






Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
If the pulse rate on the pulse ox differs from the EKG monitor the O2 saturation reading is ✔✔not reliable, the child needs oxygen in spite of possible O2 saturation above 94%. A BP reading of what in a neonate is considered hypotension when? ✔✔of less than 60 systolic What airway obstruction is characterized by tachypnea, increased respiratory effort, cough, stridor, and poor air oxygenation? ✔✔upper airway obstruction Typical signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction occur predomintly during the what phase of respiratory cycle? ✔✔inspiratory phase This is an abnormal breathing pattern that produces inadequate respiratory rate or effort that is usually associated with neurological disorders such as brain tumors, seizures, head injury, hydrocephalus or neuromuscular disease? ✔✔disordered control of breathing Increased work of breathing and tachypnea in a toddler may be classified as what? ✔✔as respiratory distress rather than failure
Typology: Exams
1 / 9

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
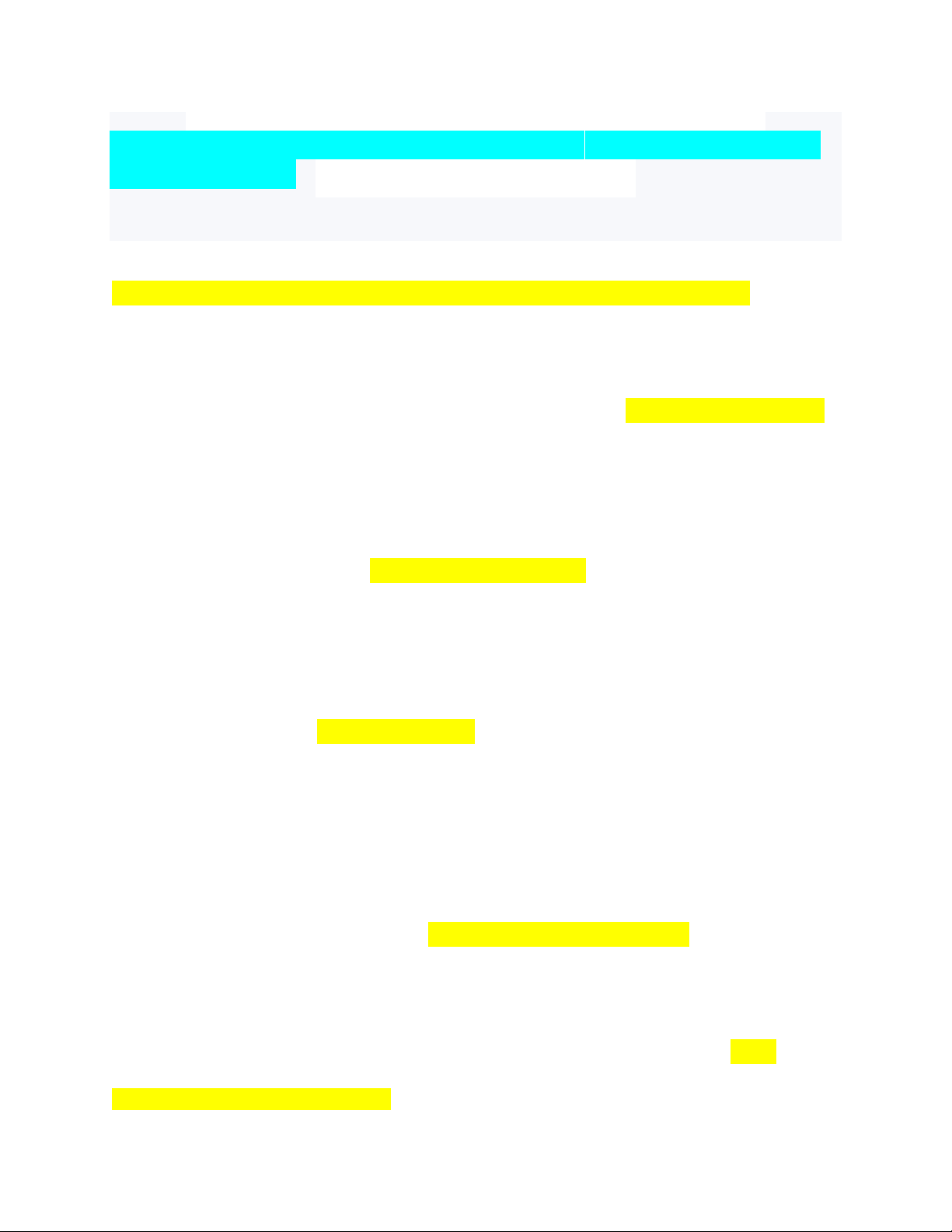





If the pulse rate on the pulse ox differs from the EKG monitor the O2 saturation reading is ✔✔not reliable, the child needs oxygen in spite of possible O2 saturation above 94%. A BP reading of what in a neonate is considered hypotension when? ✔✔of less than 60 systolic What airway obstruction is characterized by tachypnea, increased respiratory effort, cough, stridor, and poor air oxygenation? ✔✔upper airway obstruction Typical signs and symptoms of upper airway obstruction occur predomintly during the what phase of respiratory cycle? ✔✔inspiratory phase This is an abnormal breathing pattern that produces inadequate respiratory rate or effort that is usually associated with neurological disorders such as brain tumors, seizures, head injury, hydrocephalus or neuromuscular disease? ✔✔disordered control of breathing Increased work of breathing and tachypnea in a toddler may be classified as what? ✔✔as respiratory distress rather than failure
Moderate stridor and retractions along with a seal bark cough in a toddler may be best managed by administration of what? ✔✔nebulizer epi The child who presents with severe respiratory distress and signs of anaphylaxis must be treated promptly with what? ✔✔IM/IV epi/corticosteroids as well as nebulized albuterol. Defined as a critical condition that results from inadequate tissue delivery of O2 and nutrients to meet tissue metabolic demands? ✔✔shock Infants have tiny hearts and increase their cardiac output primarily by what? ✔✔increasing heart rate In order to recognize shock early, the health care provider must recognize signs of compensated shock such as what? ✔✔tachycardia, increased stroke volume, and increased cardiac contractility
In a child with serious signs and symptoms of hypovolemic shock, the quickest and best way to establish vascular access is via the what route? ✔✔IO route the correct intervention when a child presents with severe respiratory distress, low oxygen saturation, absent breath sounds on the right side of the chest, and signs of obstructive shock is what ✔✔needle decompression of the right chest when an infants heart rate falls to 70 bpm when suctioned, the health care provider must administer what ✔✔oxygen and ensure adequate oxygenation the correct treatment for a child who suddenly develops a heart rate of 240 bpm and has palpitations and dizziness is what ✔✔vagal maneuvers the correct way to perform vagal maneuvers on an infant with SVT and adequate perfusion is what ✔✔ice on the face over the upper half the correct intervention to perform when a child presents with lethargy, SVT, and signs and symptoms of inadequate perfusion is what ✔✔cardioversion at 0.5-1 J/kg
you are caring for an infant who is unresponsive and not breathing, what is the maximum amount of time you should spend palpating for a pulse ✔✔less than 10 seconds where is the appropriate place to palpate a pulse in an infant ✔✔brachial an unresponsive child presents with a rhythm that resembles sinus bradycardia but a rhythm is not accompanied by a pulse, he must be treated with what algorithm ✔✔pulseless electrical activity when a child is found in cardiac arrest, high quality CPR is initiated. when a cardiac monitor reveals ventricular fibrillation, the appropriate intervention is what ✔✔defib at a rate of 2 J/kg an infant presents with CPR in progress. the cardiac monitor shows an organized rhythm with a rate of 70 without a pulse. what is the correct intervention? ✔✔administer epi the most important drug to administer to a child in cardiac arrest while CPR is being performed is what ✔✔epi at a dose of .01 mg/kg
what is the hypotension formula for kids ✔✔70 mmhg + (childs age in years * 2) mmhg what is key to treating shock ✔✔fluid bolus of 20 ml/kg but if a known cardiac child then 10 ml/kg if nonhemorrhagic hypovolemic shock what is the treatment ✔✔ 20 ml/kg NS/LR bolus, repeat as needed. consider colloid after 3rd NS/LR bolus what is the treatment of hemorrhagic hypovolemic shock ✔✔control external bleeding 20 ml/kg NS/LR bolus repeat 2 or 3 times as needed. trasfuse PRBCs as indicated What is the treatment of anaphylactic distributive shock? ✔✔IM epi Antihistamines- Benadryl-Diphenhydramine Corticosteriods Epi infusion Albuterol
what is the treatment of neurogenic distributive shock ✔✔ 20 ml/kg NS/LR bolus, repeat as needed vasopressor what is the treatment of cardiogenic shock ✔✔ 5 to 10 ml/kg NS/LR bolus, repeat as needed vasoactive infusion consider expert consultation what is the treatment of obstructive shock- ductal dependent ✔✔prostaglandin E expert consultation what is the treatment of tension pneumo- obstructive shock ✔✔needle decompression tube thoracotomy what is the treatment of cardiac tamponade- obstructive shock ✔✔pericardiocentiss 20 ml/kg NS/LR bolus