












Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
A study guide for Exam 2 of the NUR 2115 course at Rasmussen College. It covers the nursing process, diagnosis, implementation, and evaluation. It also includes NANDA nursing diagnoses for oxygenation and gas exchange, infection, inflammation, and thermoregulation. Additionally, it covers vocabulary related to oxygenation and gas exchange, proper method for auscultation of the lungs, and the importance of coughing. examples and explanations to help students understand the concepts better.
Typology: Study Guides, Projects, Research
1 / 19

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!












Fundamentals of Nursing Study
Guide for Exam 2 By M. Iorio
Rasmussen College Summer ‘
Module 4 – Clinical Judgement and Nursing Process ➢ The nursing process consists of 5 steps.
diagnosing.
patient outcomes, select necessary interventions to achieve these outcomes and communicate the plan of care among the patient, family and other staff involved in the patients care.
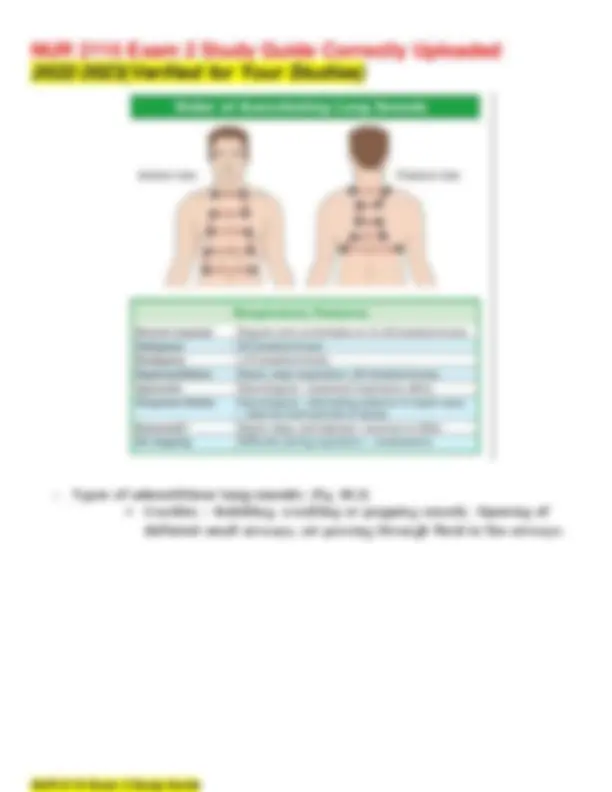
➢ Types of adventitious lung sounds: (Pg. 652)
➢ Microorganisms typically reside in a host, which is environmentally stable. If the host’s immune resistance is in a weakened state, the microorganism will thrive and result in infection. Hospital patients are susceptible hosts. The susceptibility of the host depends on the integrity of skin and mucous membranes, pH balance, WBCs, age, sex, race, heredity, immunizations, level of fatigue, nutritional status, stress level and use of invasive medical devices. ➢ An organism’s potential to produce disease in a person depends on the organism’s virulence (potential for the organism to cause disease), the persons immunity to that organism, the number of organisms present and the length/ intimacy of contact between that person and the organism. ➢ Stages of infection
proliferation. ✓ During this phase the patient has a mildly elevated body temperature and an increase in plasma WBCs.
What are the normal values for a patients vital signs?