




Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Material Type: Lab; Professor: Duva; Class: INSTRUMENTATION & MEASUREMENT; Subject: Mechanical; University: Wentworth Institute of Technology; Term: Spring 2008;
Typology: Lab Reports
1 / 6

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




There are two distinguished models for describing the events in science and engineering. One is the deterministic model, in which the relationship among a dependent variable and independent variables is strictly and accurately described by a governing equation. In this type of model, the outcome is predictable and solely determined by independent variables. The physical meaning of this type of models is that all possible mechanism or issues about the relationship among the dependent and independent variables are fully understood and fully considered. Another model is the statistical or probabilistic model. In this model, the outcome is not predictable so that the value of the dependent variable should be described by a random variable. There are two main causes for this phenomenon: (1) Some mechanism for governing the relationship among the dependent variable and independent variables are not fully understood. When these mechanisms are fully understood, the statistical or probabilistic model can be replaced by the deterministic model. Weather forecast is a good example. With more advanced technology, current weather forecast is more reliable. (2) Some mechanisms are very hard to be fully controlled. For example, human error is very hard to be fully controlled. For another example, the microstructure of a material is very hard to be fully controlled. If the material composition and the microstructure of material are fully controlled, the yield strength of this material will be a constant. Actually, the yield strength of the same brand material is not a constant due to the variation of composition and the microstructure of the material. The statistical analysis or probability theory is a good tool to deal with uncertainty or randomness. People will use information based on probabilistic theory to make their decision. However, proper interpretation of information, data or conclusion from probabilistic theory is a must because statistical model can only provide imperfect and incomplete information..
In this statistical analysis lab, the main goal is to apply the several basic concepts in statistical theory discussed in class to assess measurement uncertainty. The objectives of this statistical analysis lab are: To calculate the mean and standard deviation of a set of data To create the histogram To determine the confidence intervals with given confidence level To apply the 6 sigma principle to judge some data To run simple linear regression and determine the uncertainty of the fitting line.
Question 1: A steel manufacturer produces a brand of steel for a long time. A lot of data about the yield strength of this material have been cumulated from tensile experiment and measurement. 200 test data of the yield strength of this material is listed in the attached excel file. Use Microsoft Excel as a tool to complete following question. (1) The mean and standard deviation of this data a. Use “AVERAGE ( number1 , number2,...)” to calculate the mean b. Use “ STDEVPA ( value1 , value2,...)” to calculate the standard deviation (2) Based on these 200 measurements, the yield strength is in the range of from 94 ksi to 142 ksi. Use the bin listed in column B to create frequency histogram by use of the data analysis tool “Histogram” in Excel. (Read the appendix to learn how to use “Histogram” in Excel if you don’t know how to “histogram”.) (3) It is assumed that the test data of the yield strength can be described by the normal distribution. Use the mean and standard deviation obtained from question (1) as the mean and standard deviation of the normal distribution. Calculate the probability of a yield strength which is larger than 100 ksi and less than 140 ksi, that is, (^) ^ ^ ^ b a x P x e dx 2 2 1 2 1 ( 100 140 )^
. Use the equation provided in the lecture and table 3.2 on page 50 to run the calculation. (4) The test engineer used the steel produced in a week to make the tensile test sample and did three tensile tests. The yield strength for those three tests was 151 ksi, 149 ksi and 143 ksi. Then the test engineer told the production manager that something might be wrong with the steel manufacturing process. Can you explain to the production manager why? (Hint: try to use 6 sigma principles to support your argument.) (5) Provide the 95% confidence level for mean of yield strength of this brand steel. Question 2:
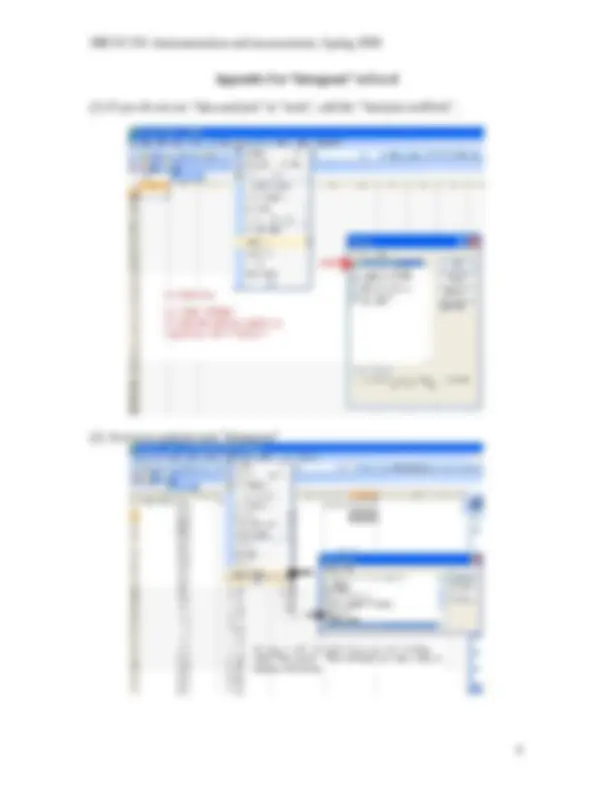
Appendix Use “histogram” in Excel (1) If you do not see “data analysis” in “tools”, add the “Analysis toolPack”. (2) Access to analysis tool “histogram”
(3) Use the Histogram Select the “input range”, which is the test data. And select the “bin range” and “output location”. Also check “chart output”.