









Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
A comprehensive overview of the skeletal and muscular systems, covering key topics such as the vertebral column, the structure and function of different types of muscles, and the innervation of various muscle groups. It delves into the detailed anatomy of the bones, joints, and associated structures, including the cranial nerves, the central and peripheral nervous systems, and the autonomic nervous system. The document also discusses common injuries and conditions related to the musculoskeletal system, making it a valuable resource for students and healthcare professionals interested in understanding the complex interplay between the skeletal and muscular systems.
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 15

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!










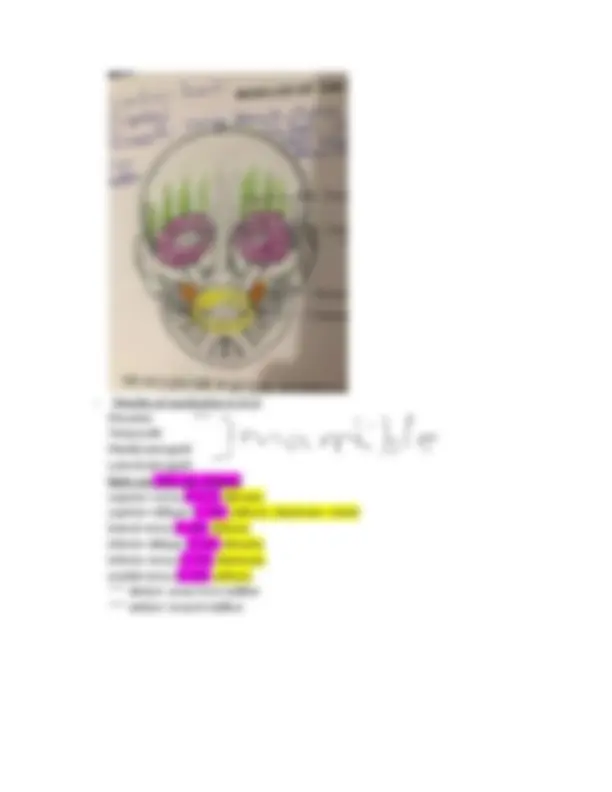
Skeleton Know: # vertebrae/ characteristics/region
*** b/w the radius and the ulna: nodial notch *** olecranon process (ulna): triceps tendon *** radial tuberosity (radius): biceps tendon
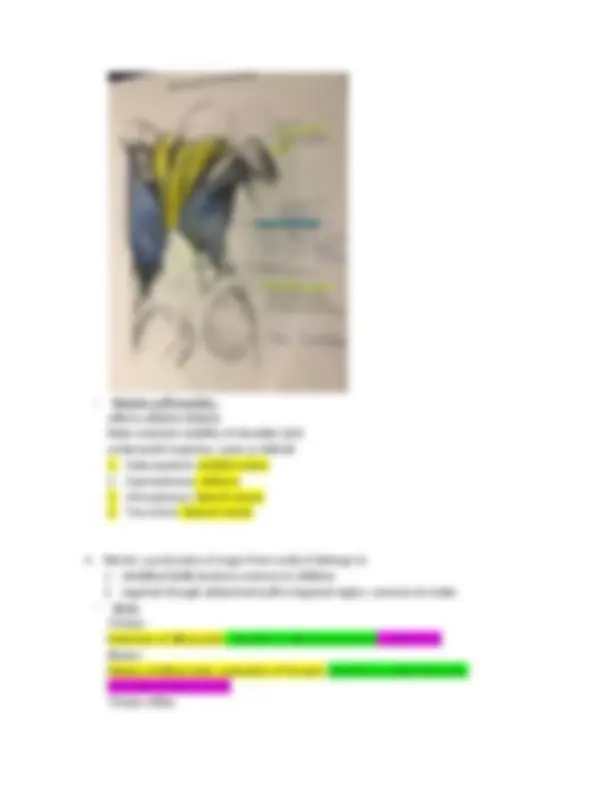
Muscular Know: origin/insertion/action/innervation Three types of muscles
Extension of elbow, testing for radial nerve, palpitate olecranon process, MUST START WITH FLEXED ELBOW Biceps reflex: Flexion of the elbow, testing for musculocutaneous nerve, MUST START WITH EXTENDED ELBOW
Primary motor area: movement face/arm (ex: left hemisphere will create movement right side) LOCATED IN THE PRE-CENTRAL GYRUS Primary sensory area: sensation (ex: left hemisphere, sensation on right side) located in the POST-CENTRAL GYRUS Paracentral lobule: contains both primary motor/sensory necessary for movement of leg, located in LOWER EXTREMETIES Blood supply of brain: Aorta: main vessel