
































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
The outline of the first lecture for the special topics in wireless communications course offered by professor yasamin mostofi at the university of new mexico, spring 2009. The lecture covers the course syllabus, wireless vision, current and emerging wireless systems, and technical challenges. Students are introduced to various wireless communication concepts, including channel impairment modeling, digital modulation, and multiple access techniques.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 43

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




































Microwave Mobile Communications, W. C. Jakes, Wiley, 1974 Wireless Communications - Principles and Practice by T. Rappaport,2nd Ed. Prentice Hall, 2001 Principles of Mobile Communications by G. L. Stuber, 2nd Ed, KluwerAcademic Publishers, 2001 Digital Communications, J.G. Proakis, 4th Ed., McGraw-Hill, 2001 Digital Communications over Fading Channels, A Unified Approach toPerformance Analysis M. K. Simon and M.-S, Alouini, Wiley, 2000
Cellular systems Wireless data networks Sensor networks and networked control systems
History of Wireless Comm. Wireless communication in old times: Smoke Signals Radio invented by Marconi in the 1880s From Isle of Wight to a tugboat 18 miles away Many radio systems were developed during WW Several existing examples today Cellular systems have enjoyed exponential growthsince 1988 around 2 billion users worldwide today
First Mobile Radio Phone, 1924 Courtesy of www.bellsystemmemorial.com/oldphotos_1.html
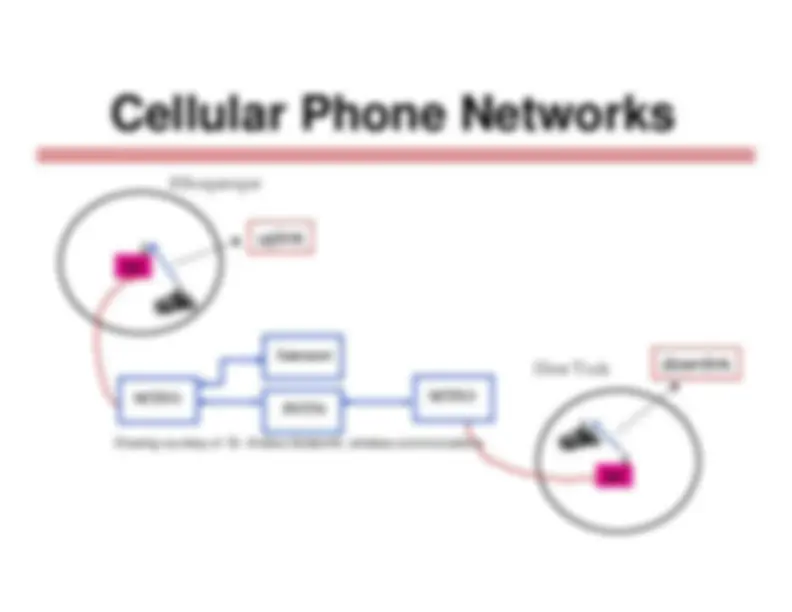
Cellular Concept: Reuse Channels First proposed at Bell Labs by D. Ring, 1947 Geographic areas divided into cells Resources like frequencies, timeslots or codes are reused at spatially-separated locations Co-channel interference MTSOs handle handoff and control functions smaller cell size increases capacity
Base Station
BS MTSO PSTN MTSO BS Albuquerque New York Internet Drawing courtesy of Dr. Andrea Goldsmith, wireless communications downlink uplink
Multiple Access Techniques Courtesy of Petri Possi, UMTS World
Code Division Multiple Access
Originally developed for the military Resists jamming and interference All users share the same spectrum All accepted 3G radio standards arebased on CDMA
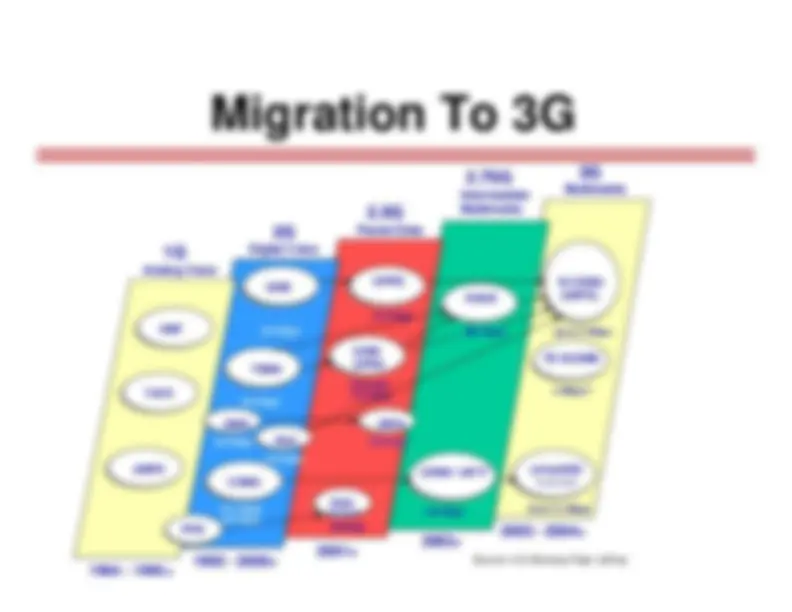
Cellular: was fastest growing sector of communication industry exponential growth since 1982, with over 2 billion users worldwidetoday Three generations of cellular systems First Generation (1980s): Analog 30 KHz FM, voice only AMPS in USA, TACS in Europe Second Generation (1990s): Digital voice and low bit-rate data,portable units, 30-70 kbps Unified GSM in Europe, TDMA, slow frequency hopping, FSK In US:
-^ 900 MHz: IS-136 (TDMA), IS-95 (CDMA) -^ 1.9 GHz: IS-136, IS-95, GSM 2.5G increased data transmission capabilities Third Generation: Wideband CDMA, CDMA 2000, voice and highbit-rate data, portable units, data rate from 144 kbps to a few Mbps,development slow
CDMA GSM TDMA PHS(IP-Based) 64 Kbps GPRS 115 Kbps CDMA 1xRTT^ 144 Kbps EDGE 384 Kbps cdma2000^ 1X-EV-DV Over 2.4 Mbps W-CDMA(UMTS) Up to 2 Mbps 2G 2.5G 2.75G 3G 1992 - 2000+ 2001+ 2003+ 1G 2003 - 2004+ TACS NMT AMPS GSM/GPRS (Overlay)115 Kbps 9.6 Kbps 9.6 Kbps 14.4 Kbps/ 64 Kbps 9.6 Kbps PDC Analog Voice Digital Voice Packet Data IntermediateMultimedia Multimedia PHS TD-SCDMA 2 Mbps? 9.6 Kbps iDEN (Overlay) iDEN Source: U.S. Bancorp Piper Jaffray