







Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Information on various heart rhythms and their corresponding ecg waveforms. It covers normal heart rhythms, such as sinus tachycardia and sinus bradycardia, as well as abnormal rhythms, such as atrial fibrillation and ventricular fibrillation. The document also discusses the significance of p waves, qrs complexes, and st segments in identifying different heart conditions. It is essential for nursing students and healthcare professionals involved in cardiac care.
Typology: Summaries
1 / 29

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!






















Exit
Due Jan 21, 2024 by 11:59 pm
26 out of 29 questions answered correctly Completed on Jan 16, 2024 10:51 am Incorrect (3) Report content error
Automaticity is the heart’s ability to initiate an impulse spontaneously and continuously. Excitability is the ability to be electrically stimulated. Conductivity is the ability to transmit an impulse along a membrane in an orderly manner. Contractility is the ability to respond mechanically to an impulse. Test-Taking Tip: Identify option components as correct or incorrect. This may help you identify a wrong answer. p. 888 Report content error
Excitability Automaticity Conductivity Contractibility P wave Q wave
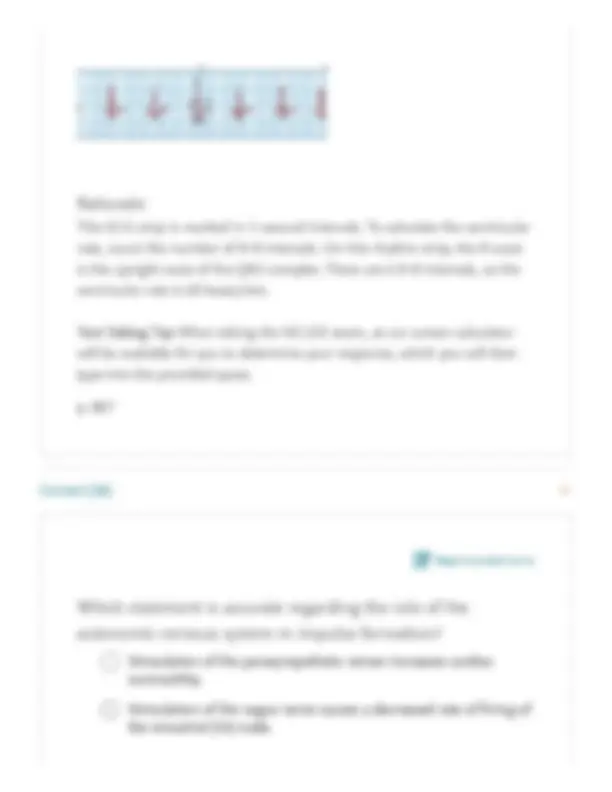
This ECG strip is marked in 1-second intervals. To calculate the ventricular rate, count the number of R-R intervals. On this rhythm strip, the R wave is the upright wave of the QRS complex. There are 6 R-R intervals, so the ventricular rate is 60 beats/min. Test-Taking Tip: When taking the NCLEX exam, an on-screen calculator will be available for you to determine your response, which you will then type into the provided space. p. 887 Correct (26) Report content error
Stimulation of the parasympathetic nerves increases cardiac contractility. Stimulation of the vagus nerve causes a decreased rate of firing of the sinoatrial (SA) node.
The autonomic nervous system plays an important role in the rate of impulse formation, the speed of conduction, and the strength of cardiac contraction. Stimulation of the vagus nerve causes a decreased rate of firing of the sinoatrial node. Stimulation of the parasympathetic system decreases cardiac contractility. Stimulation of the sympathetic nerves increases atrioventricular node impulse conduction. Stimulation of the vagus nerve decreases impulse conduction of the atrioventricular node. Vagus nerve fibers of the parasympathetic nervous system and nerve fibers of the sympathetic nervous system are the components of the autonomic nervous system that affect the heart rate. Test-Taking Tip: Identify option components as correct or incorrect. This may help you identify a wrong answer. p. 884 Report content error
Stimulation of the sympathetic nerves decreases atrioventricular (AV) node impulse conduction. Stimulation of the vagus nerve causes increased impulse conduction of the AV node. Ventricular repolarization Depolarization of both ventricles Passage of the electrical impulse through the atrium
pp. 891, Report content error
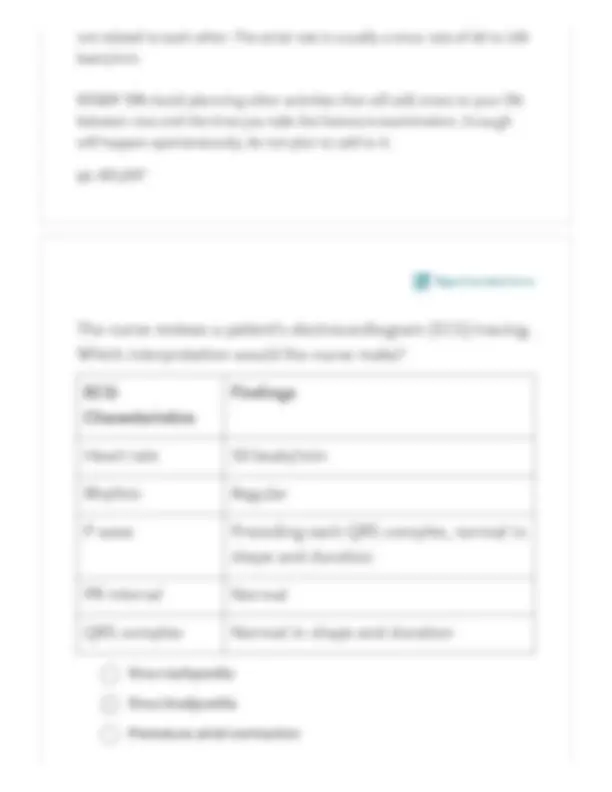
VT is associated with a rate of 150 to 250 beats/minute; the P wave normally is not visible. Rate and rhythm are not measurable in ventricular fibrillation. P wave inversion and a normal QRS complex are not associated with VT. pp. 891, Report content error Unmeasurable rate and rhythm Rate 140 beats/minute; inverted P wave Rate 200 beats/minute; P wave not visible Rate 125 beats/minute; normal QRS complex
The V lead should be placed at the fifth intercostal space at the left midaxillary line. The V lead is placed at the fifth intercostal space at the left midclavicular line. The V lead is placed at the fifth intercostal space at the left anterior axillary line. The V lead is placed at the fourth intercostal space at the right sternal border. p. 885 Report content error
6 Fifth intercostal space at the left midaxillary line Fifth intercostal space at the left midclavicular line Fifth intercostal space at the left anterior axillary line Fourth intercostal space at the right sternal border 6 4 5 1 Slower than 60 beats/min Between 61 and 100 beats/min Between 101 and 150 beats/min Between 151 and 220 beats/min
the upper right atrium. This impulse travels through the intermodal fibers and spreads over the atrial musculature. This causes atrial contraction. The impulse then reaches the atrioventricular (AV) node. From the AV node, the impulse moves down through the bundle of His and ends at the Purkinje fibers. Impulses from the Purkinje fibers cause ventricular contractions. p. 884 Report content error
A premature atrial contraction occurs at the atrium and before the next sinus beat. A premature atrial contraction occurs in either the left atrium or right atrium and travels along the atria. The ECG of a premature atrial contraction usually shows hidden P waves in preceding T waves with prolonged PR interval. The QRS complex remains normal. The electrocardiogram of ventricular fibrillation has absent P waves and an undetectable PR interval and QRS complex. The ECG of junctional dysrhythmia shows a distorted P wave and reduced PR interval. The QRS complex remains normal. The ECG of premature ventricular contractions Ventricular fibrillation Junctional dysrhythmia Premature atrial contractions Premature ventricular contractions
shows a rare occurrence of P waves. The PR interval cannot be measured with a disturbed and elongated QRS complex and T wave. p. 892 Report content error
The electrical impulse in the heart must travel from the SA node through the AV node and into the Purkinje fibers for synchronous atrial and ventricular contraction to occur. When measuring the PR interval (the time from the beginning of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS), the nurse is identifying the length of time it takes for the electrical impulse to travel from the SA node to the Purkinje fibers. The P wave represents the length of time it takes for the impulse to travel from the SA node through the atrium, causing depolarization of the atria (atrial contraction). Atrial repolarization occurs during ventricular depolarization and is hidden by the QRS complex. The length of time it takes for the electrical impulse to travel from the SA node to the AV node is the flat line between the end of The length of time it takes to depolarize the atrium The length of time it takes for the atria to depolarize and repolarize The length of time for the electrical impulse to travel from the sinoatrial (SA) node to the Purkinje fibers The length of time it takes for the electrical impulse to travel from the SA node to the atrioventricular (AV) node
A centralized monitoring system is a type of telemetry monitoring system. It requires continuous observation of a group of patients’ electrocardiograms at a central location. Centralized monitoring systems observe heart rate and rhythm remotely, at a site distant from the patient. A centralized monitoring system helps to detect dysrhythmias, ischemia, or infarction in patients. p. 888 Report content error
It measures the patients’ heart rate remotely. It cannot diagnose dysrhythmias. It cannot rapidly detect myocardial ischemia. It requires continuous observation of patients’ electrocardiograms (ECGs). The patient is shivering. The patient has dry skin. The conductive gel is moist.
Muscle activity caused by shivering of the patient, electrical interference, or loose leads and electrodes can cause distorted baseline and waveforms called an artifact on the ECG. Oily skin is wiped dry with alcohol to prepare the patient for ECG. Electrodes may have to be replaced if conductive gel has dried out. pp. 887- Report content error
Typical ECG changes that are seen in myocardial ischemia include ST segment depression and/or T wave inversion. The typical ECG change seen during an acute myocardial infarction is ST segment elevation. Depression of the ST segment and T wave inversion occur in response to an Electrical interference is present. The leads and electrodes are not secure. Sinus arrhythmia Normal T wave Pathologic Q wave ST segment depression
Test-Taking Tip: Sometimes the reading of a question in the middle or toward the end of an exam may trigger your mind with the answer or provide an important clue to an earlier question. p. 892 Report content error
The patient is at greatest risk if the ectopic impulse falls on the T wave (label 4 on the graph) of a preceding beat. This is called the R-on-T phenomenon. This is especially dangerous because the premature ventricular contraction (PVC) is firing during the relative refractory period of ventricular repolarization. Excitability of the heart cells increases during this time, and the risk for the PVC to start ventricular tachycardia (VT) or ventricular fibrillation (VF) is great. Label 1 on the graph represents the P wave, label 2 represents the QRS complex, and label 3 represents the ST segment of the cardiac cycle. p. 897 Report content error
Clip excessive hair with scissors. Gently rub the skin with dry gauze. Affix the electrodes. Monitor for artifact.
fibrillation elicits the absence of P waves, and the PR interval and QRS interval cannot be measured. In premature atrial contraction, there are distorted P waves in the ECG. pp. 891- Report content error
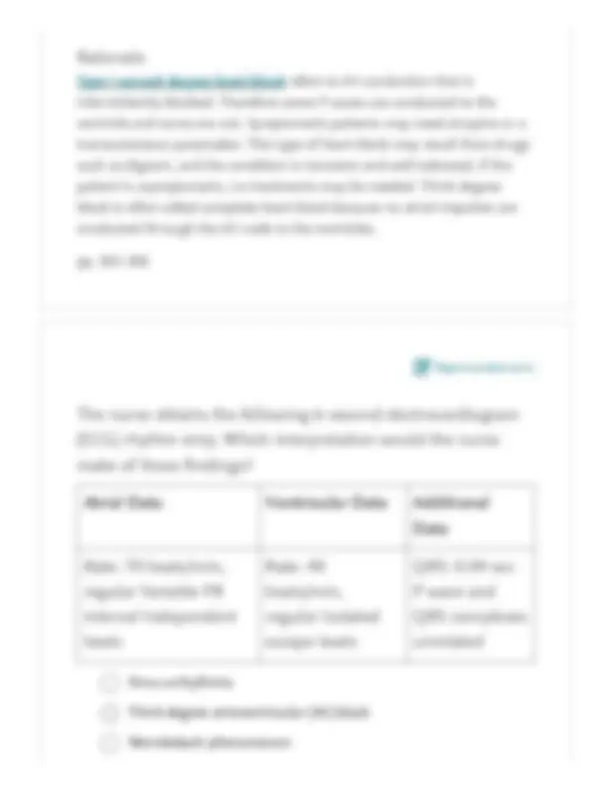
A third-degree AV block is often called a complete heart block because no atrial impulses are conducted through the AV node to the ventricles. In such situations, the atria and ventricles beat independently because the AV node is completely blocked to the sinus impulse and, therefore, it is not conducted to the ventricles. One of the characteristics of a third-degree heart block is that the P waves have no association with the QRS complexes and appear throughout the QRS waveform. The P wave has a normal shape. The atrial and ventricular rhythms are regular, but these are The PR interval is variable. The P wave has a normal shape. The ventricular rate is irregular. The atrial rate is more than 100 beats/min. The atrial and ventricular rhythms are regular but unrelated.
not related to each other. The atrial rate is usually a sinus rate of 60 to 100 beats/min. STUDY TIP: Avoid planning other activities that will add stress to your life between now and the time you take the licensure examination. Enough will happen spontaneously; do not plan to add to it. pp. 891, Report content error
Sinus tachycardia Sinus bradycardia Premature atrial contraction