







Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Material Type: Notes; Class: Radiation Science; Subject: Physics; University: University of Mississippi Main Campus; Term: Unknown 1989;
Typology: Study notes
1 / 11

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!







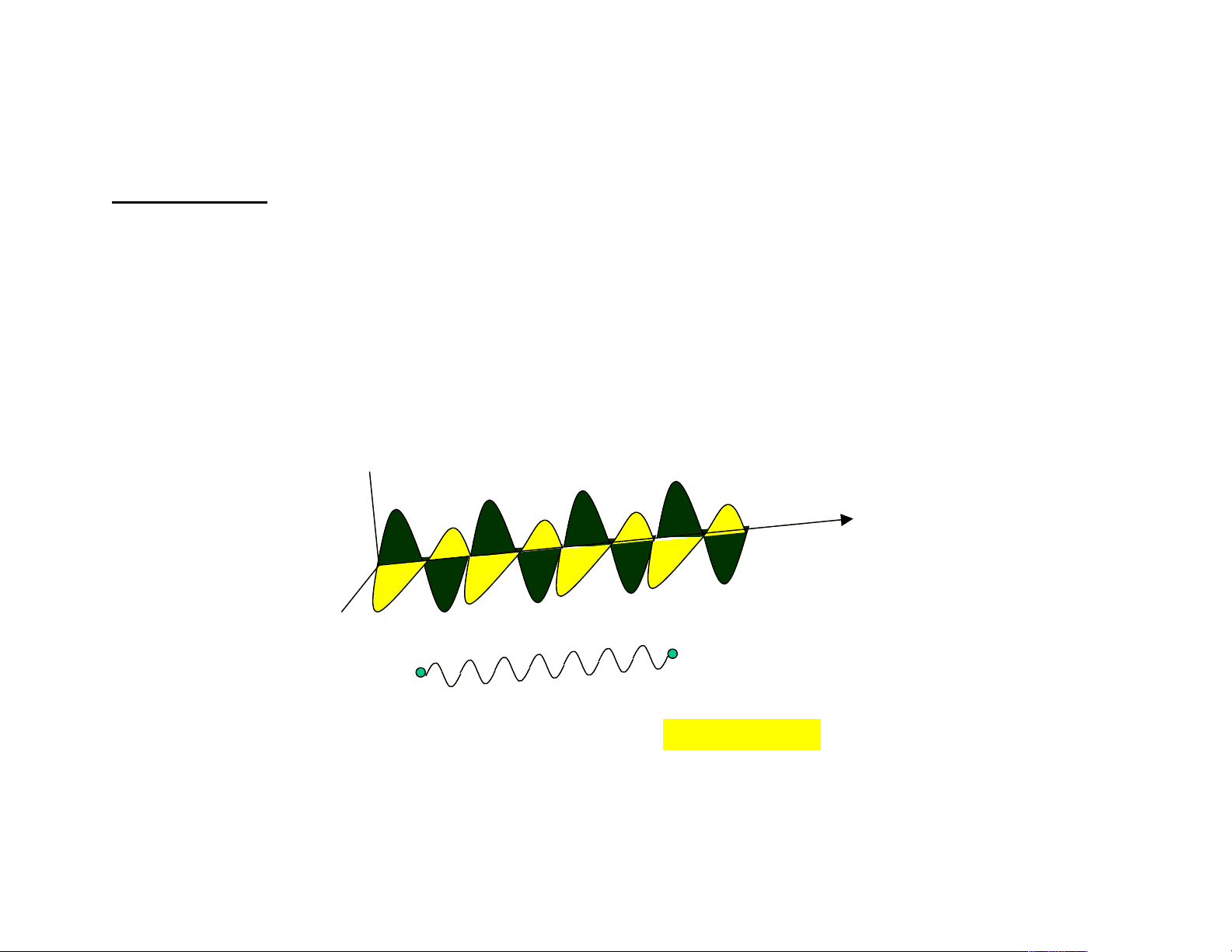
E
B
Plane Wave
v = c
a
b
Consider a dipole antenna emitting EM radiation. The E-field follows the charge up and down, The B-field circulates about the current I flow up and down.
E = ( V/d ) k d = length of the antenna B = ( μo I/ 2πR ) i R = radius of the antenna wire
S = ( V /d) ( μo I/ 2πR ) k x i = ( V /d) ( μo I / 2πR ) j
Power emitted from the surface of the antenna P = S x Area P = 1/ μo {(V/d) ( μo I/ 2πR )} 2πR d = I V P =IV (Watts) V = IR (Ohm’s Law)
R
d
V - Oscillator i
j
I k
Hertz Dipole Antenna Waves
E
V
V=
c
V
θ
V
V
7
ETHER HYPOTHESIS BUSTED - NO ETHER!!
Light source 2nd slit
Mirror- 1
Mirror- 2
Beam Splitter - 0 L
Interference Pattern or not? Not?
V Ether Wind
β = V/c Relative speed 0 1
γ = (1- β^2 )-1/^2 Lorentz factor 1
EINSTEIN’s POSTULATES OF RELATIVITY
A
B c
c c +V
Consider light of frequency fo being emitted from a source. An outside Observer will measure a shifted frequency coming from the source
!
f = fo^1 "^ # 1 + #
Source moving away from the Observer with relative speed β. RED SHIFT
!
f = fo^1 +^ " 1 # "
Source moving toward the Observer with relative speed β. BLUE SHIFT
λ = f / c
600nm 500nm 400nm
fo
f <fo (^) f >fo
Einstein used the Lorentz transformation to form a 4-dimensional spacetime.
Let x’ t’ denote the position and time in the laboratory system Let x t denote the position and time in the moving system.
Lorentz Transform Derivative x’ = γ (x + vt) dx’ = γ (dx + v dt) t’ = γ (t + v x/c^2 ) dt’ = γ (dt + v dx/c^2 )
Velocity Transform Vx’ = dx’/dt’ = (dx + β cdt ) / (cdt + β dx )
v= relative velocity Vx = velocity of an object in the moving frame. Vx’ = velocity of the same object as measured in the Lab frame.
Vx << c Vx’ = Vx + v NEWTON Vx = c (flashlight) Vx’ = c EINSTEIN
Lab
Moving β=v /c
x ct
x’ ct’
!
Vx '= Vx^ +^ v 1 + Vx • v / c^2
Lab
Vx=c
Vx’=?
β=v/c