






Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An introduction to representing information using binary, hexadecimal, and ascii systems. It covers the basics of binary and hexadecimal number systems, converting between decimal, binary, and hexadecimal, and the use of ascii for character representation. Students will gain a foundational understanding of these systems and their applications in computer science.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 19

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!












Watch Newman on YouTube
AND Gate Input Wires Output Wire
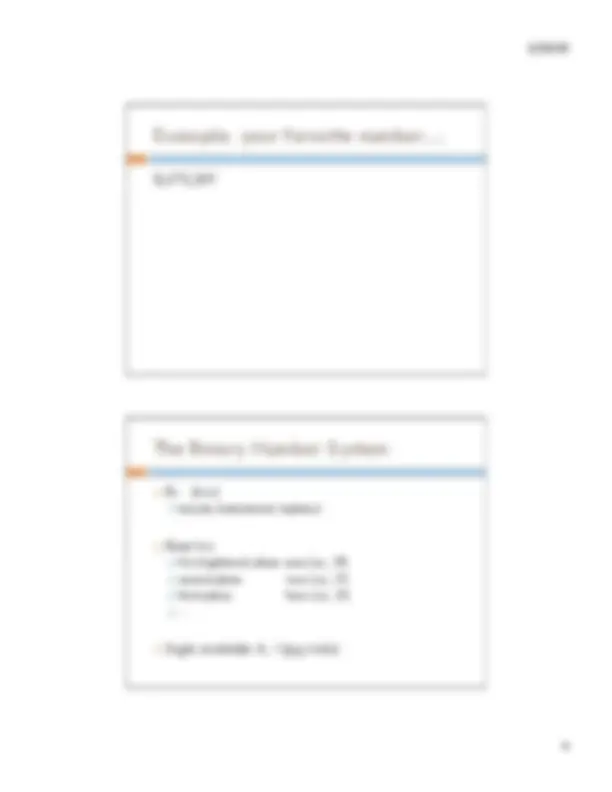
8,675,
! Bi- (two)
! Base two
! Digits available: 0, 1 (two total)
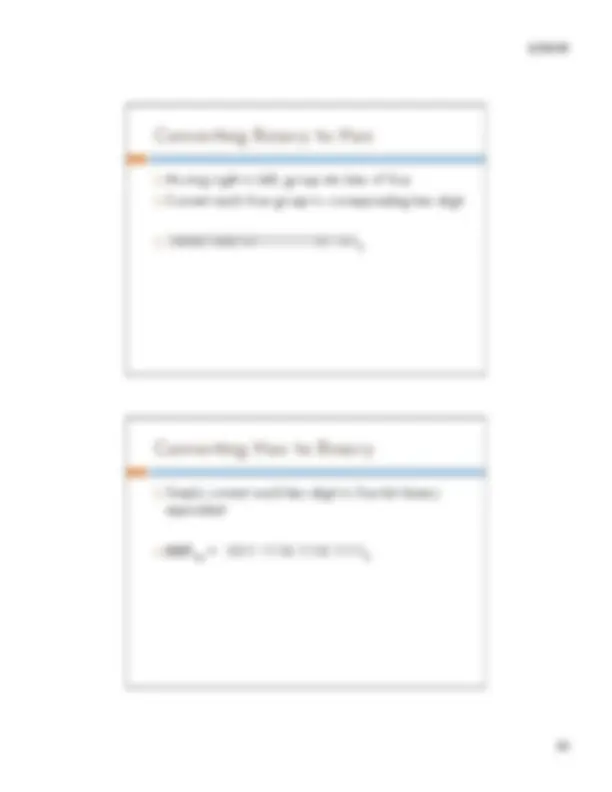
! Moving right to left, include a "slot" for every power of two <= your decimal number ! Moving left to right: Put 1 in the slot if that power of two can be subtracted from your total remaining Put 0 in the slot if not Continue until all slots are filled
! 8,675,309 10
(^1000010001011111111011012) ! Fewer available digits in binary: more space required for representation
THERE ARE 10 TYPES OF PEOPLE IN THE WORLD: THOSE WHO CAN COUNT IN BINARY AND THOSE WHO CAN'T
! What if this was km to landing?
! Hex- (six) Deci- (ten) ! Base sixteen first (rightmost) place: ones (i.e., 16^0 ) second place: sixteens (i.e., 16^1 ) third place: two-hundred-fifty-sixes (i.e., 16^2 ) … ! Digits available: sixteen total 0, 1, 2, …, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F
! Can convert decimal to hex and vice-versa process is similar, but using base 16 and 0-9, A-F ! Most commonly used as a shorthand for binary ! Avoid this
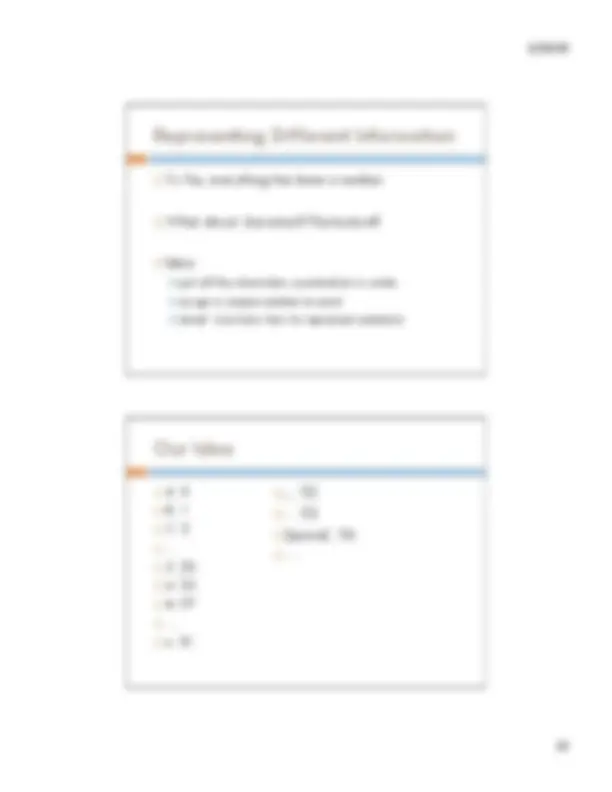
! How many different things can you represent using binary: ! with only one slot (i.e., one bit)? ! with two slots (i.e., two bits)? ! with three bits? ! with n bits?
! One slot in hex can be one of 16 values 0, 1, 2, …, 9, A, B, C, D, E, F ! How many bits do you need to represent one hex digit? ! 4 bits can represent 2^4 = 16 different values
0 0000 1 0001 2 0010 3 0011 4 0100 5 0101 6 0110 7 0111 8 1000 9 1001 A 1010 B 1011 C 1100 D 1101 E 1110 F 1111
! Moving right to left, group into bits of four ! Convert each four-group to corresponding hex digit ! (^1000010001011111111011012)
! Simply convert each hex digit to four-bit binary equivalent ! BEEF 16 = 1011 1110 1110 1111 2
'A' = 65 10 = ??? 2 'q' = 90 10 = ??? 2 '8' = 56 10 = ??? 2
256 total characters… How many bits needed?
! What about Greek characters? Chinese? ! UNICODE: use 16 bits ! How many characters can we represent?
! What is this? 01001101 ! Depends on how you interpret it: ! 010011012 = 77 10 ! 010011012 = 'M' ! 0100110110 = one million one thousand one hundred and one ! You must be clear on representation and interpretation