

























Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
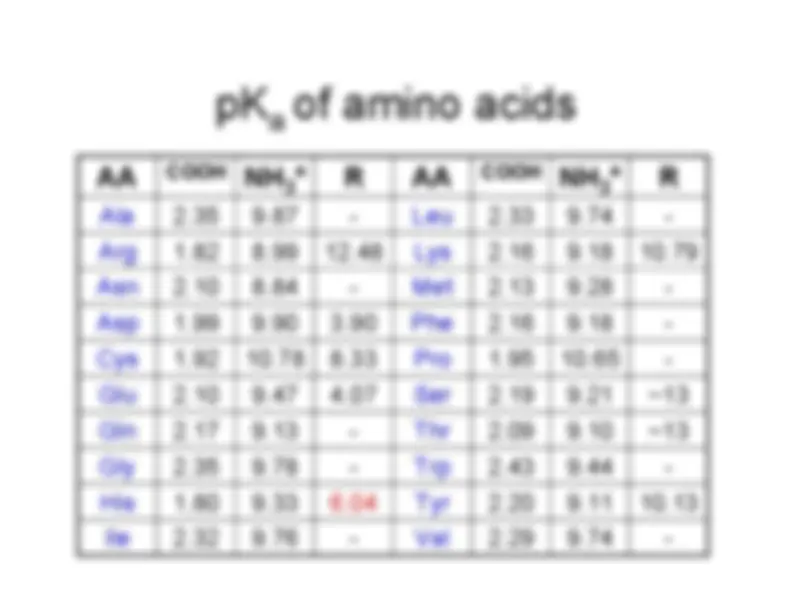
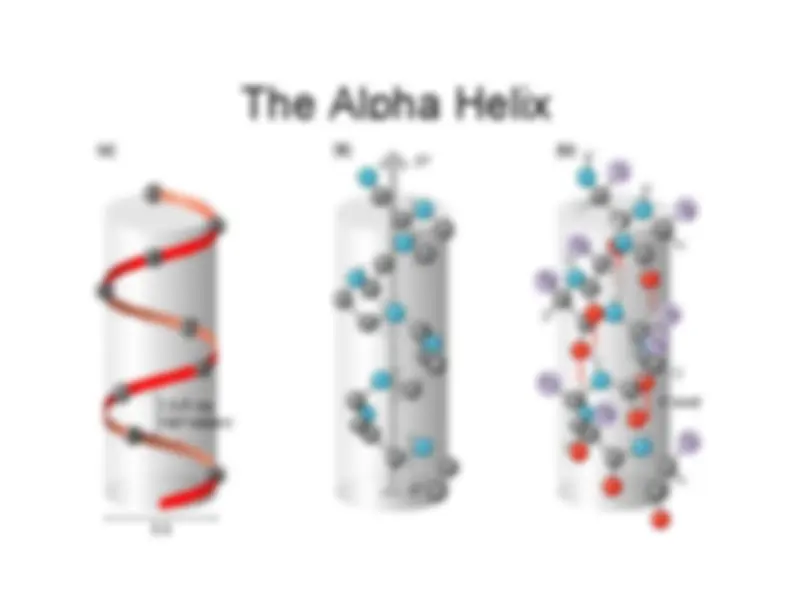
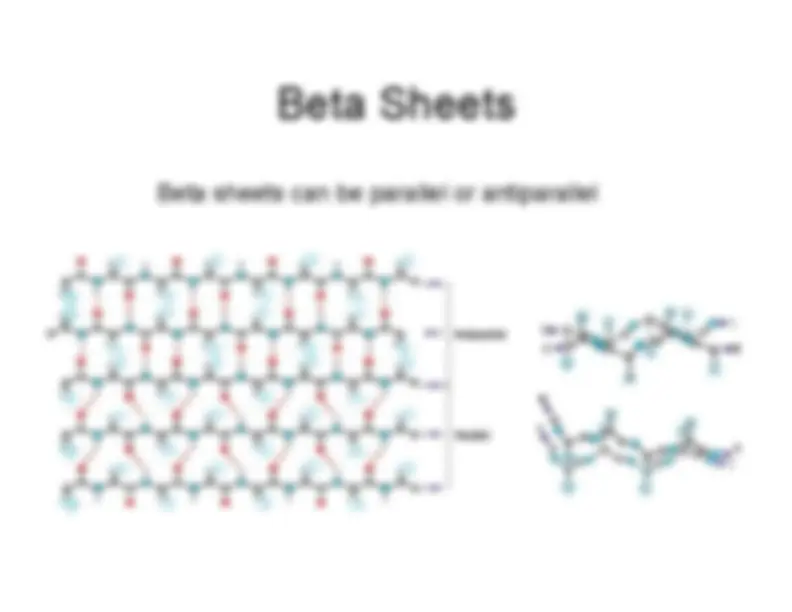
An overview of protein structure, focusing on the role of amino acids and their properties, including pKa values. It covers the formation of peptide bonds, the organization of proteins into secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures, and the importance of non-covalent bonds. The document also discusses methods for determining protein structures.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 40

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!

































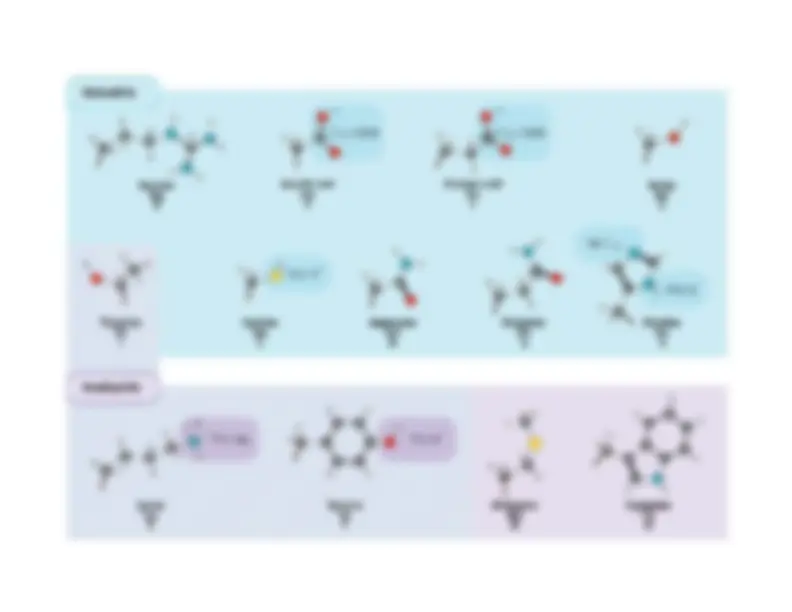
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. All AA’shave the same basic structure:
CarboxylGroup
AlphaCarbon AminoGroup
SideChain
More depictions from Petsko and Ringe
−
a
Val
Ile
Tyr
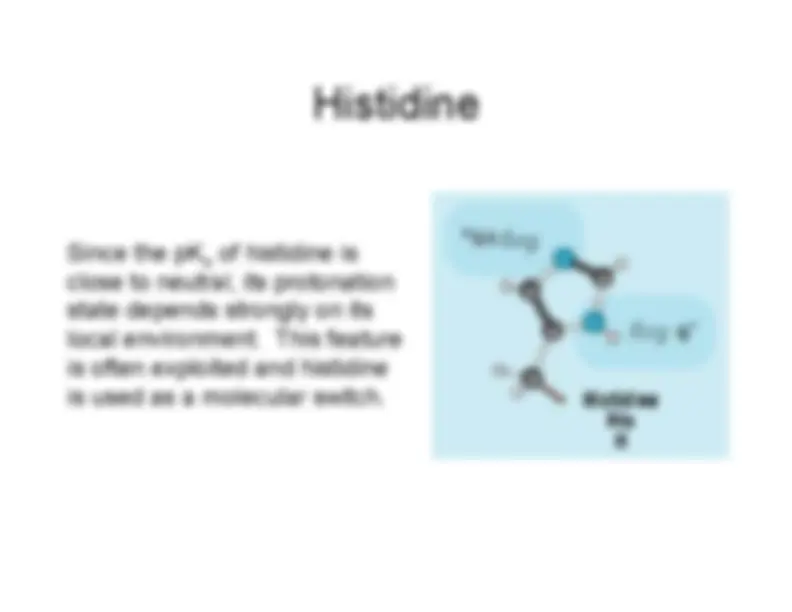
His
Trp
Gly
Thr
Gln
Ser
Glu
Pro
Cys
Phe
Asp
Met
Asn
Lys
Arg
Leu
Ala
+ 3
COOH
+ 3
COOH
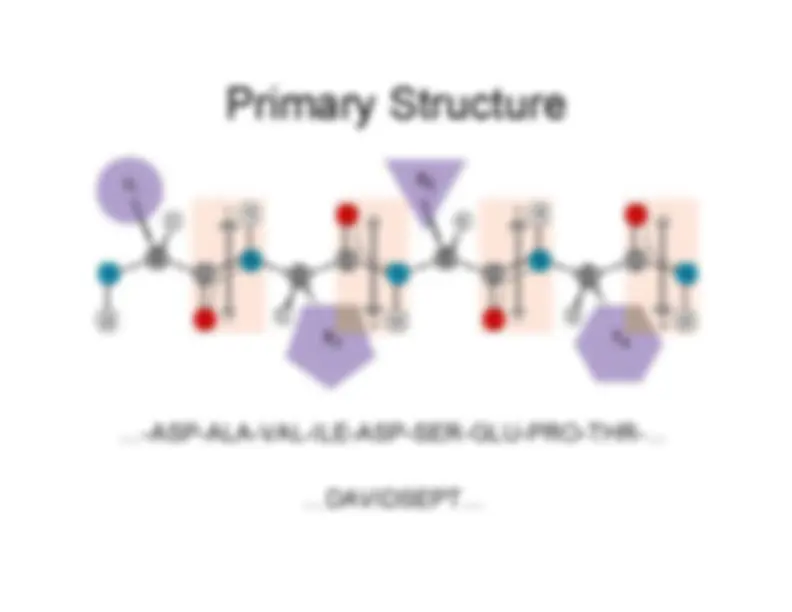
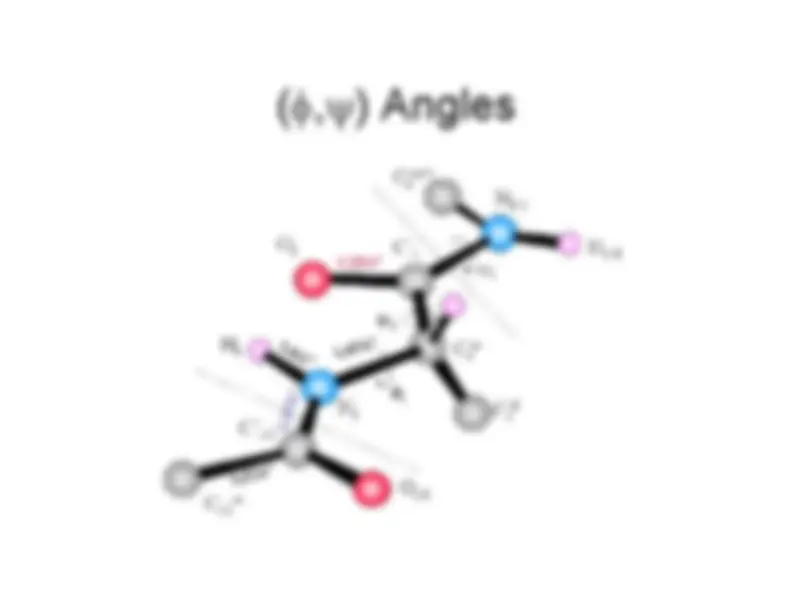
To make a protein, these amino acids are joined togetherin a polypeptide chain through the formation of a peptidebond.
-^ Proteins are nothing more than long polypeptide chains.•^ Chains that are less than 40-50 amino acids or residuesare often referred to as polypeptide chains since they aretoo smal to form a functional domain.•^ Larger than this size, they are called proteins•^ The structure, function and general properties of aprotein are all determined by the sequence of aminoacids that make up its primary sequence.
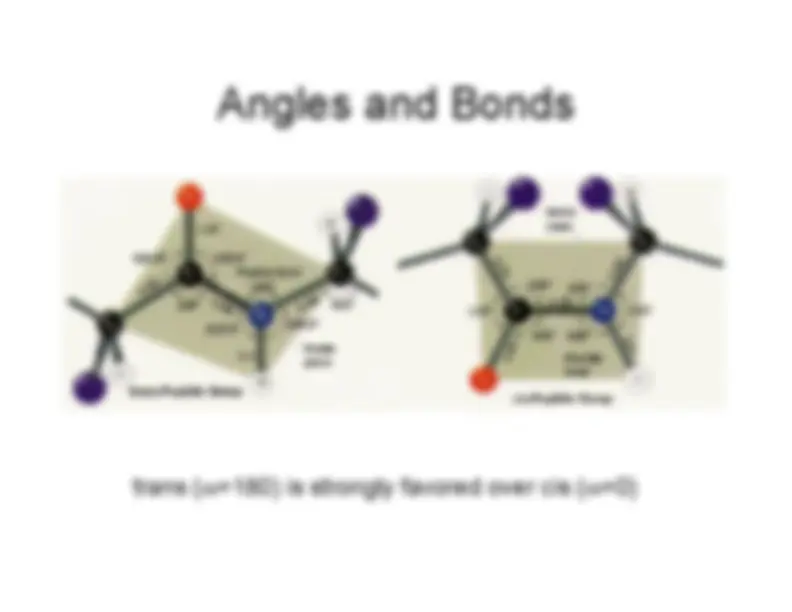
trans (
ω=180) is strongly favored over cis (
ω=0)