


























Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
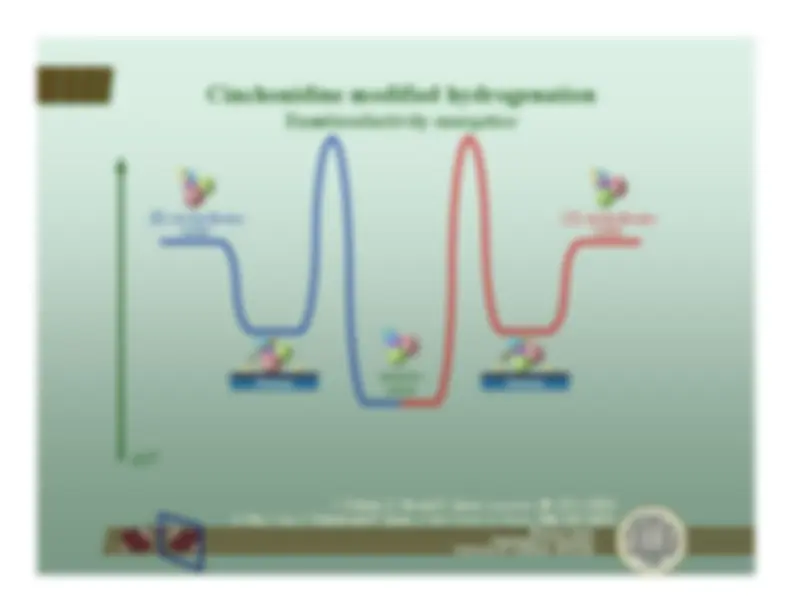
This document, authored by francisco zaera from the university of california, riverside, explores the organic chemistry of alkanes and alkenes on metal solid surfaces. Topics include alkane-alkene conversion, h-d exchange, and stereoselectivity in hydrogenation. The document also discusses the role of cinchona derivatives in enhancing enantioselectivity in hydrogenation reactions.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 63

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
























































Francisco ZaeraDepartment of Chemistry University of California, Riverside
by Francisco Zaera Department of Chemistry University of California Riverside, CA 92521, USA Phone: 1 (951) 827-5498 Fax: 1 (951) 827-3962 Email: zaera@ucr.edu http://www.zaera.chem.ucr.edu
General References:
Z. Ma and F. Zaera,
Surf. Sci. Rep.
,^ 61(5) , 229-282 (2006).
F. Zaera,
Catal. Lett.
,^ 91(1-2)
, 1-10 (2003).
F. Zaera,
Chem. Rev.
,^^95 , 2651-2693 (1995).
F. Zaera,
Appl. Catal.
,^^229 , 75 (2002).Francisco ZaeraDepartment of Chemistry University of California, Riverside A selective process:• Consumes less reactants• Avoids separation problems
n-Hexane
AromatizationCyclizationIsomerizationHydrogenolysis
BenzeneMethylcyclopentane2-MethylpentanePropane
(ON ~ 40)
(ON ~ 95)(ON ~ 90)(ON ~ 80)(gas)
Dehydrogenation
2-Hexene
Desirable Undesirable
Introduction
Francisco ZaeraDepartment of Chemistry University of California, Riverside
Outline
CH^3
γ-H
Francisco ZaeraDepartment of Chemistry University of California, Riverside
Outline
CH^3
γ-H elimination.
β -hydride elimination
F. Zaera,
J. Am. Chem. Soc.
,^^111 , 8744 (1989).
A. J. Gellman,
Acc. Chem. Res.
,^^33 , 19 (2000).
B. E. Bent,
Chem. Rev.
^96 , 1361 (1996).
Francisco ZaeraDepartment of Chemistry University of California, Riverside
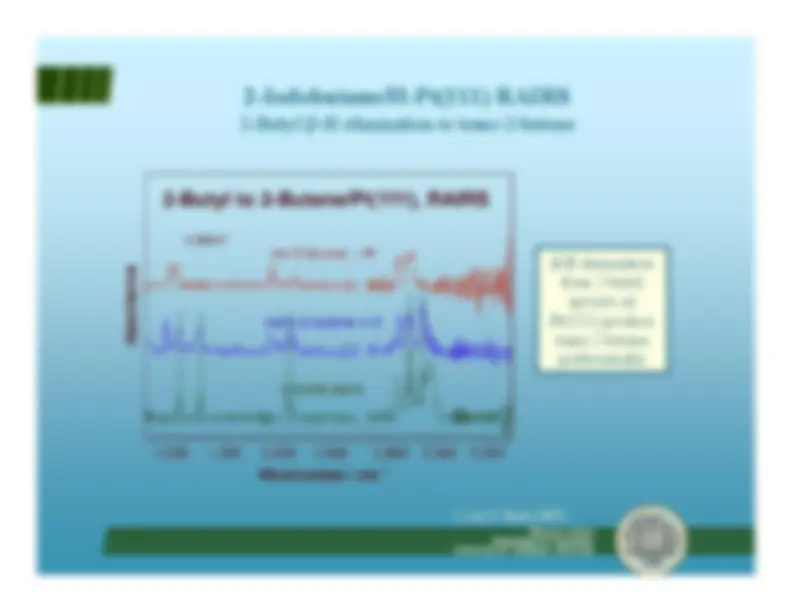
Alkane-alkene equilibria via
β -H
F. Zaera,
Molec. Phys.
,^^100 , 3065-3073 (2002). F. Zaera,
Catal. Lett.
,^ 91(1-2)
, 1-10 (2003).
F. Zaera,
Top. Catal.
,^ 34 (1-4)
, 129-141 (2005).
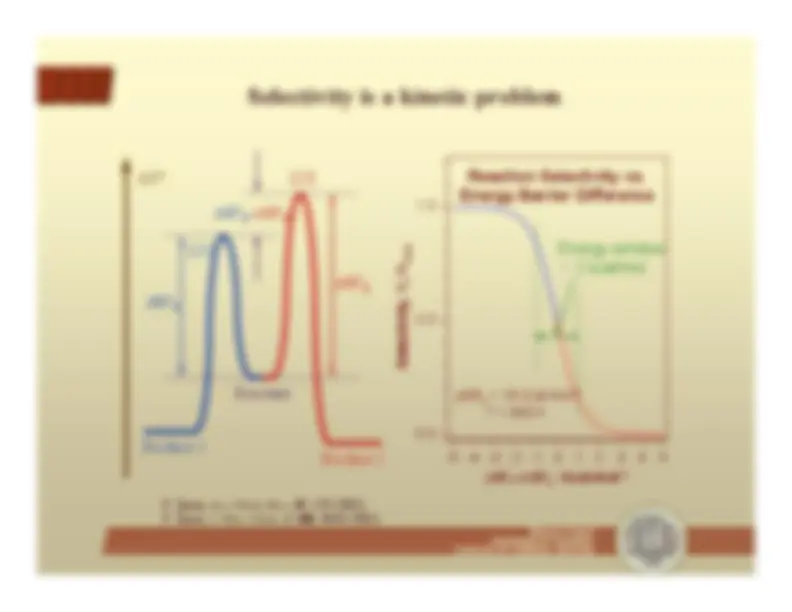
-^ β-hydride elimination accounts for fast alkane-alkene equilibria - Reforming requires
α- and
γ-hydride elimination
Francisco ZaeraDepartment of Chemistry University of California, Riverside
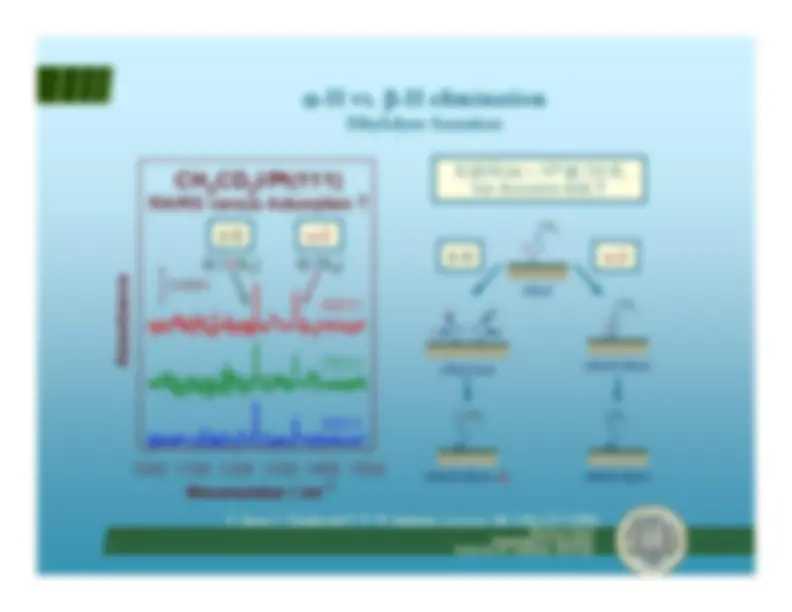
α -H vs.
β -H elimination Ethylidyne formation
F. Zaera, S. Tjandra and T. V. W. Janssens,
Langmuir
,^^14 , 1320-1327 (1998).
Francisco ZaeraDepartment of Chemistry R(β)/R( University of California, Riverside
α) ~ 10
but decreases with T D H C–C^ H ethylene D
CH^3 D C (^2) ethyl
CH DC ethylidene 3 CH^3 C ethylidyne
ethylidyne- C d^1 CDH^2
α-D
β-H
δ[CDH
δ[CH^3 α-D ]^ β-H
Wavenumber / cm
-
bancer Abso
CH^3
CD^2
I/Pt(111)
α -H vs.
β -H elimination
A. Loaiza, M. Xu and F. Zaera,
J. Catal.
,^^159 , 127 (1996).
A. Loaiza, D. Borchardt and F. Zaera,
Spectrochim. Acta A
,^^53 , 2481 (1997).
A. Loaiza and F. Zaera
J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom.
,^^15 , 1366 (2004).
Francisco ZaeraDepartment of Chemistry University of California, Riverside
amu b. unitsra / er essur tial Pr Pa
x C^ D^2 MS/CID-MS 2nd Stage, 34 amuP= 50 TorrCD^2 6 P= 500 TorrH^2 T = 675 K55% Conversion
+ H 6
/Pt 2
P= 50 TorrCH^26 P= 500 TorrD^2 T = 625 K20% Conversion^ δ^ / ppm C^2 13 C NMR of Mixture H^ + D 6
/Pt 2
5.^
H^ ethylene
H C–C H H
CH HC ethylidene α-H^3 β-H^
H^ C–CH^3 ethaneCH^3 H^ C^2 ethyl
3 ethane-
d^2 DH^ C–CH^2
D 2
ethane-
d^2 D^ HC–CH^2
3
R(β) ~ 5·R(
α) @ 625K
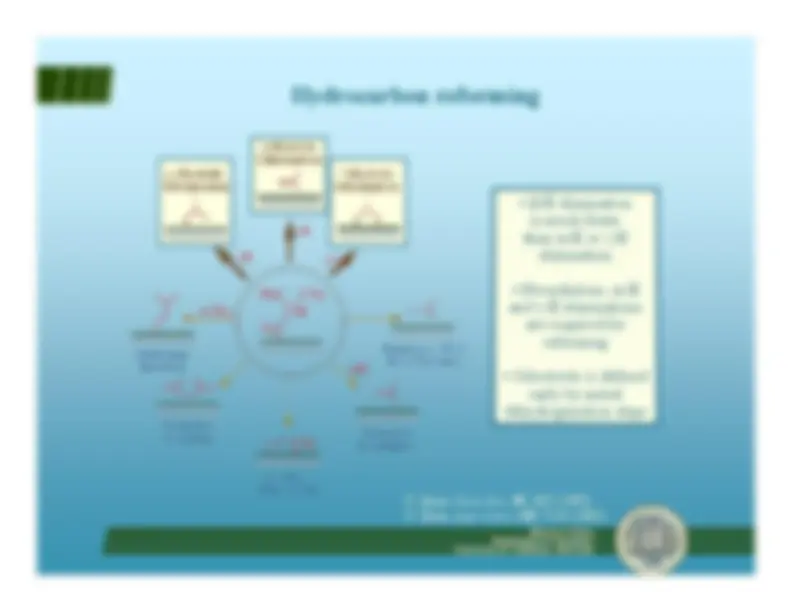
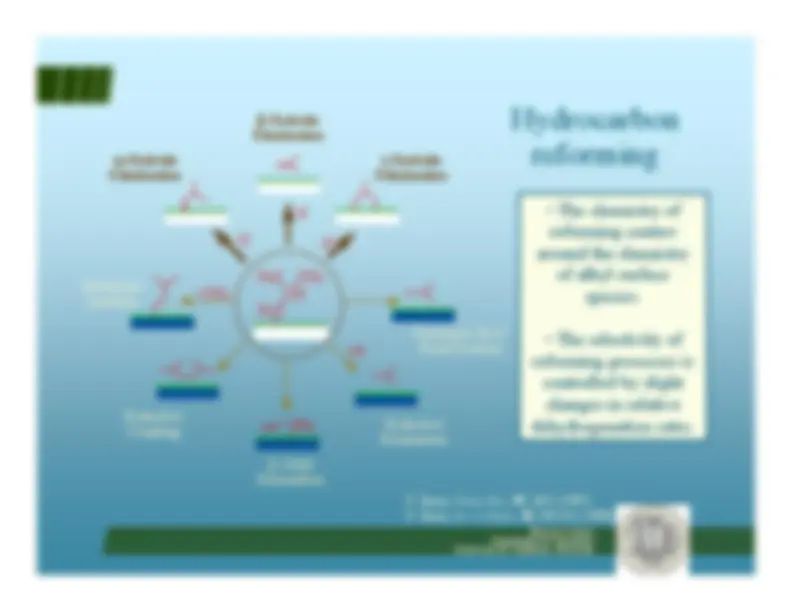
Hydrocarbon reforming^ Isomerization vs. hydrogenolysis
T. V. W. Janssens, G. Jin and F. Zaera,
J. Am. Chem. Soc.
,^^119 , 1169 (1997).
F. Zaera and S. Tjandra,
J. Am. Chem. Soc.
,^^118 , 12738 (1996).
Francisco ZaeraDepartment of Chemistry University of California, Riverside Ni^ Ni
PtNi Pt CH^2 C–CH
3 H HC H
CH^3 CH^3 C H H^3 C^ CH^2 H HC
CH^2 C–CH
3 H HC
CH^3
CH^2 C–CH
3 H HC
CH^3 CH^3 H 3C C CH H H 2C
Metallacyclobutane
CH^3 H 3C C CH H H 2C
CH^3 CH 3 –C=CH^2 C
H^2
CH^ 3–C–CH^2 CH
H CH^3 Neopentylidene
CH^3 CH 3 –C–CH^2 H CH H Neopentyl
α-H elimination(Hydrogenolysis)^ γ-H elimination(Isomerization)
F. Zaera,
Chem. Rev.
,^^95 , 2651 (1995). F. Zaera,
Appl. Catal.
,^^229 , 75-91 (2002).Francisco ZaeraDepartment of Chemistry University of California, Riverside
-^ β-H eliminationis much fasterthan^ α
-H or^ γ
elimination• Nevertheless,
α-H and^ γ-H eliminationsare required forreforming• Selectivity is definedearly by initialdehydrogenation steps
Hydrocarbon reforming
F. Zaera,
Catal. Lett.
,^^91 , 1 (2003),
F. Zaera,
Molec. Phys.
,^^100 , 3065 (2002).
Francisco ZaeraDepartment of Chemistry University of California, Riverside
β -H elimination in Horiuti-Polanyi mechanism
H^ CH^ alkene
3 C–C^ CH
3 H
H^ CH H C 2 alkyl
(^3) C CH 3
H^ CH H C 3 alkane
(^3) C CH 3
alkenes
H^ HC alkylidene β-H CH^3 C CH^3
smaller alkanes
α-H^
Hydrogenolysis
H H C (^2) metallacycle CH^3 C CH^2
branched alkanes
γ-H
Isomerization
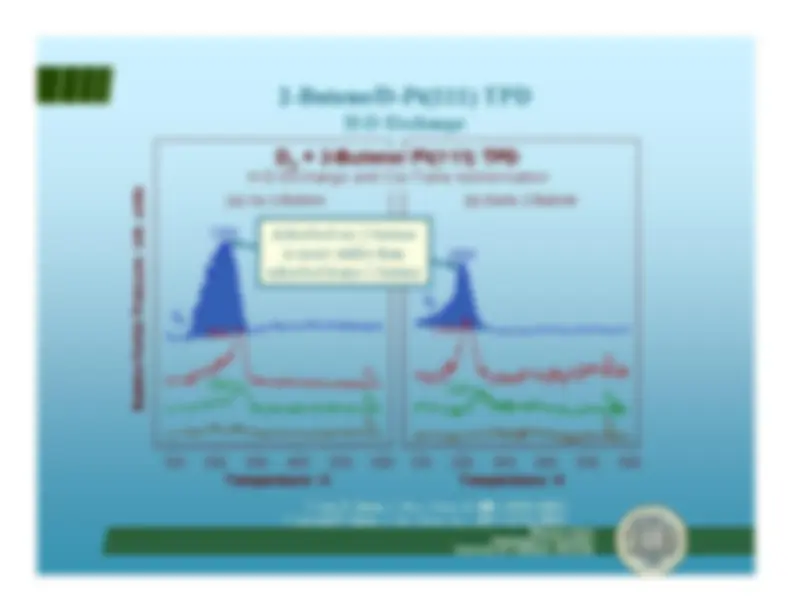
Explains:
C=C double bond migration^ R. Morales and F. Zaera,
J. Phys. Chem. B
,^ 110(19)
, 9650-9659 (2006).Francisco ZaeraDepartment of Chemistry University of California, Riverside
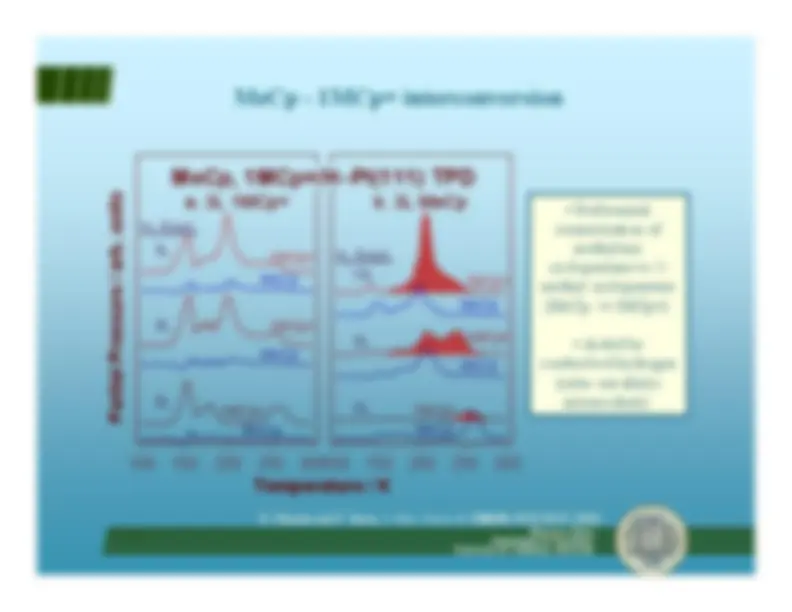
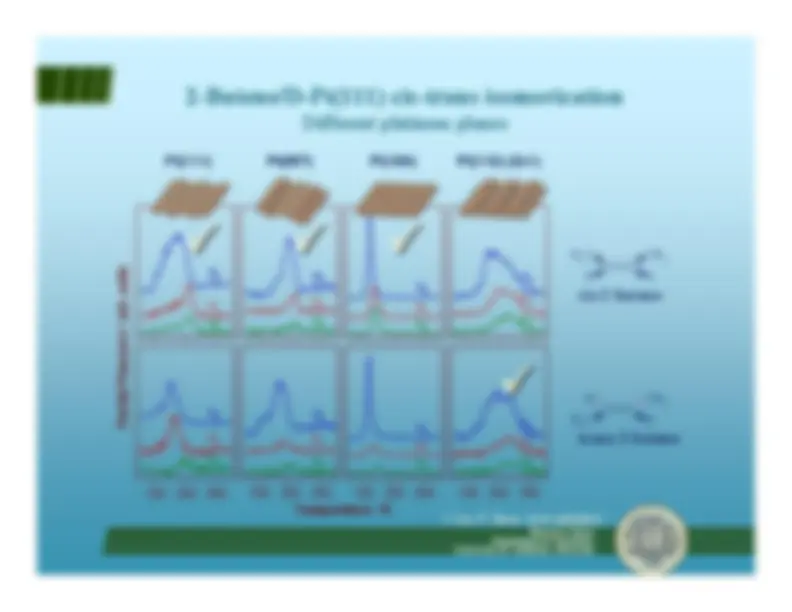
CH^3 1-methyl cyclopentene (1MCp=)
CH methylenecyclopentane (MeCp) 2
1-methyl 1-cyclopentyl (1MCpyl)
CH^3
CH^3 1-methylcyclopentene (ads)
H H methylenecyclopentane (ads)
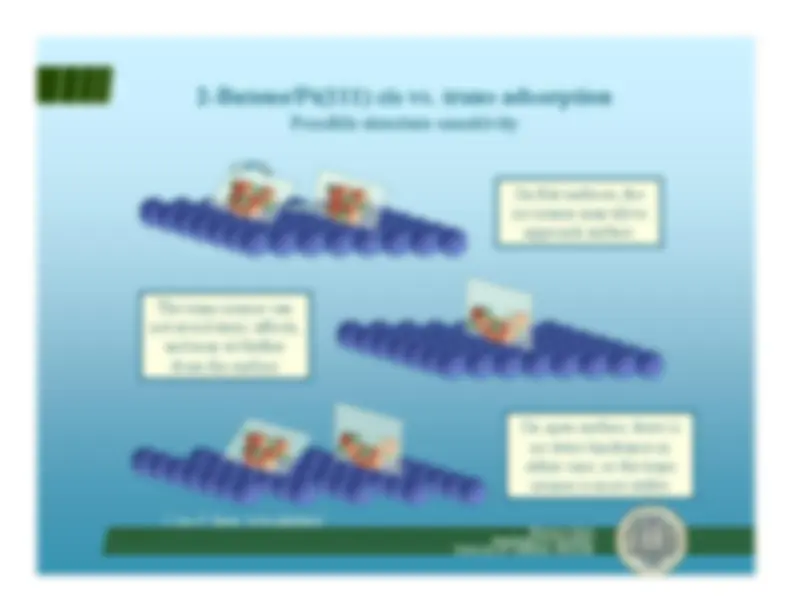
Isomerization depends onregioselectivity of
β-H
elimination step from thealkyl intermediate
Temperature / K
arb. units / Partial Pressure
200
300
x0.5 x
amu b. Molecular Ion
82 83 84 86
100
200
(^67686971300)
x0.1 x0.5 x
amu
D
DD
D D
DD
Francisco ZaeraDepartment of Chemistry University of California, Riverside
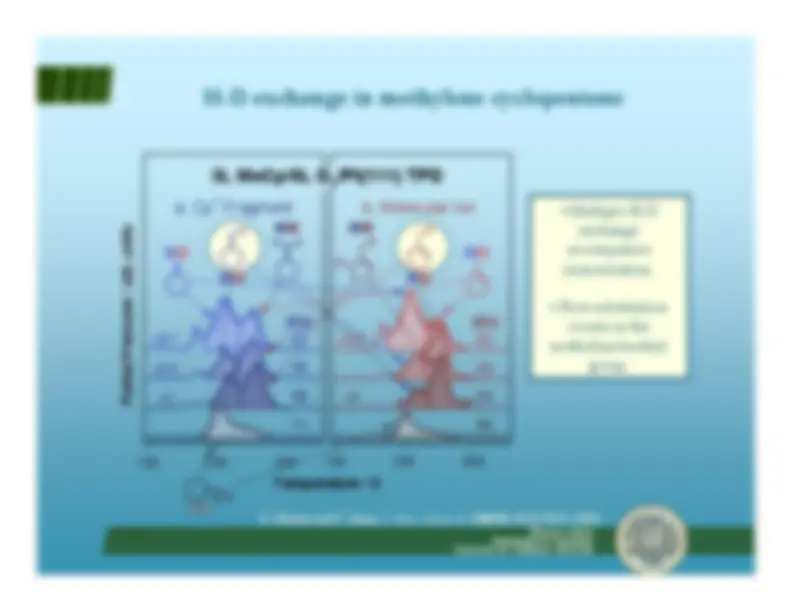
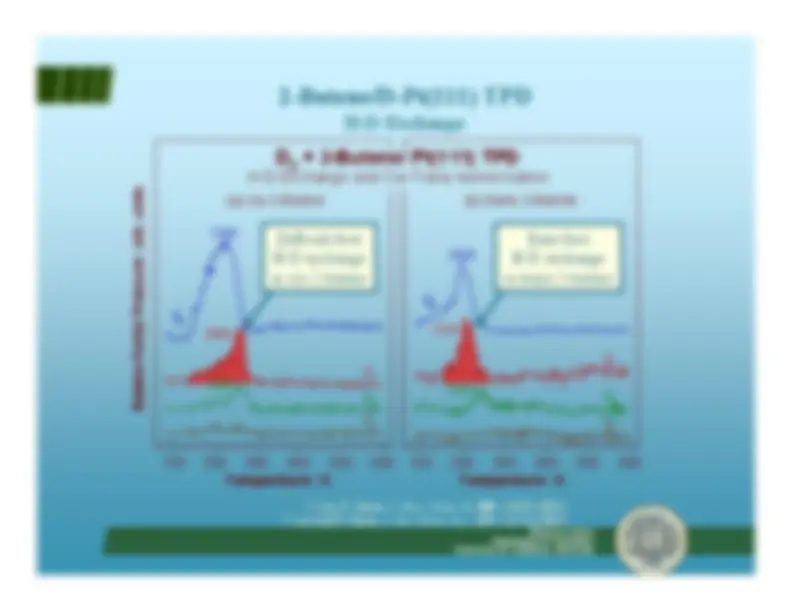
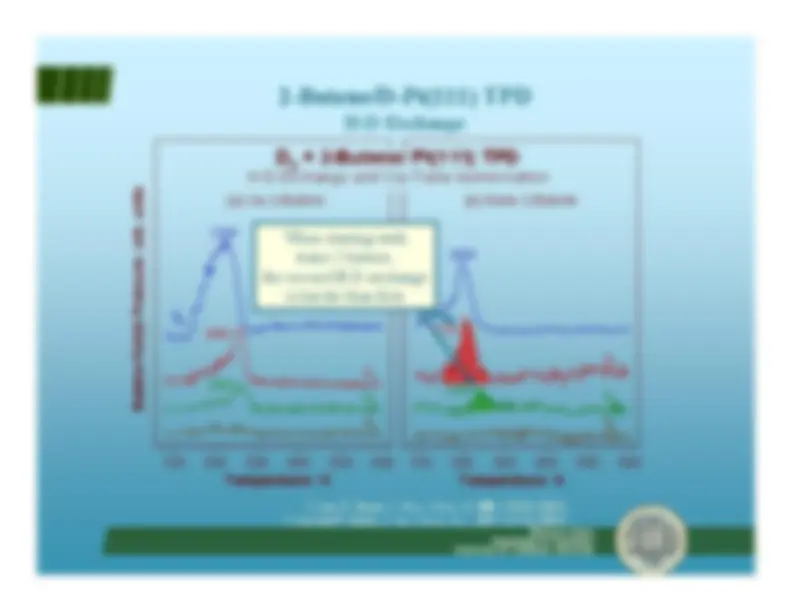
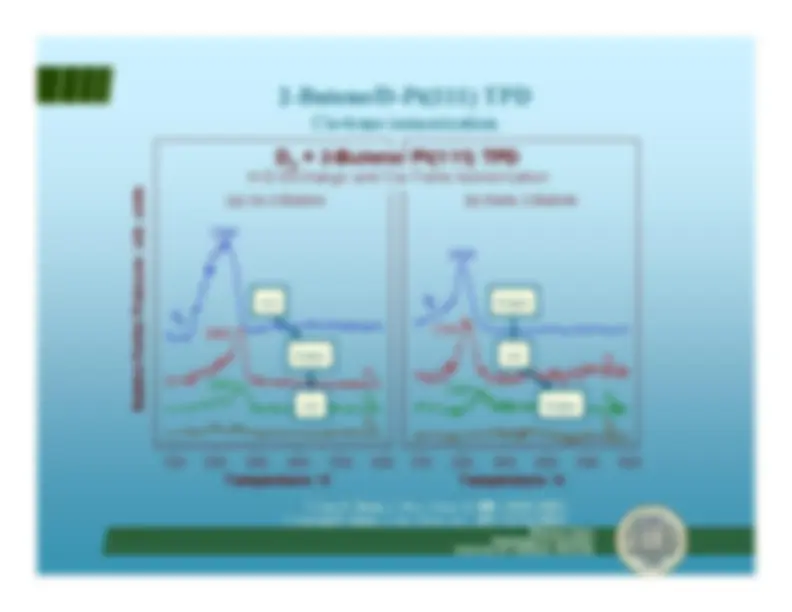
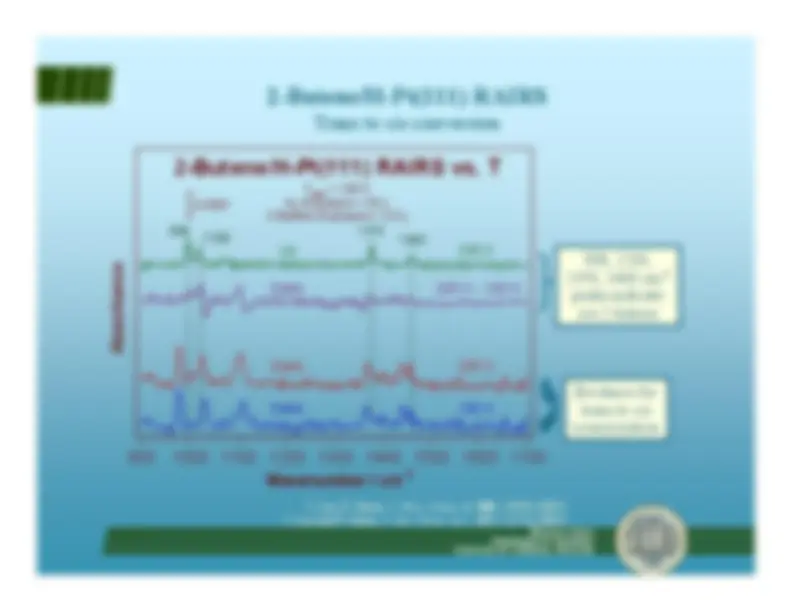
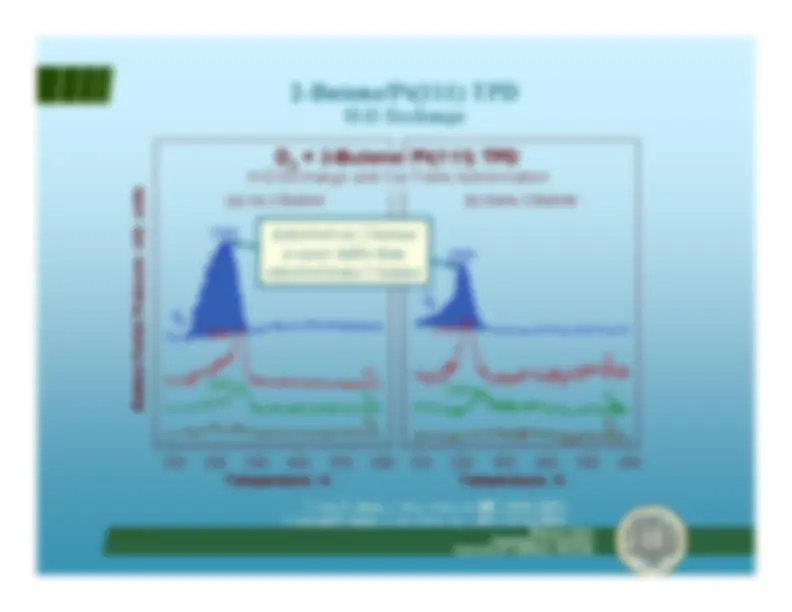
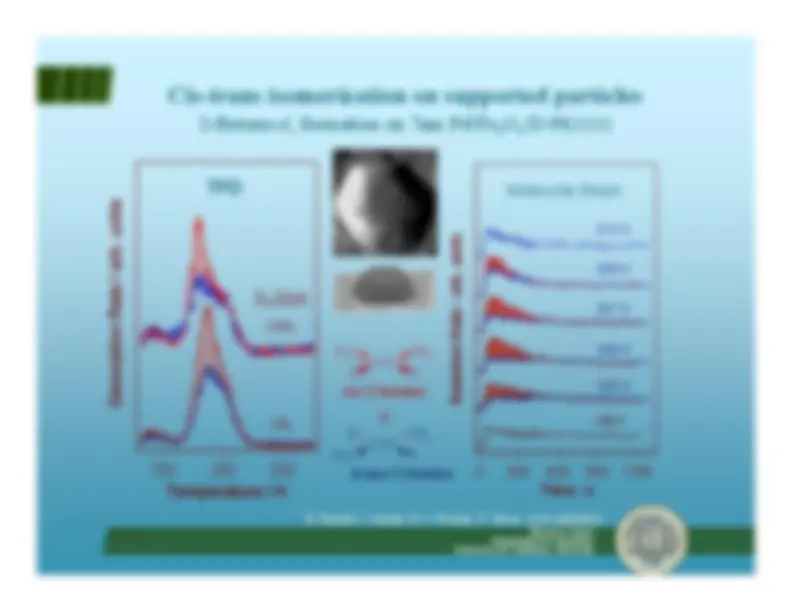
H-D exchange in methylene cyclopentane
R. Morales and F. Zaera,
J. Phys. Chem. B
,^ 110(19)
, 9650-9659 (2006).
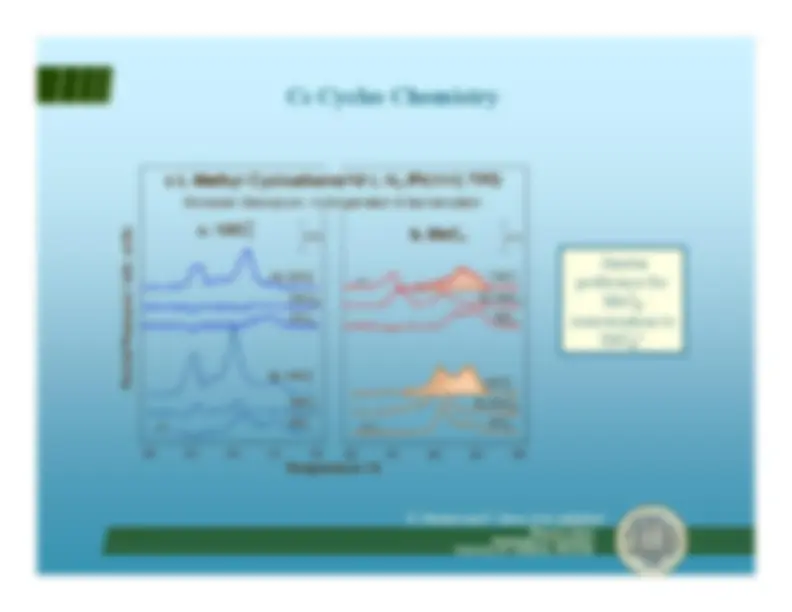
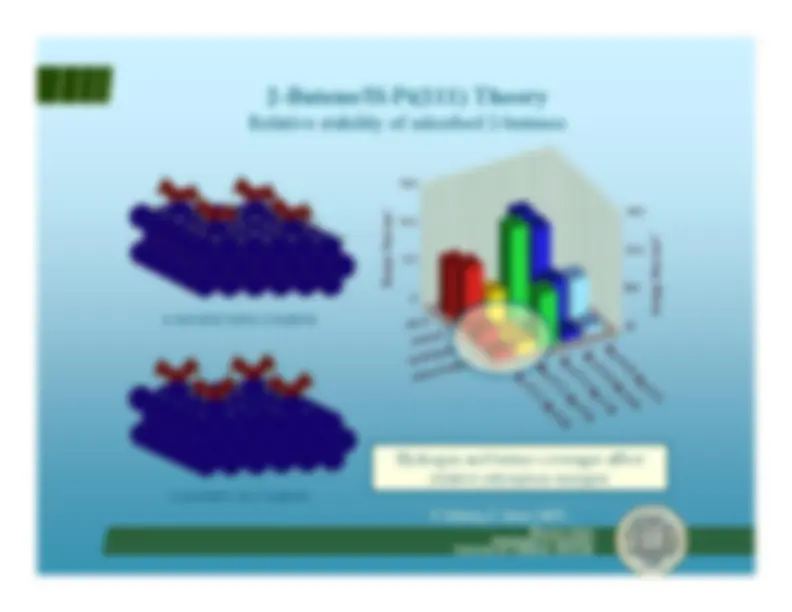
C=C double bond migration^ Regioselectivity energetics
Francisco ZaeraDepartment of Chemistry University of California, Riverside
R. Morales and F. Zaera,
J. Phys. Chem. B
,^ 110(19) H H^ MeCp , 9650-9659 (2006). CH^3 1MCpyl CH^3 1MCp=
β-H from methyl
β-H from cycle
∆H° / kcal·mol
CH^3 1MCp=
CH^2 MeCp
~3 kcal/mol