




























Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An in-depth explanation of One-Way Analysis of Variance (ANOVA), a statistical method used to compare three or more population means. Learn the principles, assumptions, and steps involved in conducting an ANOVA, including calculating sums of squares, degrees of freedom, and the F-ratio. Discover how to interpret the results and perform post hoc tests.
Typology: Summaries
1 / 36

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





























ANOVA: A Framework
The basic principle behind ANOVA Produces a test statistic termed the F-ratio Systematic Variance Unsystematic Variance If the model explains a lot more variability than it can’t explain, then the experimental manipulation has had a significant effect on the outcome (DV).
SST = based on differences between each data point and the grand mean SSM = differences between predicted values (group means) and the grand mean Grand Mean =
XPlacebo = 2. XLowDose = 3. XHighDose = 5. SSR = based on differences between person’s score and their group mean. Basis for SST Basis for SSR Basis for SSM Partitioning the Variance
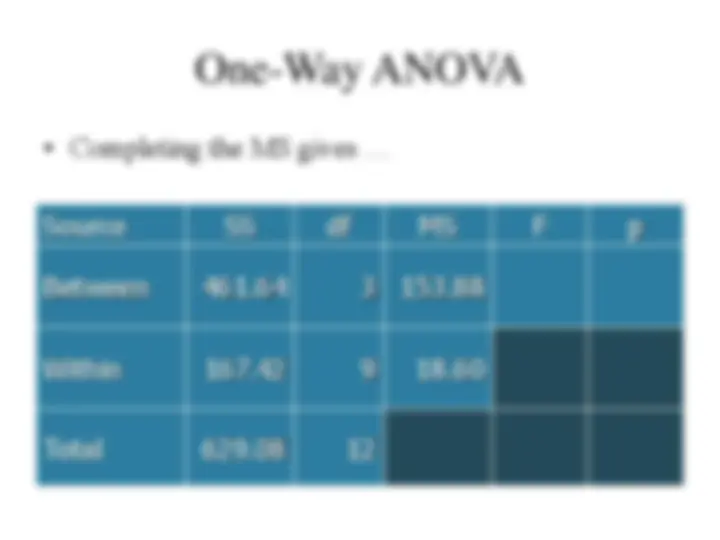
Mean Squares (MS M and MS R ) SSM = amount of variation explained by the model (exp. manipulation). SSR = amount of variation due to extraneous factors. These are “summed” scores and will therefore be influenced by the number of scores. To eliminate this bias we calculate the average sum of squares (mean squares) by dividing by the appropriate degrees of freedom. Calculating Degrees of Freedom (for one-way independent groups ANOVA) df total = N - 1 (number of all scores minus 1) dfM / between = k - 1 (number of groups minus 1) df (^) R / within = N - k (number of all scores minus number of groups)
The F-ratio
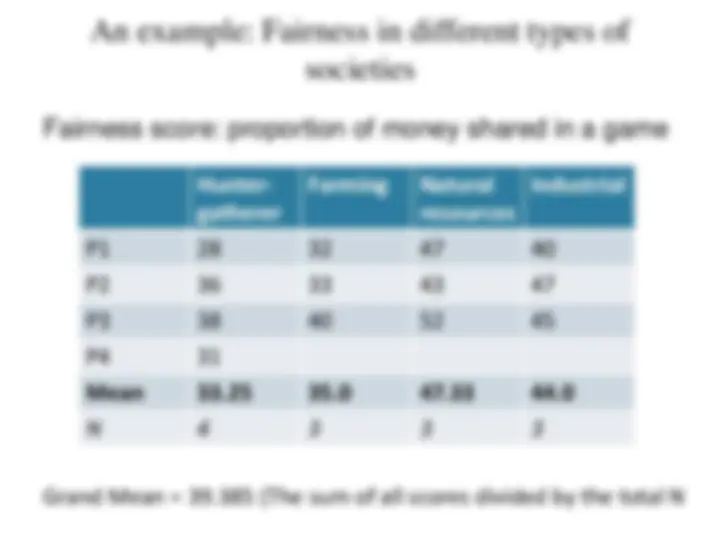
Fairness score: proportion of money shared in a game Hunter- gatherer Farming Natural resources Industrial P1 28 32 47 40 P2 36 33 43 47 P3 38 40 52 45 P4 31 Mean 33.25 35.0 47.33 44. N 4 3 3 3 Grand Mean = 39.385 (The sum of all scores divided by the total N
2 ( ) T i grand SS x M
M