

















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
The relationship between peer associations, moral beliefs, and delinquent behaviors through the lens of Social Learning Theory. The study presents survey results on the proportion of closest friends engaging in various illicit activities and their corresponding moral beliefs. Additionally, the document discusses Subcultural Theories, Control Theories, and critiques of each. Useful for students studying criminology, sociology, or psychology.
What you will learn
Typology: Slides
1 / 27

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




















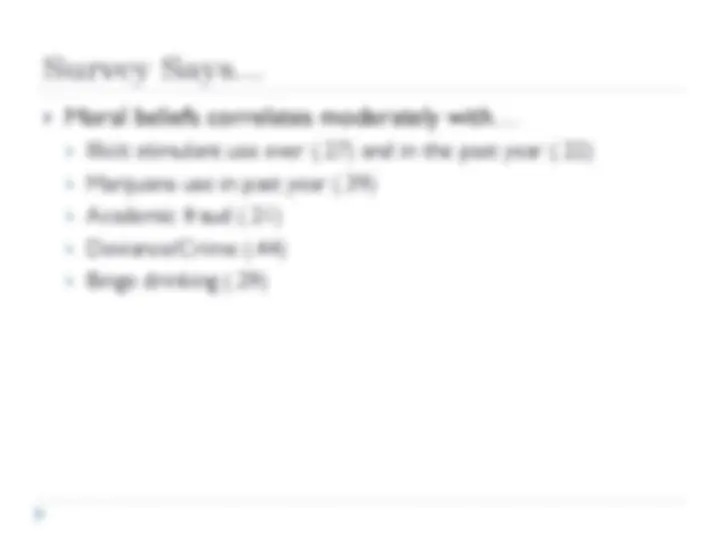
What proportion of your closest friends… Cheated on exams or papers Sold marijuana Sold drug other than marijuana Pirated things off the Internet Bought something they thought might be stolen Stole something worth less than $ Stole something worth more than $ Purposely damaged property without the owner’s permission
Differential Opportunity Theory (2 of
Assumptions about “Motivation towards crime”
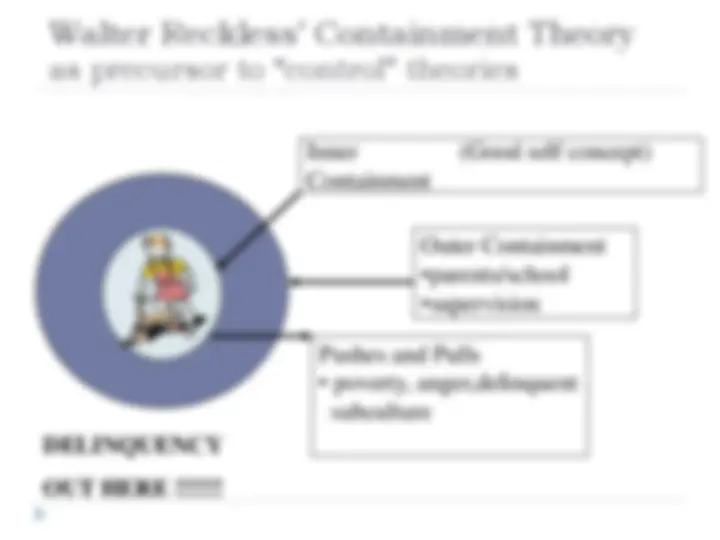
as precursor to “control” theories Pushes and Pulls
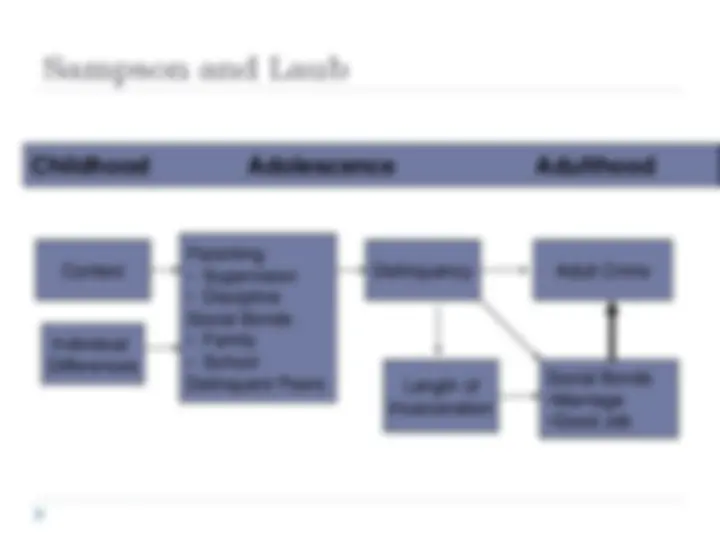
The Social Bond
Crime
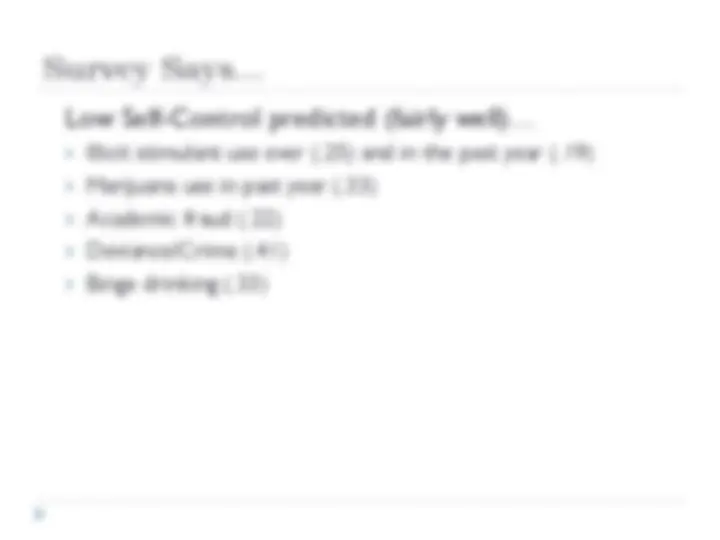
Nature of Crime, Nature of Low Self-Control Criminal Acts… Provide immediate gratification of desires Are risky/thrilling Are easy/simple Require little skill/planning Provide few/meager long term benefits Result in pain/discomfort to a victim People with low self-control are therefore… Impulsive Risk-taking Physical (as opposed to mental) Low verbal ability Short-sighted Insensitive