















































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
These slides address chapters 1 through 3 of the textbook, with some information already found in the earlier “Sustainable Demand Chain Management: an Introduction” de-emphasized
Typology: Exams
1 / 56

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!

















































These slides address chapters 1 through 3 of the
textbook, with some information already found in the earlier “Sustainable Demand Chain Management: an Introduction” de-emphasized
While the slide decks are based on the textbook, they
have been customized for this class
The “best” solution to a Supply Chain problem may not win
Supply Chain Practitioners need soft skills
Supply Chain Practitioners need hard skills
The class is designed for you to practice both hard and soft skills
Freight Transportation $809, $856 Billion Inventory Expense $446, $487 Billion Administrative Expense $50, $54 Billion Total Logistics Costs $1.31, $1.4 Trillion Logistics Related Activity 10%, 10.1% of GNP
But supply chain is more than logistics….
Source: 18th^ and 19th^ Annual State of Logistics Report – Logistics Magazine
What is a Supply Chain? (We covered this earlier)
Decision Phases in a Supply Chain
Process View of a Supply Chain
The Importance of Supply Chain Flows
Typical stages: (from a demand chain perspective)
customers<retailers<distributors<manufacturers<suppliers
The obvious flow is the movement of products from
suppliers to the customer, but also includes movement of information , funds , and products in both directions
Example: Dell receives $1000 from a customer for a computer (revenue)
Supply chain incurs costs (information, storage, transportation, components, assembly, etc.)
Difference between $1000 and the sum of all of these costs is the supply chain profit
Supply chain profitability is the total profit to be shared across all stages of the supply chain
Supply chain success should be measured by total supply chain profitability, not profits at an individual stage
Definition of a set of policies that govern short-term
operations - typically a quarter to a couple years
Fixed by the supply configuration from previous phase
Planning decisions:
Must consider demand uncertainty, exchange rates,
competition over the time horizon
Time horizon is weekly or daily
Decisions regarding individual customer orders
Supply chain configuration is fixed and operating policies are determined
Goal is to implement the operating policies as effectively as possible
Allocate orders to inventory or production, set order due dates, generate pick lists at a warehouse, allocate an order to a particular shipment, set delivery schedules, place replenishment orders
Much less uncertainty (due to short time horizon)
Actions initiated from Suppliers Retail/Customer Initiated Action
The barrier between push And pull may vary for different companies and industries
PUSH PROCESSES PULL PROCESSES
Supply chain processes fall into one of two categories
depending on the timing of their execution relative to customer demand
Push/pull boundary separates push processes from
pull processes
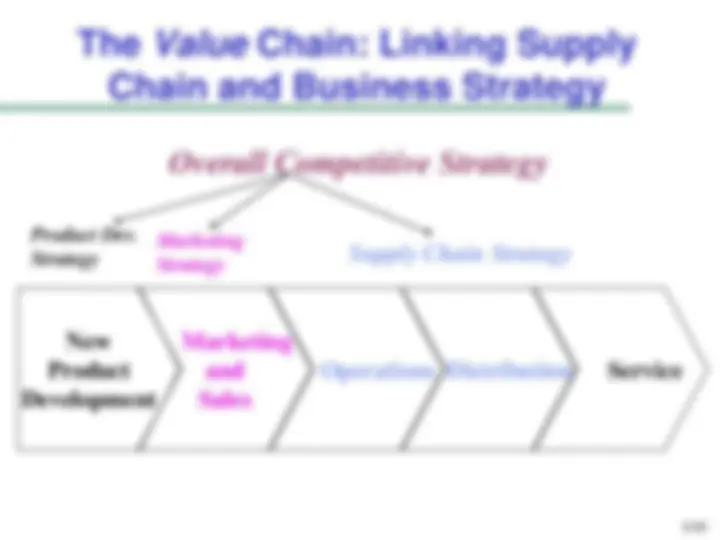
Competitive strategy: defines the set of customer needs a firm seeks to satisfy through its products and services
Product development strategy: specifies the portfolio of new products that the company will try to develop
Marketing and sales strategy: specifies how the market will be segmented and product positioned, priced, and promoted
Supply chain strategy:
New Product Development
Marketing and Sales
Operations Distribution Service
Product Dev. Strategy
Marketing Strategy Supply Chain Strategy