Download Carbon and Organic Compounds: Structure, Properties, and Health Implications - Prof. Maria and more Study notes Biology in PDF only on Docsity!
Organic compounds
- (^) Nearly all the molecules a cell makes are Carbon-based (= organic compounds )
- (^) Carbon is unparalleled in its ability to form large, diverse molecules
- (^) The outer electron shell of Carbon has 4 electrons
- (^) Carbon completes its outer shell by sharing electrons with other atoms (Carbon and other elements) in 4 covalent bonds
Organic Compounds
- (^) By sharing its electrons, Carbon can bond to four other atoms
- (^) By doing so, it can branch in up to four directions, enabling the formation of diverse compounds
- (^) Methane, CH 4 is one of the simplest organic compounds (1 Carbon atom shares its electrons with 4 Hydrogen atoms) http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.5/
Organic compounds
- (^) The unique properties of an organic compound depend on the size and shape of its Carbon skeleton (the chain of Carbon atoms, can be branched or unbranched) and on the groups of atoms that are attached to that skeleton http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_skeleton#Carbon_skeleton
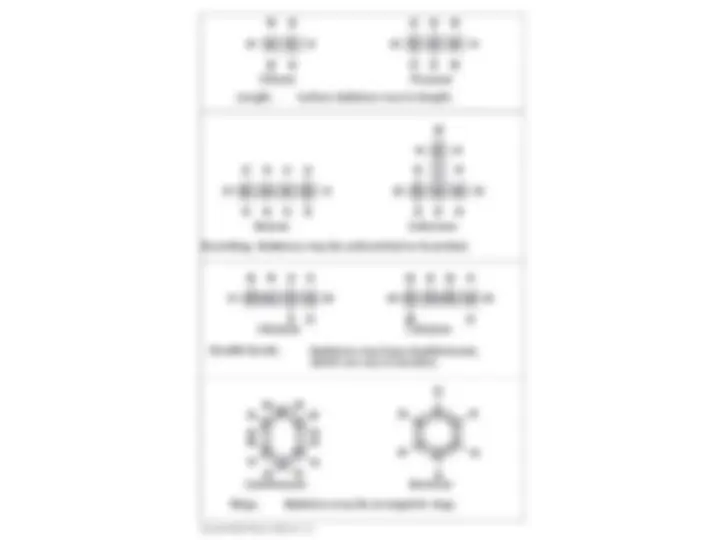
Carbon skeletons vary in length. Branching. Skeletons may be unbranched or branched. Butane Isobutane Ethane Propane Double bonds. 2-Butene Skeletons may have double bonds, which can vary in location. Cyclohexane Length. 1-Butene Benzene Rings. Skeletons may be arranged in rings.
Hydroxyl group – polar , consists of a Hydrogen bonded to an Oxygen Carbonyl group – polar , Carbon linked by a double bond to an Oxygen Carboxyl group – polar , a Carbon double-bonded to both an Oxygen and a Hydroxyl group Amino group – polar , composed of a Nitrogen bonded to 2 Hydrogen atoms and the Carbon skeleton Phosphate group – polar , consists of a Phosphorus atom bonded to 4 Oxygen atoms Methyl group – nonpolar and not reactive ,Carbon bonded to 3 Hydrogen
Organic Compounds
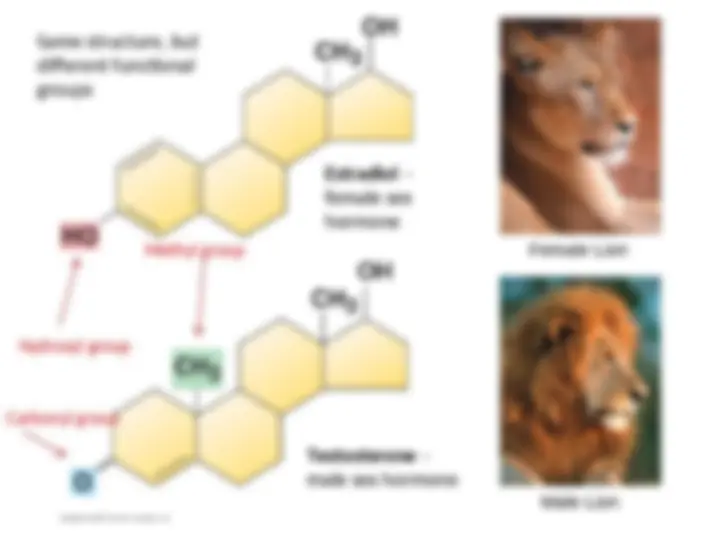
- (^) Isn’t organic chemistry fun???!!! How about a working example….
- (^) Male and female sex hormones differ ONLY by functional group
- (^) This change in functional group may seem subtle, but results in different actions of these molecules, which help produce the physical features (characteristics) of males and females
Organic Chemistry is great!
- (^) In addition to water, all other biological molecules are organic (carbon-based) molecules
- (^) There are many organic molecules, but four of them are extremely important: - (^) Carbohydrates - (^) Lipids - (^) Proteins - (^) Nucleic Acids
Polymers
- (^) Cells make most of their large molecules by joining smaller molecules into chains called polymers
- (^) A polymer is a ‘macromolecule’ because of its great size
- (^) Polymers consist of many identical or similar building blocks (monomers) strung together, much like a long train consists of many individual cars
Polymers
- (^) The key to the great diversity of proteins and DNA is arrangement – the variation in the sequence in which monomers are strung together
- (^) DNA is built of only four monomers (nucleotides) and proteins are built from only 20 kinds of amino acids; both of which are incredibly diverse: the proteins in you and a fungus are made with the same 20 amino acids
Polymers
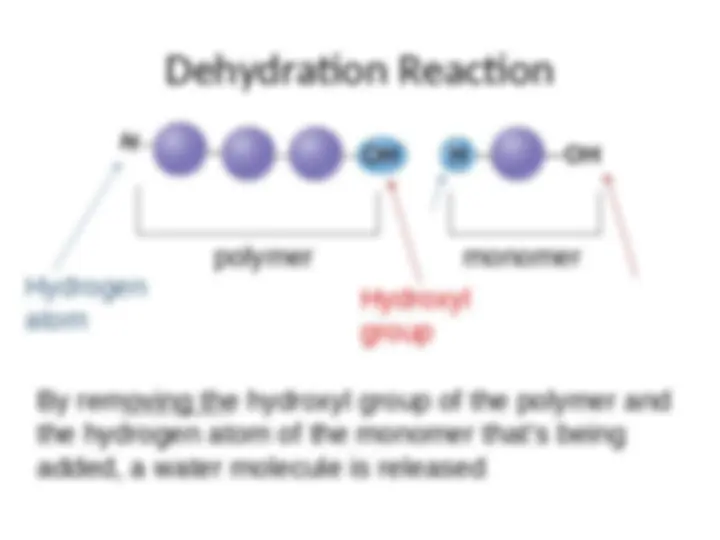
- (^) A cell links monomers together to form polymers by a dehydration reaction (a reaction that removes a molecule of water)
- (^) An unlinked monomer has a hydroxyl group (---OH) at one end, and a hydrogen atom (--- H) at the other end
- (^) For each monomer added to the chain, a water molecule is removed
Dehydration Reaction
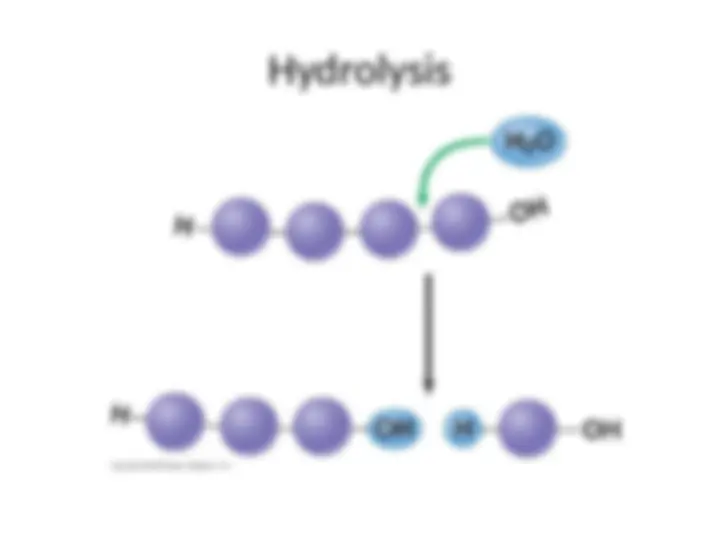
Hydrolysis
- (^) Just as removing a water molecule builds a polymer, the addition of a water molecule breaks a polymer chain
- (^) Cells frequently must break down polymers because they are otherwise too large to enter the cell
Enzymes
- (^) Both dehydration reactions and hydrolysis require the help of enzymes to make and break bonds
- (^) Enzymes are specialized ‘macromolecules’ that speed up the chemical reactions in cells
- (^) Enzymes are extremely important – without them, many reactions cannot take place. If you lack lactase, you cannot hydrolyze the bond in lactose
Carbohydrates
http://michaelscomments.files.wordpress.com/2007/12/spaghetti-meatballs.jpg