







Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
A study guide or review material for a final exam in a political science course (pls 101). It covers a wide range of topics related to civil liberties, constitutional rights, and legal concepts such as the bill of rights, due process, free speech, and discrimination. Definitions, explanations, and key court cases for these important legal and political topics. This information could be useful for students preparing for a final exam in an introductory political science or constitutional law course. The level of detail and breadth of coverage suggests this document could serve as comprehensive study notes, lecture notes, or a summary for exam preparation.
Typology: Exams
1 / 12

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
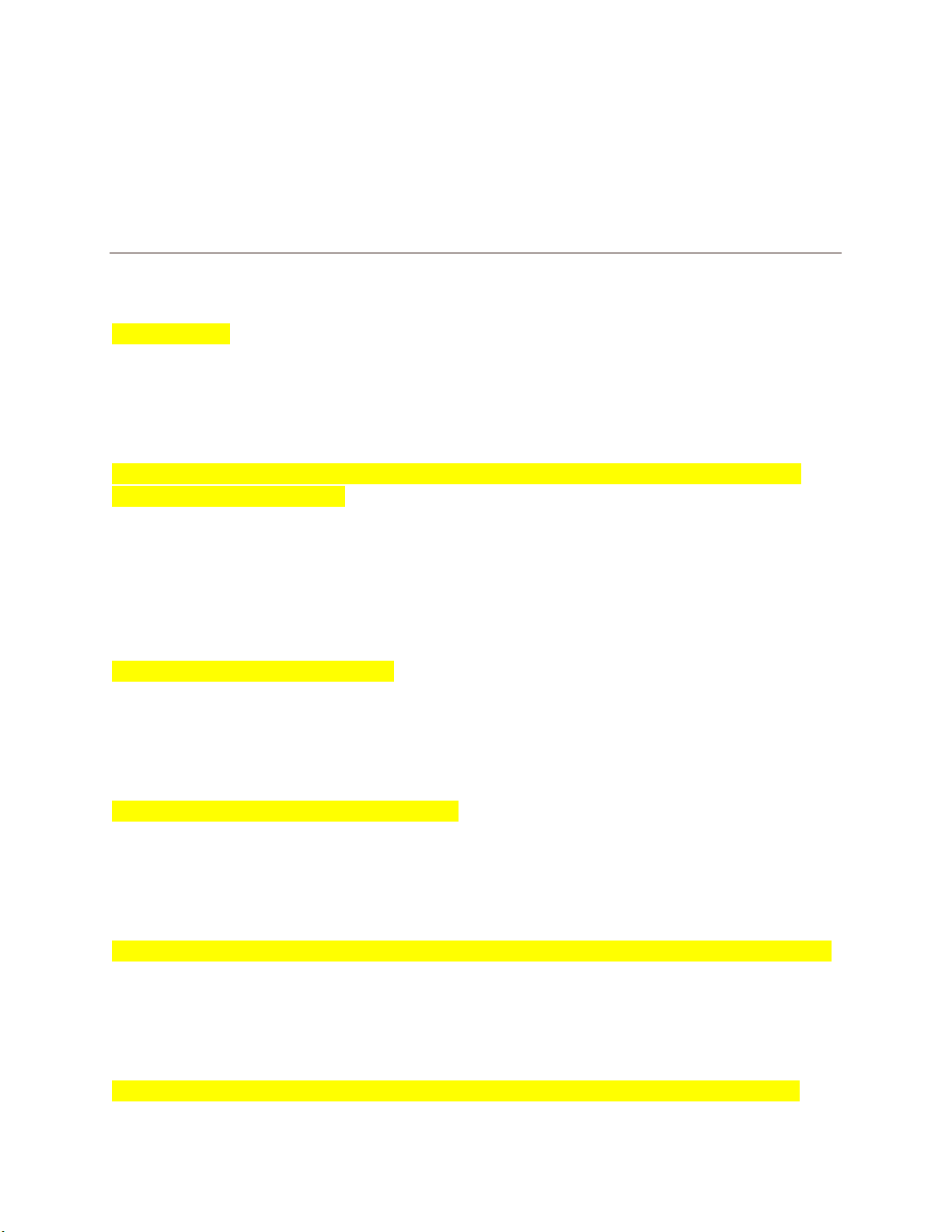






Amendments protecting the accused 4th, 5th, 6th, 8th bad tendency test Interpretation of the First Amendment that would permit legislatures to forbid speech encouraging people to engage in illegal action. Bill or Rights First 10 amendments to the Constitution Civil Liberties Constitutional freedoms guaranteed to all citizens clear and present danger test law should not punish speech unless there was a clear and present danger of producing harmful actions commerical speech communication in the form of advertising; can be restricted more than many other types of speech
Due Process fair treatment through the normal judicial system, especially as a citizen's entitlement. Establishment Clause Clause in the First Amendment that says the government may not establish an official religion. exclusonary rule a rule of evidence, illegally seized items should be excluded from or suppressed from trial, even if law enforcement does an illegal search and don't find anything but information leads them to evidence it is still suppressed Free Exerise Clause Clause in the First Amendment that states that Congress shall make no law prohibiting the free exercise of religion. free-expression clauses The press and speech clauses of the First Amendment. Habeas Corpus An order to produce an arrested person before a judge. Incorporation
right to privacy The right to a private personal life free from the intrusion of government. selective incorporation The process by which provisions of the Bill of Rights are brought within the scope of the Fourteenth Amendment and so applied to state and local governments. Slander spoken defamation symbolic speech nonverbal communication, such as burning a flag or wearing an armband. The Supreme Court has accorded some symbolic speech protection under the first amendment. time, place, and manner restrictions regulations regarding when, where, or how expression may occur; must be content neutral invidious discrimination discrimination against persons or groups that works to their harm and is based on animosity Jim Crow Laws
Laws designed to enforce segregation of blacks from whites literacy test A test given to persons to prove they can read and write before being allowed to register to vote Plessy v. Ferguson a 1896 Supreme Court decision which legalized state ordered segregation so long as the facilities for blacks and whites were equal poll tax A requirement that citizens pay a tax in order to register to vote University of California v. Bakke 1978 The supreme court ruled that a white man Allan Bakke had been unfairly denied admission to medical school on the basis of quotas. the court did not ruleout all forms of affirmative action, but it did strike down the quota system seperate but equal doctrine The doctrine established in Plessy v. Ferguson that African Americans could constitutionally be kept in seperate but equal facilities. strict scrutiny test a test applied by the court when a classification is based on race; the government must show that there is a compelling reason for the law and no other less restrictive way to meet the interest
Civil Disobedience A form of political participation that reflects a conscious decision to break a law believed to be immoral and to suffer the consequences. civil rights the rights of citizens to political and social freedom and equality. Civil Rights Act of 1964 outlawed discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin Voting Rights Act of 1965 a law designed to help end formal and informal barriers to African-American suffrage Civil War Amendments 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments de facto segregation Segregation resulting from economic or social conditions or personal choice. de jure segregation segregation by law
equality of opportunity giving people an equal chance to succeed equality of outcome The concept that society must ensure that people are equal, and governments must design policies to redistribute wealth and status so that economic and social equality is actually achieved. Equal Protection Clause 14th amendment clause that prohibits states from denying equal protection under the law, and has been used to combat discrimination inherent characteristics individual attributes such as race, national origin, religion, and gender convergence the state of separate elements joining or coming together equal opportunities The right to access the same opportunities, regardless of factors such as race, age, sex, mental or physical capability reasonable access rule
market-driven journalism both reporting news and running commercials geared to a target audience defined by demographic characteristics mass media Forms of communication, such as newspapers and radio, that reach millions of people. Muckrakers Journalists who attempted to find corruption or wrongdoing in industries and expose it to the public Narrowcasting targeting media programming at specific populations within society Newsworthiness the degree to which a news story is important enough to be covered in the mass media objective journalism A model of news reporting that is based on the communication of "facts" rather than opinions and that is "fair" in that it presents all sides of partisan debate. interpretive reporting
reporting that places the facts of a story in a broader context by relying on the reporter's knowledge and experience Descriptive Journalism a style in which journalists provide a straightforward description of events Partisan Press Newspapers and other communication media that openly support a political party and whose news in significant part follows the party line. Roles of the Media gatekeeper, scorekeeper, watchdog television hypothesis the belief that television is to blame for the low level of citizens' knowledge about public affairs Yellow Journalism Journalism that exploits, distorts, or exaggerates the news to create sensations and attract readers media effects the influence of news sources on public opinion