













Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Chadwick's sign: bluish discoloration of vagina. ▫. Hypertrophy and hyperplasia. ▫. Leukorrhea, acid pH 3.5 to 6.
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 22

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!















Physiological changes during pregnancy
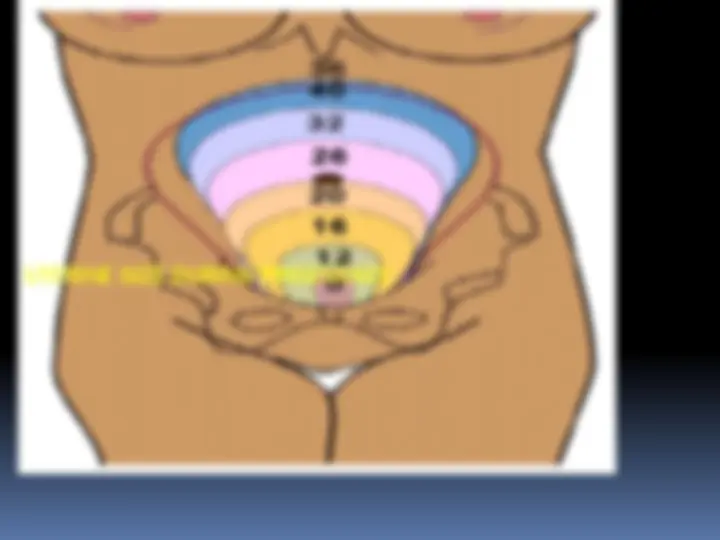
Uterus Size: increases to 20 times of its non-pregnant size due to hyperplasia and hypertrophy. Wall: changes from almost a solid globe to a hollow vessel. Weight: increases from 50 grams -1000 grams. Volume: increases from less than 10 ml to 5000 ml, Contractions: Braxton Hicks (irregular, painless contraction). Shape: changes from that of an inverted pear to that of soft globe. Endometrium: consists of 3 layers: Decidua basalis: uterine lining beneath implantation. Decidua capsularis: portion of the decidua that covers the embryo. Decidua vera: all of the uterine lining that is not in contact with the fetus.
Cervix
Goodell's sign: softening of the cervix, formation of operculum (mucous plug). Ovaries and Fallopian Tubes
Involution due to suppression of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). Vagina
Chadwick's sign: bluish discoloration of vagina. Hypertrophy and hyperplasia. Leukorrhea, acid pH 3.5 to 6.
Vulva
Increased vascularity.
Fat deposition causes labia majora to close and partially cover introitus.
Breasts
3-4 weeks: prickling, tingling sensation.
6 weeks: developing ducts and glands.
8 weeks: bluish surface veins are visible.
8-12 weeks: Montgomery's glands become more prominent, primary areola become darker.
16-18 weeks: colostrum expresses. Secondary areola appears.
Cardiovascular System Slight enlargement of myocardium. Shift in chest contents: Heart is displaced upwards and to the left. Heart rate increases by 10 to 15 beats/minute. Blood volume increases 40-50% physiological anemia. Increase in clotting factors. Hemoglobin and hematocrit decrease in relation to increased plasma volume. Cardiac output increases by 30% during the first and second trimesters.
Urinary System Frequency of macturation due to pressure of the growing uterus. Decreased bladder capacity and bladder tone. Renal Function Changes Changes occur to accommodate an increased workload while maintaining stable electrolyte balance. Increased glomerular filtration rate. Glucosuria may occur (may not be abnormal, warrants further evaluation).
Gastrointestinal System Mouth and Teeth Gums become hyperemic and have a tendency to bleed. Ptyalism is seen in some women. Gastrointestinal Tract Smooth muscle relaxation occurs related to increased progesterone production. This can cause: Decreased peristalsis and constipation. Heartburn, slowed gastric emptying and esophageal regurgitation. Hemorrhoids from the pressure of the gravid uterus. Appetite usually increases, after a temporary decrease due to nausea and vomiting.
Integumentary System (Cutaneous Changes)
Chloasma is the brownish" mask of pregnancy".
Linea nigra (abdomen).
Nipples, areolae, axillae, vulva and perineum all darken.
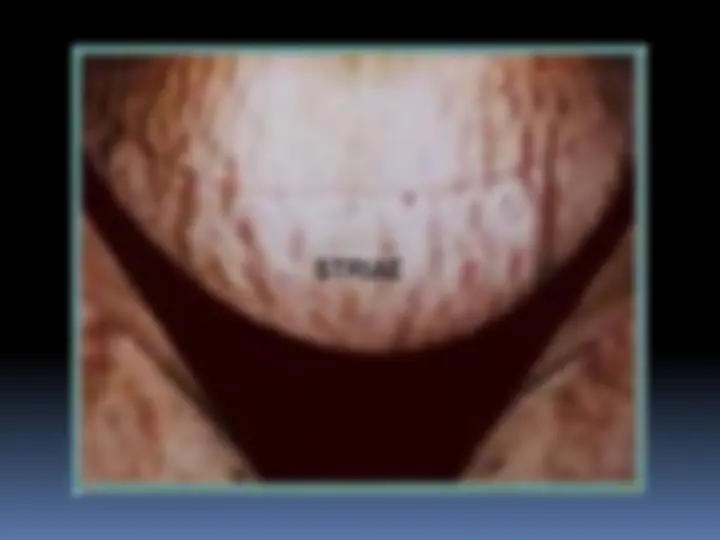
Striae gravidarum (stretch marks) appear on the breasts and abdomen. This is caused by increased fragility of the connective tissue.
LINEA NIGRA
CHLOASMAOR MELASMAGRAVIDARUM
Metabolic Changes
Increase metabolic rate.
Increase the demands for carbohydrate, protein, and minerals.
Weight gain of 9-1 I kg.
Water requirement is increased to supply fetus, placenta and amniotic fluid.
Immunological System
Resistance to infection is decreased.
Maternal IgG levels are decreased.
Maternal IgM levels remain unchanged.
Presumptive Evidence Signs: Amenorrhea. Breast changes. Chadwick's sign. Chloasma and linea nigra. Abdominal enlargement and striae.
Symptoms: Nausea and vomiting. Urinary frequency. Weight gain. Constipation. Fatigue. Quickening. Breast tenderness, tingling, and heaviness.