





Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
In the following Lecture of Structural geology, the Lecturer has explained the following terms : Rheology, Materials, Materials Fall, Elasticity, Viscosity, Plasticity, Strain Relations, Mechanical Analogues, Recoverable Versus, Real Materials
Typology: Slides
1 / 8

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





o Elasticity.
o Viscosity.
o Plasticity.
Ideal materials fall into one of the following categories:
Different materials deform differently under the same state of stress. The material response to a stress is known as rheology.
Docsity.com
Elastic
Plastic
Viscous
Mechanical analogues Stress-Strain relations
Docsity.com
Real materials exhibit a variety of behaviors:
from ic.ucsc.edu/~casey/eart150/Lectures/Rheology/13rheology.htm Docsity.com
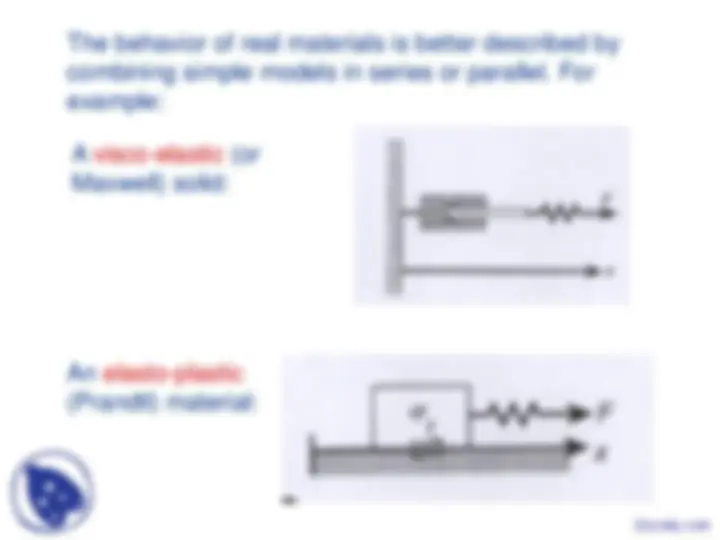
The behavior of real materials is better described by combining simple models in series or parallel. For example:
A visco-elastic (or Maxwell) solid:
An elasto-plastic (Prandtl) material:
Docsity.com
The one-dimensional stress-strain relationship may be written as:
where C is an elastic constant.
o The response is instantaneous. o Here the strain is the infinitesimal strain.
Note that:
Docsity.com
The material is said to be linear elastic if n=1.
Hooke’s law:
σ = C ε
In three dimensions, Hooke’s law is written as:
σ (^) ij = Cijkl ε kl
where Cijkl is a matrix whose entries are the stiffness coefficients.
Docsity.com