







































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
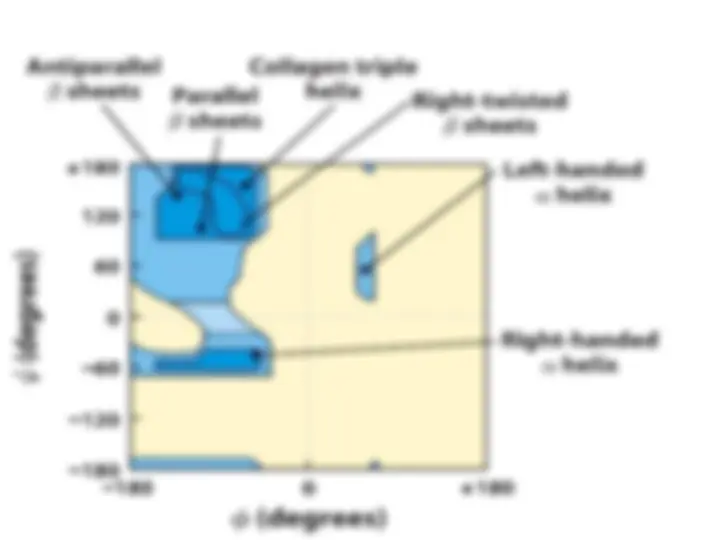
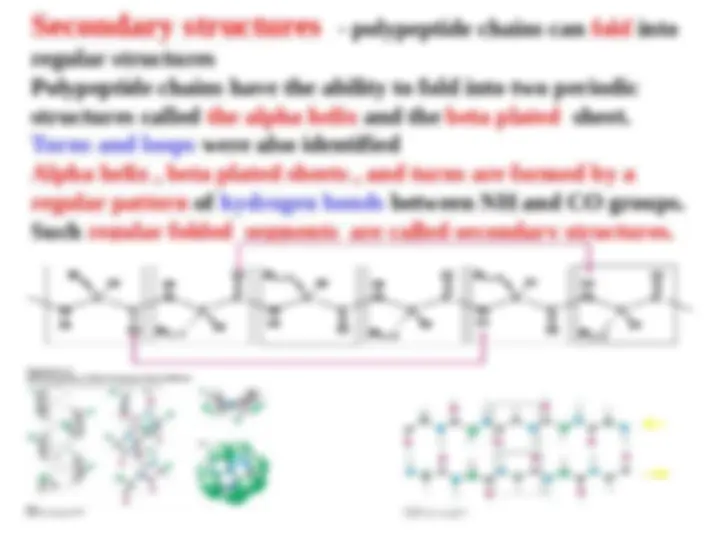
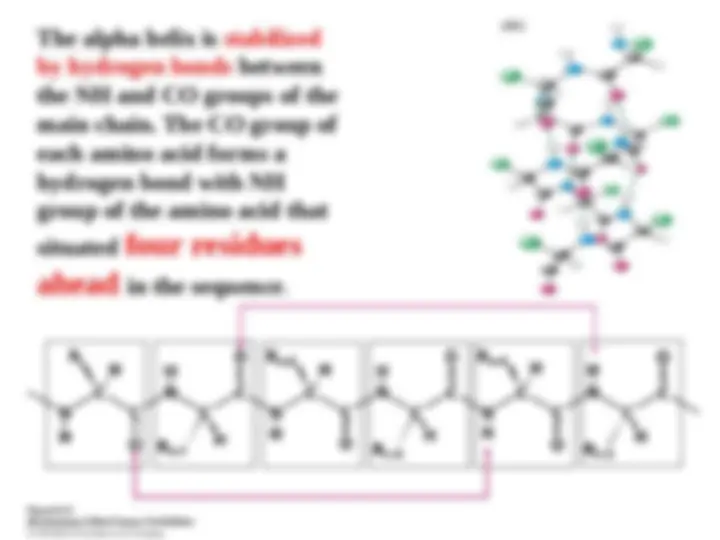
An overview of the different levels of protein structure - primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. It explains how the sequence of amino acids in a protein determines its three-dimensional structure, and discusses the importance of hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions, and disulfide bonds in protein structure. It also covers the concepts of secondary structures (alpha helix and beta sheet), tertiary structure (compact and globular), and quaternary structure (multiple polypeptide chains).
Typology: Study notes
1 / 57

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!


















































DNA encodes the sequence of amino acids that constitute the protein. The amino acid sequence is called the primary structure. Functioning proteins , are not long polymers of amino acids. These polymers fold to form discrete three- dimensional structures with specific biochemical functions.
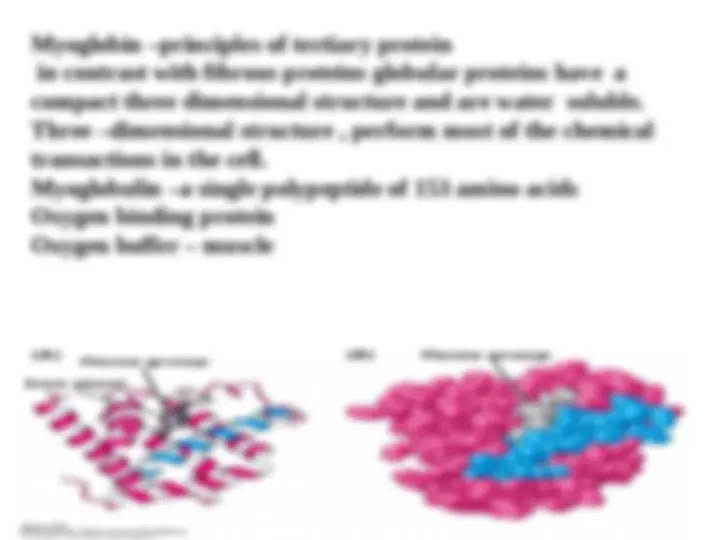
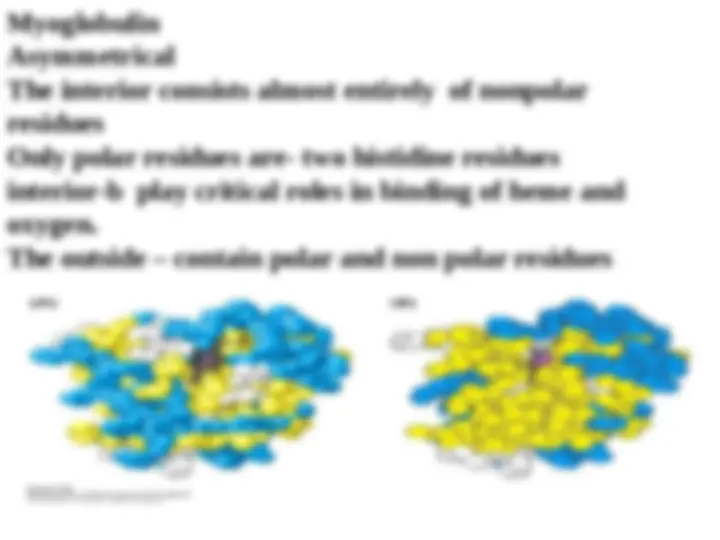
The three dimensional structure becomes more complex when the R groups of amino acids far apart in the primary structure bond with one another. this level of structure is called tertiary structure and is the higher level of structure that an individual polypeptide can attain.
Noncovalent interactions important for protein structure:
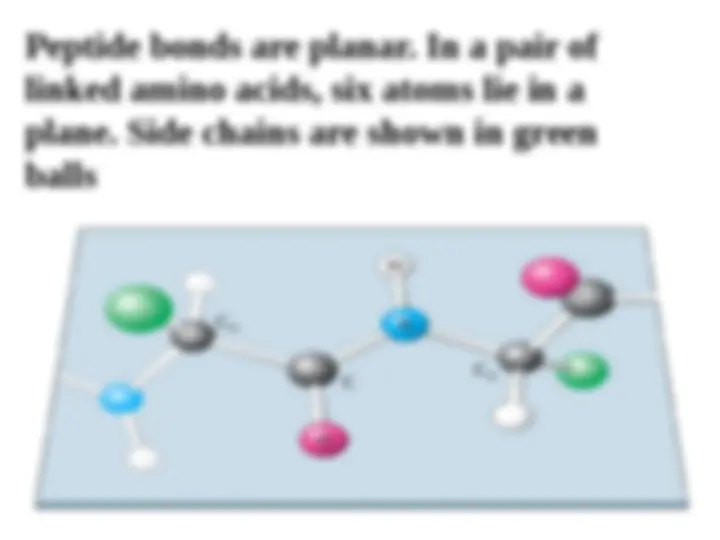
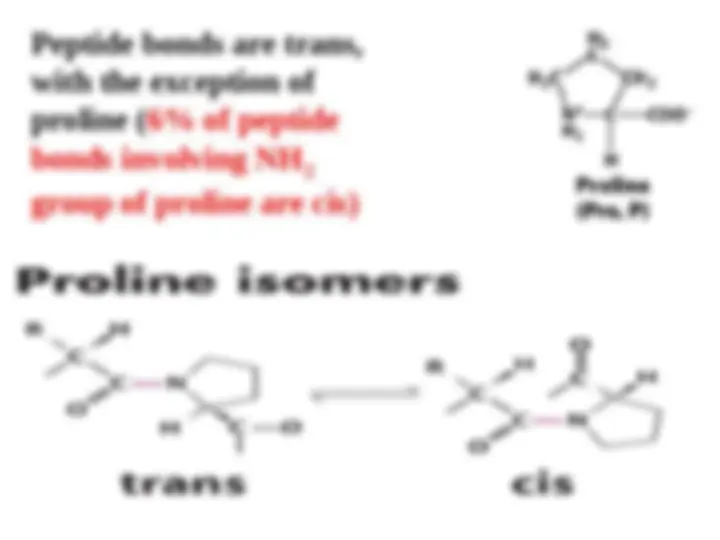
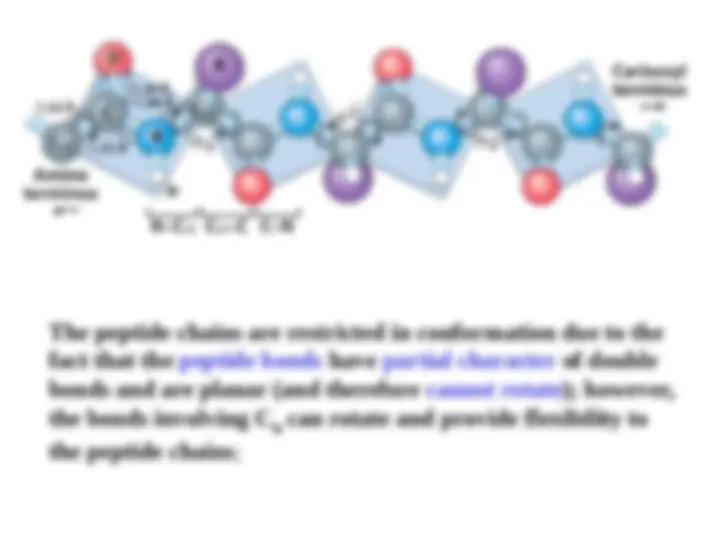
The peptide bond (CO-N) has 40% character of a double bond, therefore it is planar; it is also polar
Amino acid sequences have directions. This illustration of the polypeptide try-gly-gly-phe-leu (YGGFL) shows the sequence from the amino terminus to the carboxyl terminus. This pentapeptide , leu-enkephalin , is an opioid peptide that modulates the perception of pain. The reverse sequence , leu-phe-gly-gly –try (LFGGY) , is different pentapeptide , with different chemical properties.
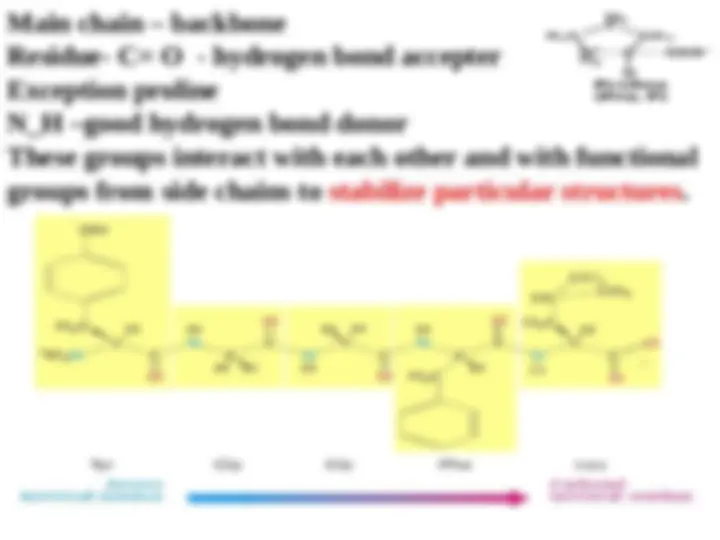
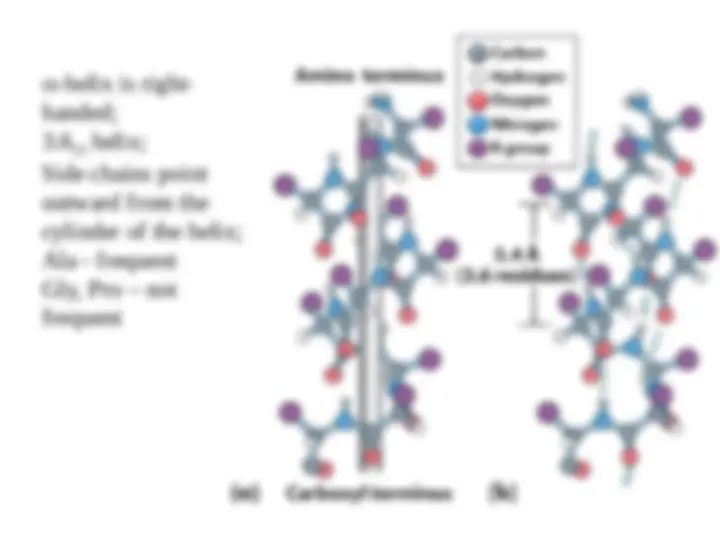
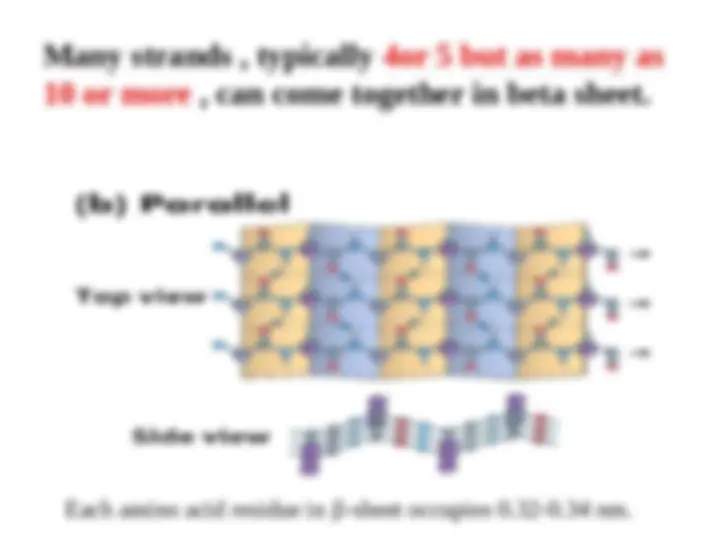
Main chain – backbone Residue- C= O - hydrogen bond accepter Exception proline N_H –good hydrogen bond donor These groups interact with each other and with functional groups from side chains to stabilize particular structures.
Proteins have unique amino acid sequences specified by genes
In 1953 Frederick Sanger won the Nobel prize for protein sequencing. Land mark in biochemistry It took 10 years, many people, and it took 100 g of protein! Today it takes one person several days to sequence the same insulin. 1021 AA b-- glactosidase
Primary structure determine the three dimensional structure of a protein, and the three dimensional structure determine the protein function. What are the rules governing the relation between an amino acid sequence and the three dimensional structure of protein?