations):
(x 1 − x 2 ) ± t
s^21
n (^1)
s^22
n (^2)
with conservative t ∗^ from t with df the smaller of n 1 − 1 and n 2 − 1 (or use software).
(independent SRSs from Normal populations):
t =
x 1 − x 2
s^21
n (^1)
s^22
n (^2)
with conservative P -values from t with df the smaller of n 1 − 1 and n 2 − 1 (or use software).
Inference About Proportions
when the population and the sample size are both large and p is not close to 0 or 1, ˆp is ap-
proximately Normal with mean p and standard deviation
p(1 − p)/n.
pˆ ± z ∗
p ˆ(1 − pˆ)
n
z ∗^ from N (0, 1)
Plus four to greatly improve accuracy: use the
same formula after adding 2 successes and two failures to the data.
z =
pˆ − p (^0)
p 0 (1 − p 0 )
n
P -values from N (0, 1)
n =
z ∗
m
p
(1 − p
)
where p ∗^ is a guessed value for p or p∗^ = 0.5.
(ˆp 1 − pˆ 2 ) ± z
SE z
from N (0, 1)
where the standard error of ˆp 1 − pˆ 2 is
SE =
p ˆ 1 (1 − pˆ 1 )
n (^1)
pˆ 2 (1 − pˆ 2 )
n (^2)
Plus four to greatly improve accuracy: use the
same formulas after adding one success and one failure to each sample.
TABLE B Random digits Line 101 19223 95034 05756 28713 96409 12531 42544 82853 102 73676 47150 99400 01927 27754 42648 82425 36290 103 45467 71709 77558 00095 32863 29485 82226 90056 104 52711 38889 93074 60227 40011 85848 48767 52573 105 95592 94007 69971 91481 60779 53791 17297 59335 106 68417 35013 15529 72765 85089 57067 50211 47487 107 82739 57890 20807 47511 81676 55300 94383 14893 108 60940 72024 17868 24943 61790 90656 87964 18883 109 36009 19365 15412 39638 85453 46816 83485 41979 110 38448 48789 18338 24697 39364 42006 76688 08708 111 81486 69487 60513 09297 00412 71238 27649 39950 112 59636 88804 04634 71197 19352 73089 84898 45785 113 62568 70206 40325 03699 71080 22553 11486 11776 114 45149 32992 75730 66280 03819 56202 02938 70915 115 61041 77684 94322 24709 73698 14526 31893 32592 116 14459 26056 31424 80371 65103 62253 50490 61181 117 38167 98532 62183 70632 23417 26185 41448 75532 118 73190 32533 04470 29669 84407 90785 65956 86382 119 95857 07118 87664 92099 58806 66979 98624 84826 120 35476 55972 39421 65850 04266 35435 43742 11937 121 71487 09984 29077 14863 61683 47052 62224 51025 122 13873 81598 95052 90908 73592 75186 87136 95761 123 54580 81507 27102 56027 55892 33063 41842 81868 124 71035 09001 43367 49497 72719 96758 27611 91596 125 96746 12149 37823 71868 18442 35119 62103 39244
TABLE C t distribution critical values Upper tail probability p df .25 .20 .15 .10 .05 .025 .02 .01 .005 .0025 .001. 1 1.000 1.376 1.963 3.078 6.314 12.71 15.89 31.82 63.66 127.3 318.3 636. 2 0.816 1.061 1.386 1.886 2.920 4.303 4.849 6.965 9.925 14.09 22.33 31. 3 0.765 0.978 1.250 1.638 2.353 3.182 3.482 4.541 5.841 7.453 10.21 12. 4 0.741 0.941 1.190 1.533 2.132 2.776 2.999 3.747 4.604 5.598 7.173 8. 5 0.727 0.920 1.156 1.476 2.015 2.571 2.757 3.365 4.032 4.773 5.893 6. 6 0.718 0.906 1.134 1.440 1.943 2.447 2.612 3.143 3.707 4.317 5.208 5. 7 0.711 0.896 1.119 1.415 1.895 2.365 2.517 2.998 3.499 4.029 4.785 5. 8 0.706 0.889 1.108 1.397 1.860 2.306 2.449 2.896 3.355 3.833 4.501 5. 9 0.703 0.883 1.100 1.383 1.833 2.262 2.398 2.821 3.250 3.690 4.297 4. 10 0.700 0.879 1.093 1.372 1.812 2.228 2.359 2.764 3.169 3.581 4.144 4. 11 0.697 0.876 1.088 1.363 1.796 2.201 2.328 2.718 3.106 3.497 4.025 4. 12 0.695 0.873 1.083 1.356 1.782 2.179 2.303 2.681 3.055 3.428 3.930 4. 13 0.694 0.870 1.079 1.350 1.771 2.160 2.282 2.650 3.012 3.372 3.852 4. 14 0.692 0.868 1.076 1.345 1.761 2.145 2.264 2.624 2.977 3.326 3.787 4. 15 0.691 0.866 1.074 1.341 1.753 2.131 2.249 2.602 2.947 3.286 3.733 4. 16 0.690 0.865 1.071 1.337 1.746 2.120 2.235 2.583 2.921 3.252 3.686 4. 17 0.689 0.863 1.069 1.333 1.740 2.110 2.224 2.567 2.898 3.222 3.646 3. 18 0.688 0.862 1.067 1.330 1.734 2.101 2.214 2.552 2.878 3.197 3.611 3. 19 0.688 0.861 1.066 1.328 1.729 2.093 2.205 2.539 2.861 3.174 3.579 3. 20 0.687 0.860 1.064 1.325 1.725 2.086 2.197 2.528 2.845 3.153 3.552 3. 21 0.686 0.859 1.063 1.323 1.721 2.080 2.189 2.518 2.831 3.135 3.527 3. 22 0.686 0.858 1.061 1.321 1.717 2.074 2.183 2.508 2.819 3.119 3.505 3. 23 0.685 0.858 1.060 1.319 1.714 2.069 2.177 2.500 2.807 3.104 3.485 3. 24 0.685 0.857 1.059 1.318 1.711 2.064 2.172 2.492 2.797 3.091 3.467 3. 25 0.684 0.856 1.058 1.316 1.708 2.060 2.167 2.485 2.787 3.078 3.450 3. 26 0.684 0.856 1.058 1.315 1.706 2.056 2.162 2.479 2.779 3.067 3.435 3. 27 0.684 0.855 1.057 1.314 1.703 2.052 2.158 2.473 2.771 3.057 3.421 3. 28 0.683 0.855 1.056 1.313 1.701 2.048 2.154 2.467 2.763 3.047 3.408 3. 29 0.683 0.854 1.055 1.311 1.699 2.045 2.150 2.462 2.756 3.038 3.396 3. 30 0.683 0.854 1.055 1.310 1.697 2.042 2.147 2.457 2.750 3.030 3.385 3. 40 0.681 0.851 1.050 1.303 1.684 2.021 2.123 2.423 2.704 2.971 3.307 3. 50 0.679 0.849 1.047 1.299 1.676 2.009 2.109 2.403 2.678 2.937 3.261 3. 60 0.679 0.848 1.045 1.296 1.671 2.000 2.099 2.390 2.660 2.915 3.232 3. 80 0.678 0.846 1.043 1.292 1.664 1.990 2.088 2.374 2.639 2.887 3.195 3. 100 0.677 0.845 1.042 1.290 1.660 1.984 2.081 2.364 2.626 2.871 3.174 3. 1000 0.675 0.842 1.037 1.282 1.646 1.962 2.056 2.330 2.581 2.813 3.098 3. z ∗^ 0.674 0.841 1.036 1.282 1.645 1.960 2.054 2.326 2.576 2.807 3.091 3. 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 95% 96% 98% 99% 99.5% 99.8% 99.9% Confidence level C