














Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
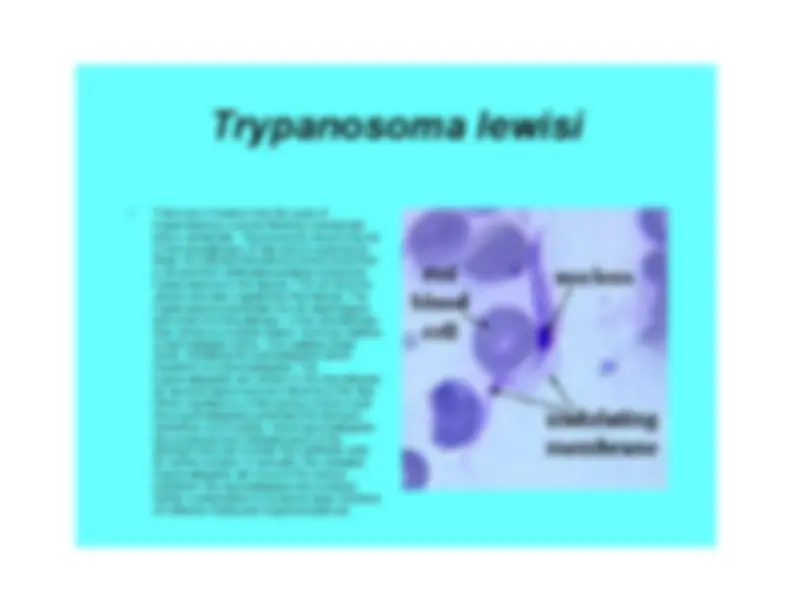
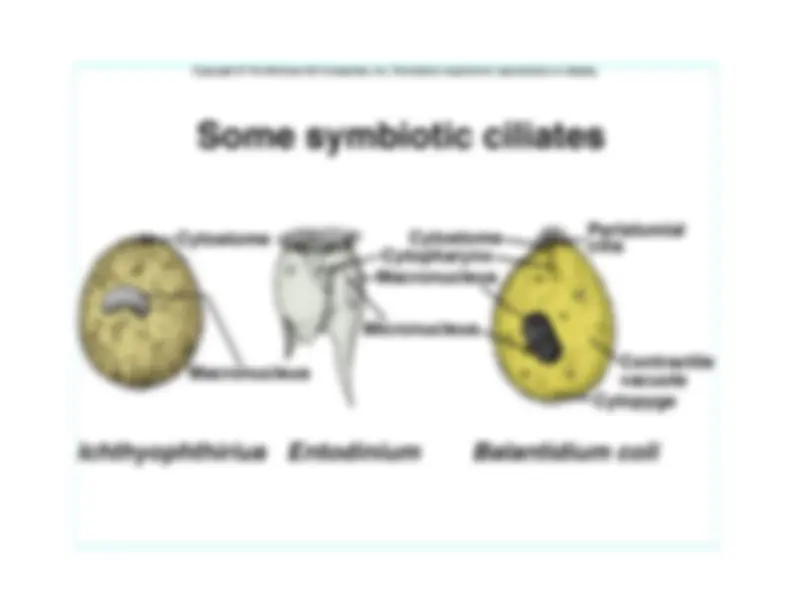
An overview of the protozoa kingdom, focusing on their classification, locomotion mechanisms, nutritional modes, osmoregulation, and reproduction. It also delves into the life cycle of trypanosoma lewisi, a parasitic protozoan that affects rats and is transmitted by fleas.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 31

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
























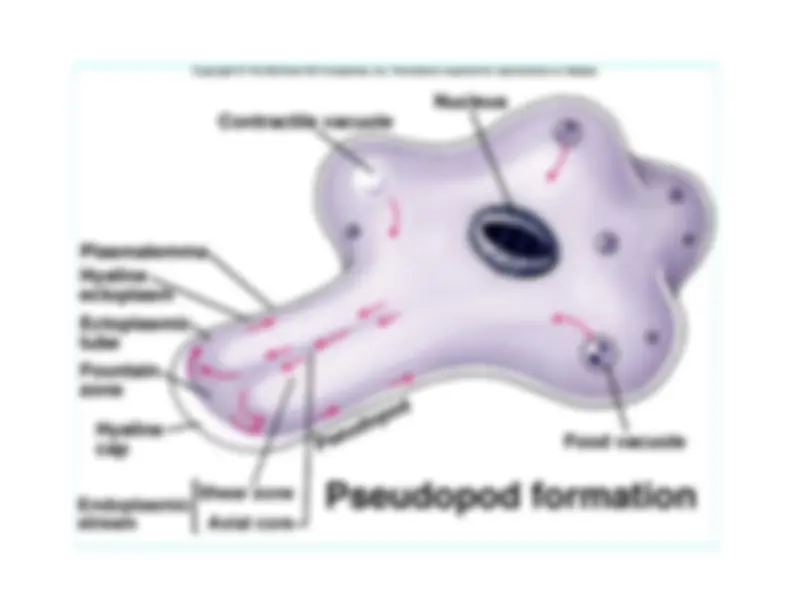
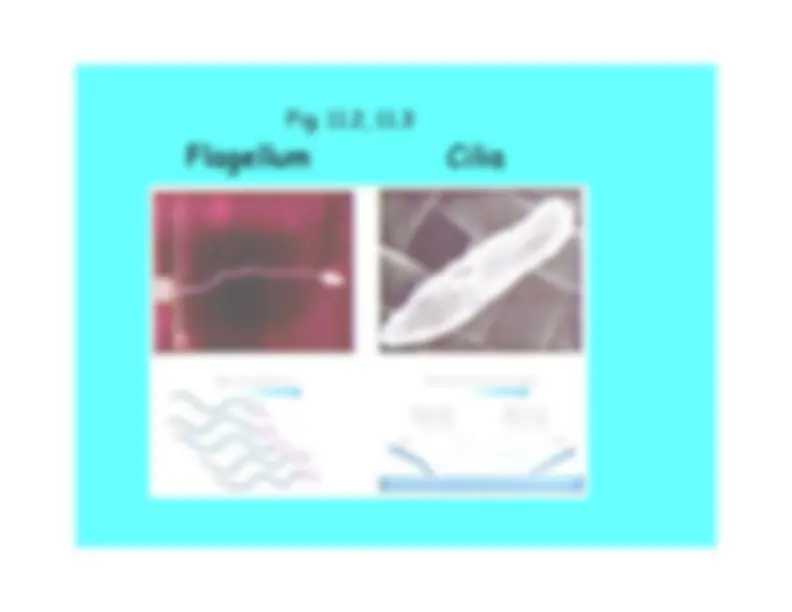
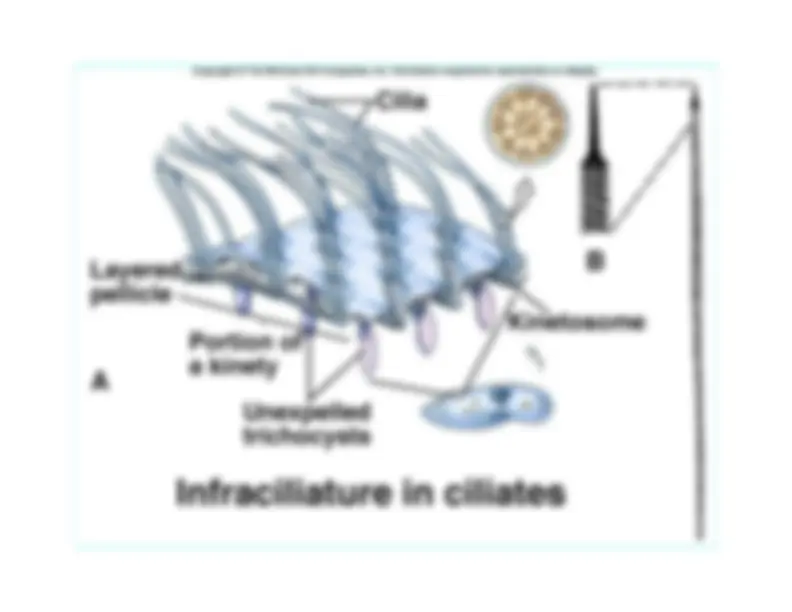
microfilaments in cell Fig. 11.
All is based on contractile fibers• mitotic spindle and centrioles• eukaryote flagellum and cilia• ameboid movement and cytoplasmic
streaming
9 + 2 double fibrils
Fig. 11.2, 11.
For example,
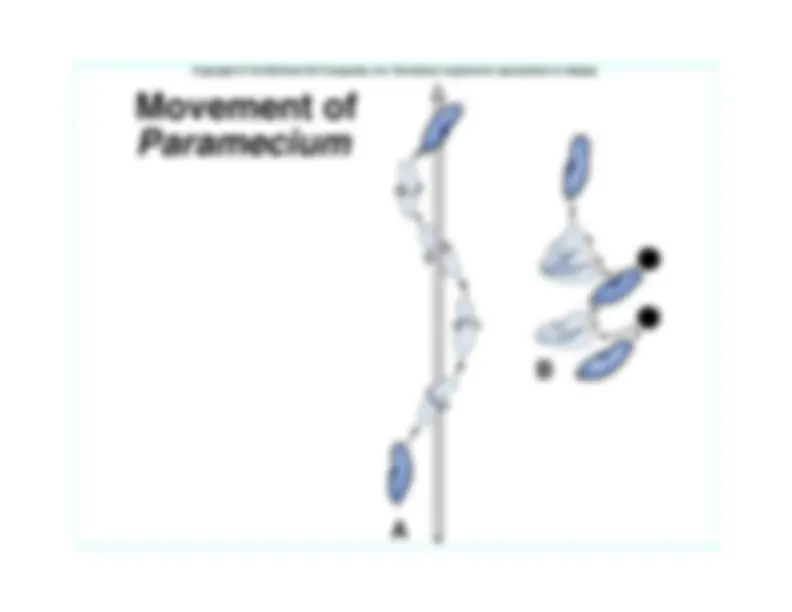
Paramecium, a protist, is
hypertonic when compared to the pond waterin which it lives.– In spite of a cell membrane that is less
permeable to water than other cells, waterstill continually enters the
Paramecium cell.
Paramecium have aspecialized organelle,the contractile vacuole,that functions as a bilgepump to force water outof the cell.
Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
Fig. 8.
In
pinocytosis
, “cellular drinking”, a cell
creates a vesicle around a droplet ofextracellular fluid.– This is a non-specific process. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
-^
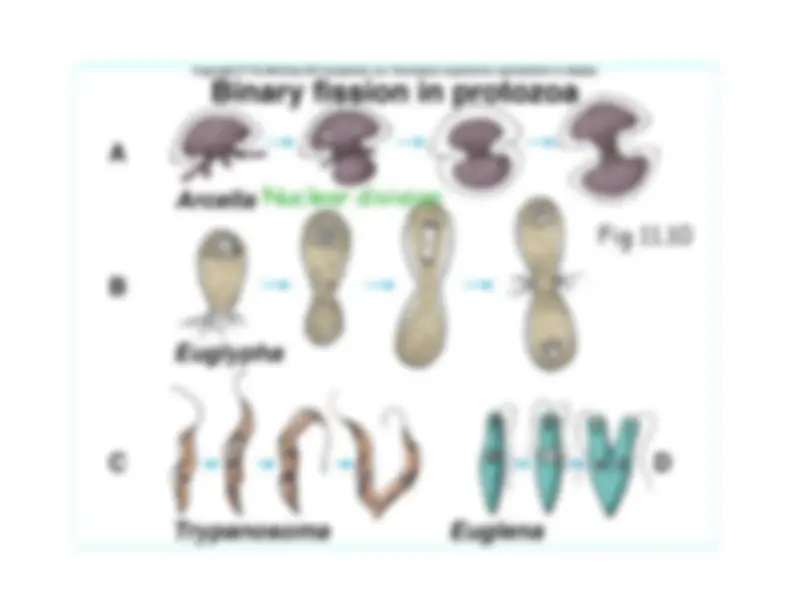
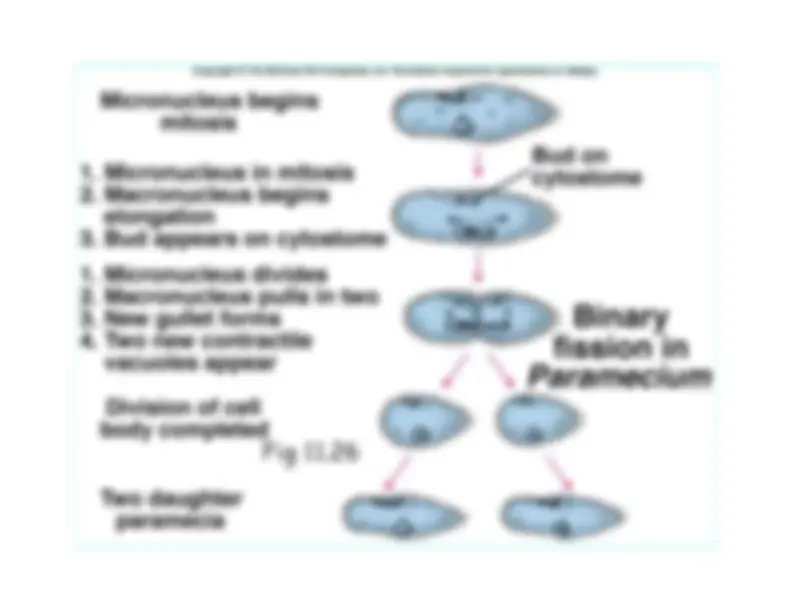
Asexual– Fission; binary fission produces two identical
cells
through cytokinesis
Sexual– Isogametes/ansiogametes– Most “protozoa” are haploid
-^
Encystment