













Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
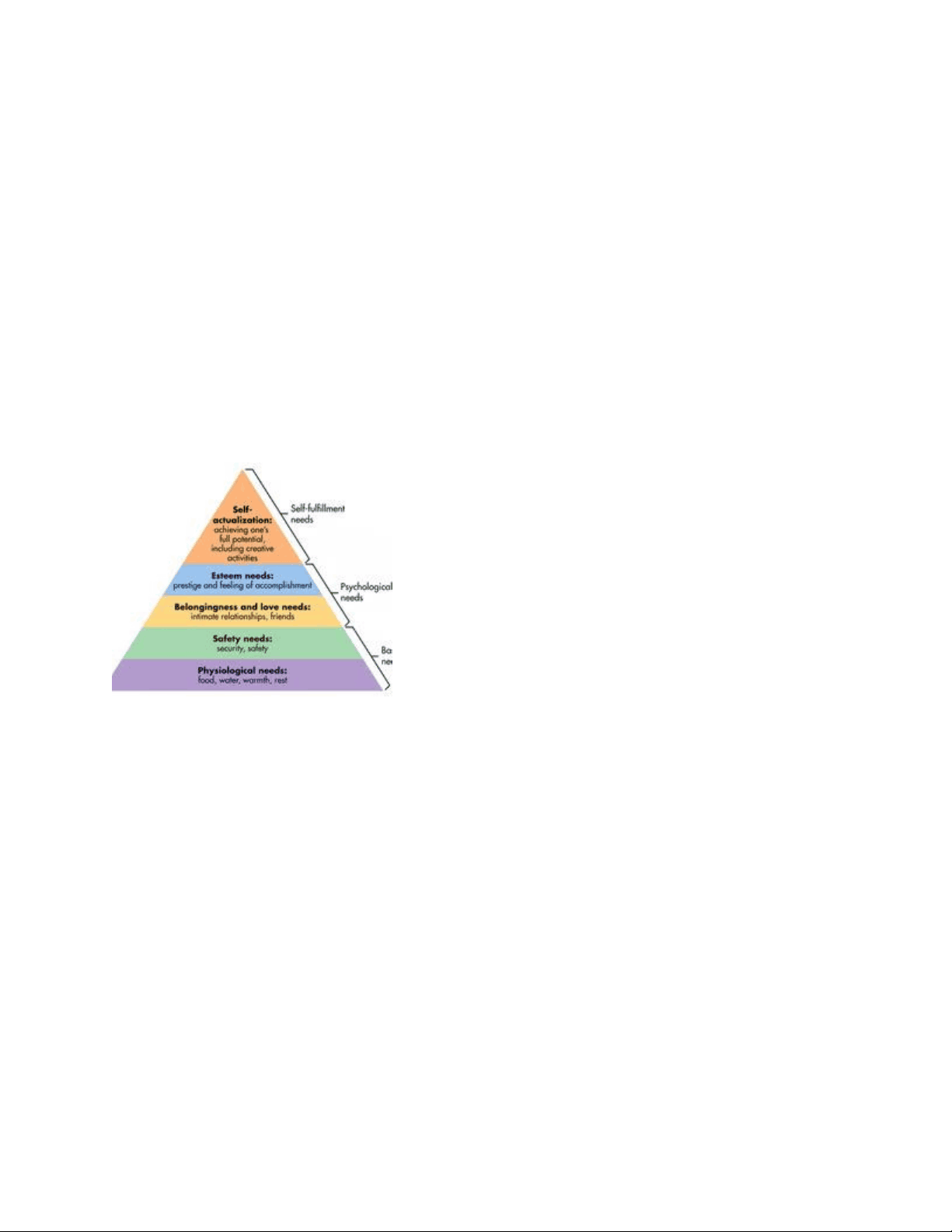
NURS 330 Age Span Assessment Exam 1 LATEST 2025 UPDATE Texas Lutheran University VERIFIED EXAM ALREADY GRADED A+ COMPLETE FULL-LENGTH EXAM Abraham Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Maslow's pyramid of human needs; must satisfy levels below before reaching to next
Typology: Exams
1 / 20

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!













Abraham Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Maslow's pyramid of human needs; must satisfy levels below before reaching to next Components of a SMART goal Specific Measurable Achievable Relevant Time-bound
Define chronic disease an ongoing condition or illness that lasts for a year or more and requires ongoing medical attention (limits daily activities) Goals of rehabilitation 1.) Assist the resident in maintaining and/or regaining the ability to preform ADLs 2.) Promote resident's independence and help resident adapt to the new disability 3.) Prevent complications of immobility Normal Age related change for cardiovascular system
chronic pain episode of pain that lasts for 6 months or longer; may be intermittent or continuous acute pain pain that is felt suddenly from injury, disease, trauma, or surgery 6 months or less macular degeneration breakdown or thinning of the tissues in the macula, resulting in partial or complete loss of central vision types: wet-abrupt onset and more damaging dry- outer layers begin to break down with drusen nursing management for macular degeneration encourage use of amsler grid Glaucoma increased intraocular pressure results in damage to the retina and optic nerve with loss of vision
nursing management for cataracts Pre-operative care Dilating eye drops or other medications as ordered Post-operative care Patient education Provide written and verbal instructions Instruct patient to call physician imediately if vision changes; continuous flashing lights appear; redness, swelling, or pain increase; type and amount of drainage increases; significant pain is not relieved by acetaminophen detached retina separation of the retina from the choroid in back of the eye ocular emergency types: rhegmatogenous, traction, exudative, combination of rhegmatogenous and traction detached retina manifestations sudden, unilateral, painless, floaters, loss of vision nursing management with detached retina educating patient and providing supportive care
Hearing Loss: Conductive results from an external ear disorder such as impacted cerumen or a middle ear disorder Hearing Loss: Sensorineural damage to structures of inner ear nursing assessment with hearing loss watch for/be alert for :
Vitamin D and Calcium Ice packs and heating pads Assistive devices Joint taping hip arthroplasty total hip replacement nurse considerations with hip arthroplasty pain, immobility, hemorrhage, neurovascular dysfunction, dislocation of prosthesis, venous thromboembolism, infection hip arthroplasty nursing interventions change dressing as ordered; diet as ordered; neurovascular checks and vital signs every 4 hours; maintain position of operative area; physical therapy will initiate ambulation and prescribe routine; encourage fluid intake; antiembolisim stockings; avoid adduction and hyper flexion of hip; encourage fluid intake and high-fiber foods; use toilet riser to prevent hyper flexion of hip
monitor wound discharge
pain, pallor, pulselessness, paralysis, paresthesia compartment syndrome Swelling in a confined space that produces dangerous pressure; may cut off blood flow or damage sensitive tissue. external fixator external metal frame attached to bone fragments to stabilize them External fixator care
goals of traction
Diagnosis Planning Implementation Evaluation The nursing process is how nurses.. think identify patient problems determine patient outcome prioritize patient care Models of Disability medical model rehabilitation model social model biopsychosocial model functional model interface model medical model a person with disability who views their disability as a problem. Healthcare providers are viewed as dependent, and people with disability are known as tragic.
rehabilitation model people with disability who need a rehabilitation specialist to fix their problem and they are a failure if the problem is not fixed social model disability is viewed as social and physical barriers, and that the disability can be removed by overcoming the barriers Biopsychosocial model- perspectives from a biologic, individual and social. interface model- addresses components of health rather than consequence of disease Activities of daily living (ADLs): self-care activities that the patient must accomplish each day to meet personal needs including bathing, grooming, dressing, feeding, and Toileting. pressure injury prevensions position patient comfortably Reposition every 2 hours
misconception of pain If patient is sleep, they don't feel painVital signs are reliable indicators of painCaregiver best judge of painPain is normal part of agingAnxiety makes pain worseIf a patient is distracted, they are no longer in pain. Pharmacologic: methods for pain opioids non-opioids adjuvants 1 scale 0 - 3) mild pain(non-opioid: ibuprofin) 2 scale (4-6) moderate pain (opioids) 3 scale (7-10) sever pain (opioid, morphine) component of pain assessment OLDCARTS
onset; location; duration; characteristic; alleviating and aggravating factors; radiation or relieving factors; timing; and severity. Interventions to prevent pressure injury: Relieving- Relieving pressure, pressure relieving devices Positioning- Positioning patient, reducing friction and shear Minimizing- Minimizing irritating moisture Improving- Improving: mobility, sensory perception, tissue perfusion Improving- Improving nutritional status