































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Graph traversal algorithms, specifically depth-first search (dfs) and breadth-first search (bfs). It also covers the concept of state-space search, which involves generating the graph as we search. Examples of state-space problems and tree search algorithms.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 61

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!






















































Oct
Many
problems
require
processing
all
graph
vertices
(and
edges)
in
systematic
fashion
Graph
traversal
algorithms:
REVIEW
REVIEW
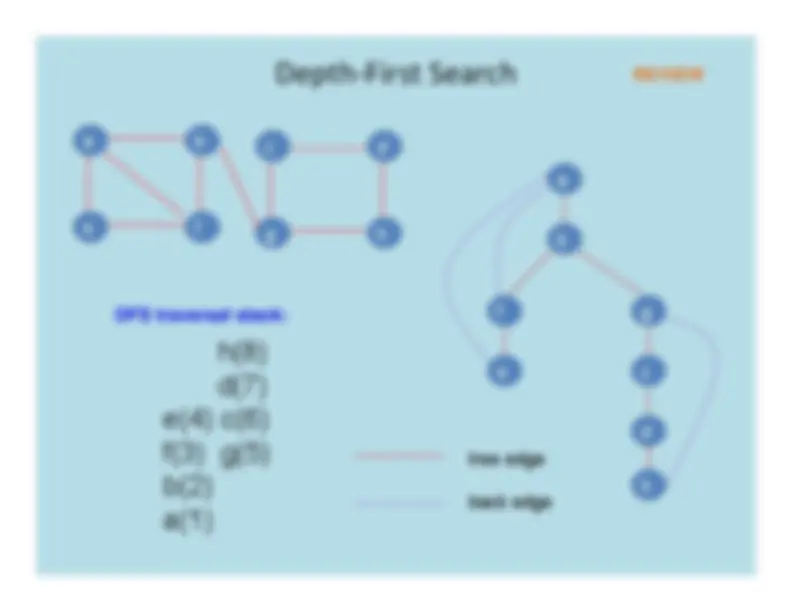
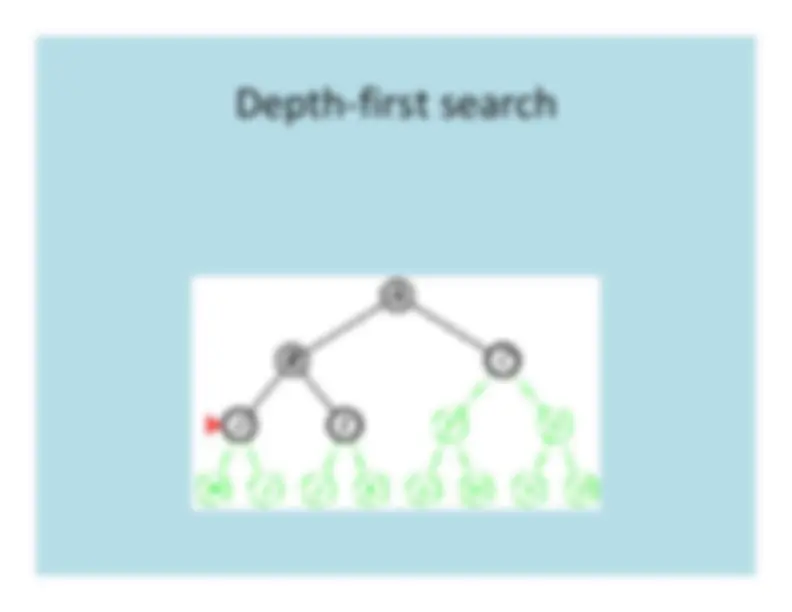
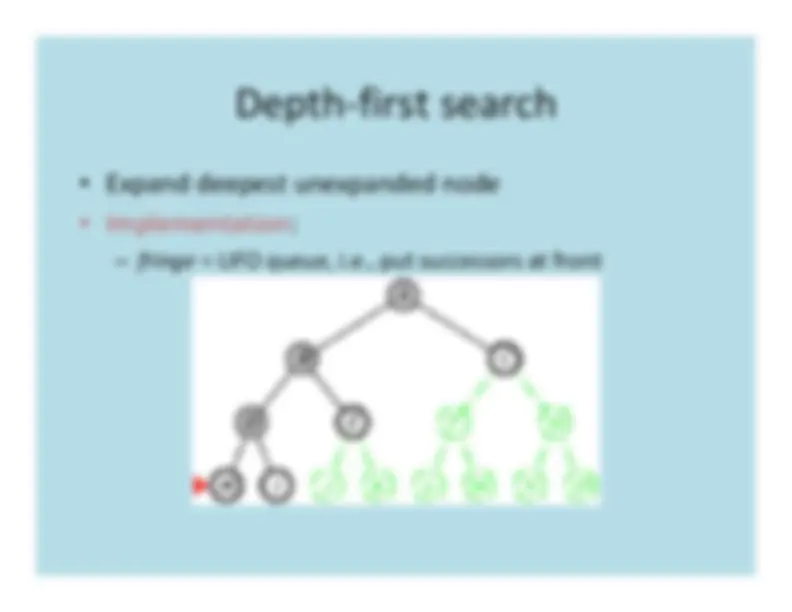
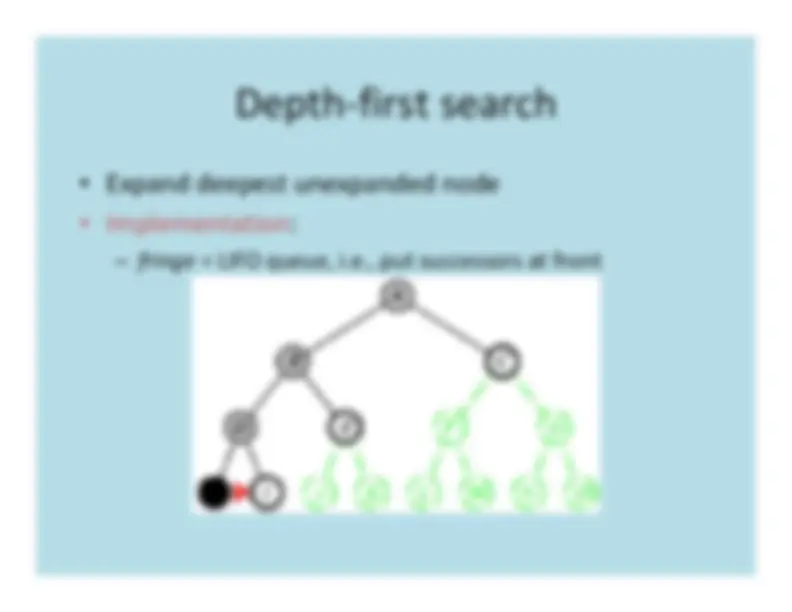
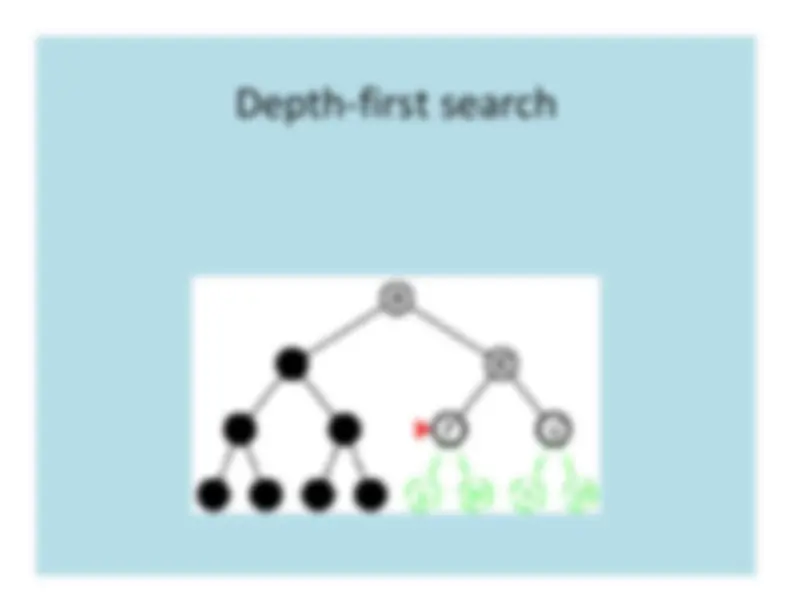
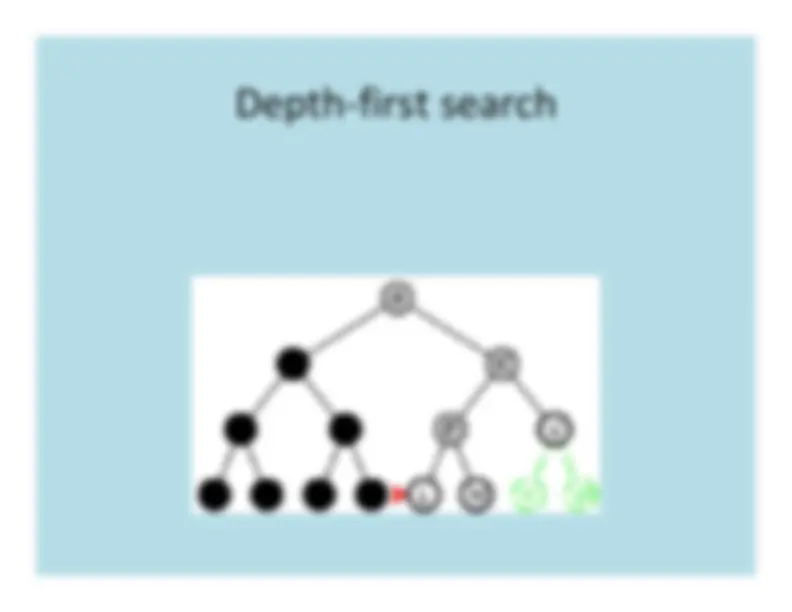
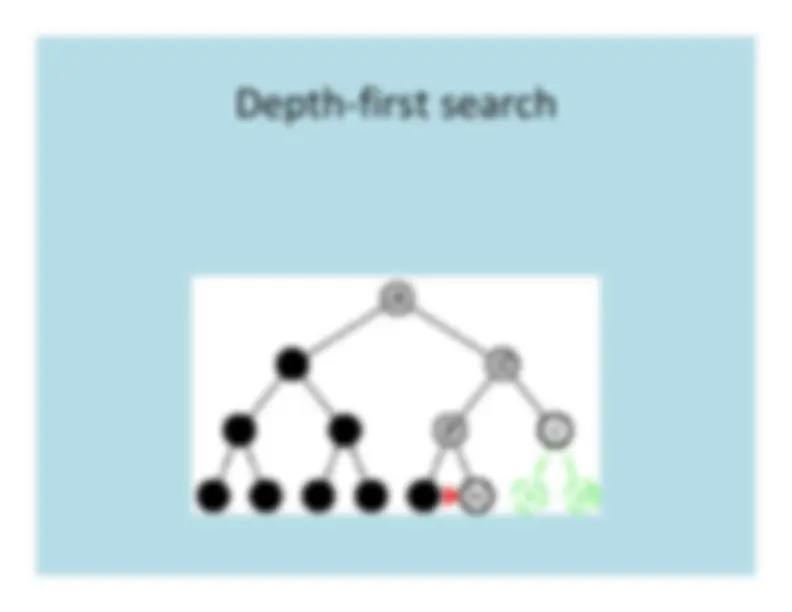
Depth
First
Search
a
b
e
f
c
d
g
h
a b
f e
g c d h
tree edgeback edge
DFS traversal stack:
h(8)d(7)
e(4) c(6)f(3) g(5)b(2)a(1)
REVIEW
REVIEW
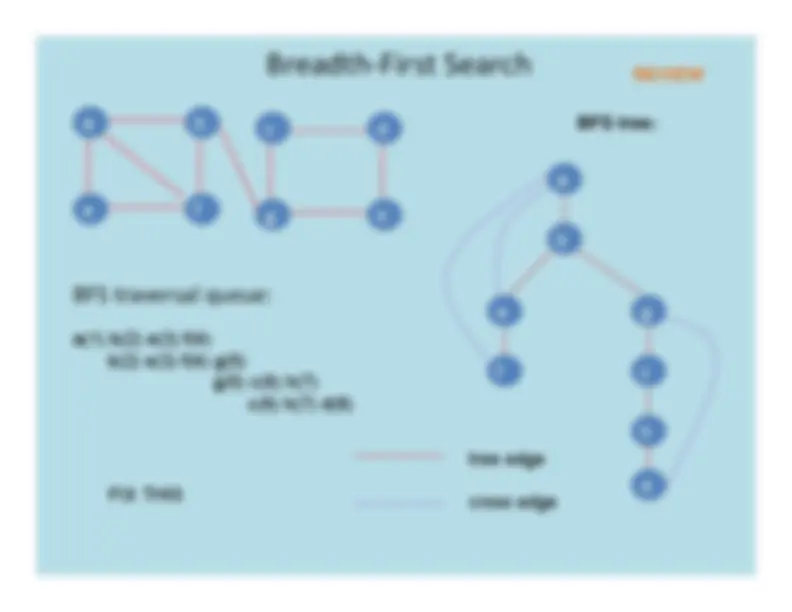
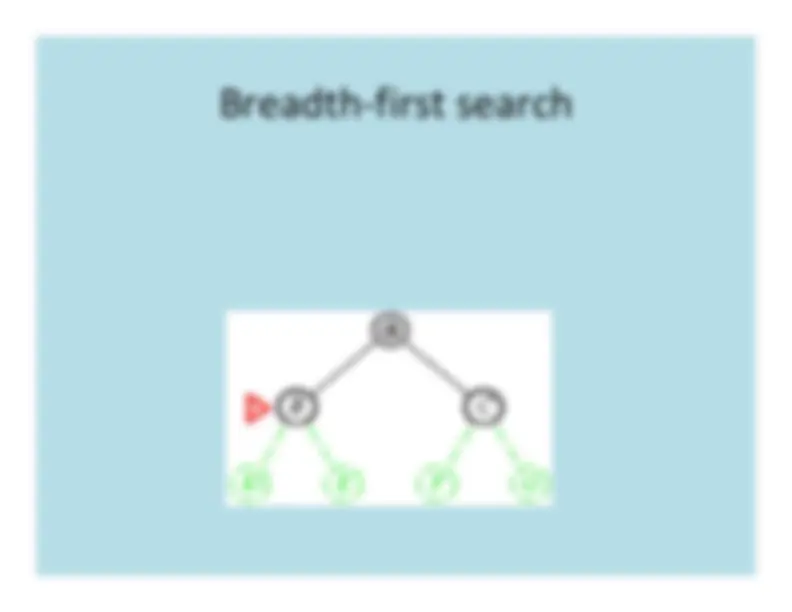
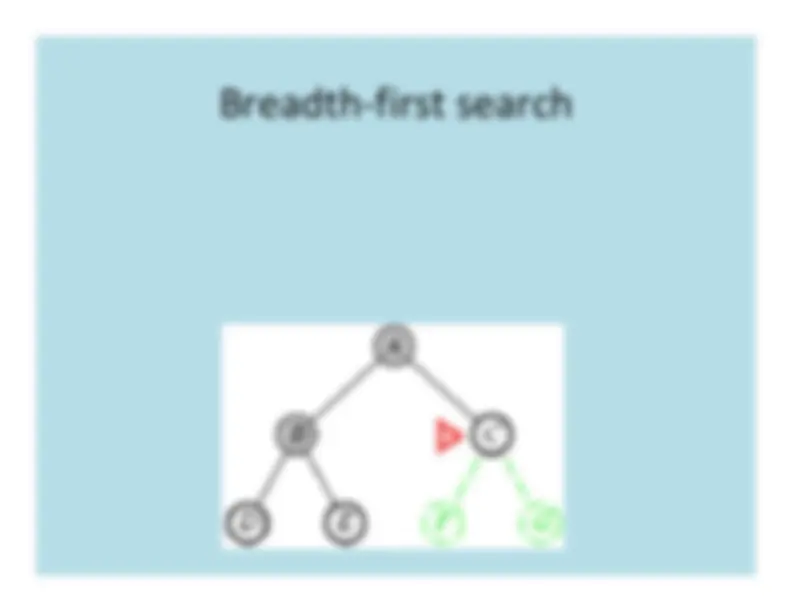
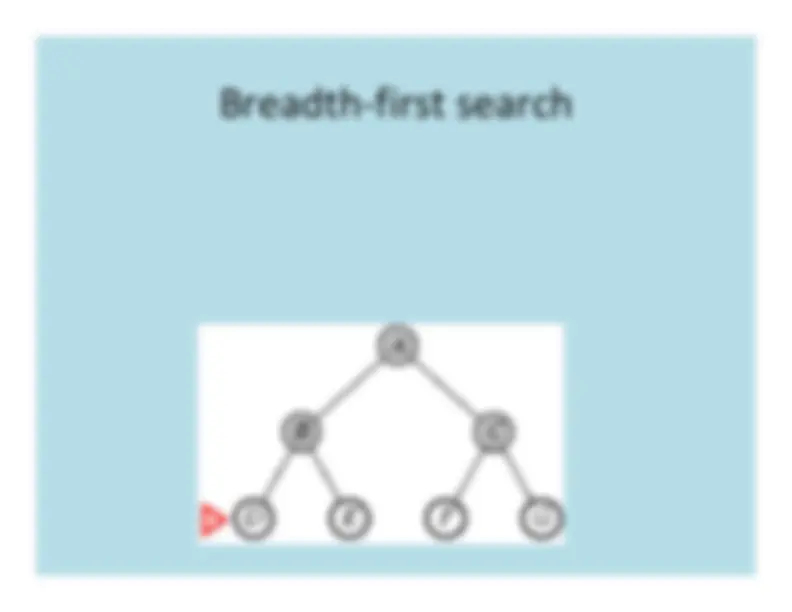
Breadth
First
Search
BFS tree: a b
e f
g c h d
tree edgecross edge
a
b
e
f
c
d
g
h
BFS
traversal
queue:
a(1) b(2) e(3) f(4)
b(2) e(3) f(4) g(5)
g(5) c(6) h(7)
c(6) h(7) d(8)
REVIEW
FIX THIS
state
space
search
problem
consists
of:
an
initial
state
a
set
of
possible
actions
-^
an
action
transforms
a
state
into
a
new
state
A
goal
state
(or
states)
path
costs
-^
cost
of
moving
from
one
state
to
another
solution
consists
of
a
sequence
of
actions
leading
from
initial
state
to
a
goal
state
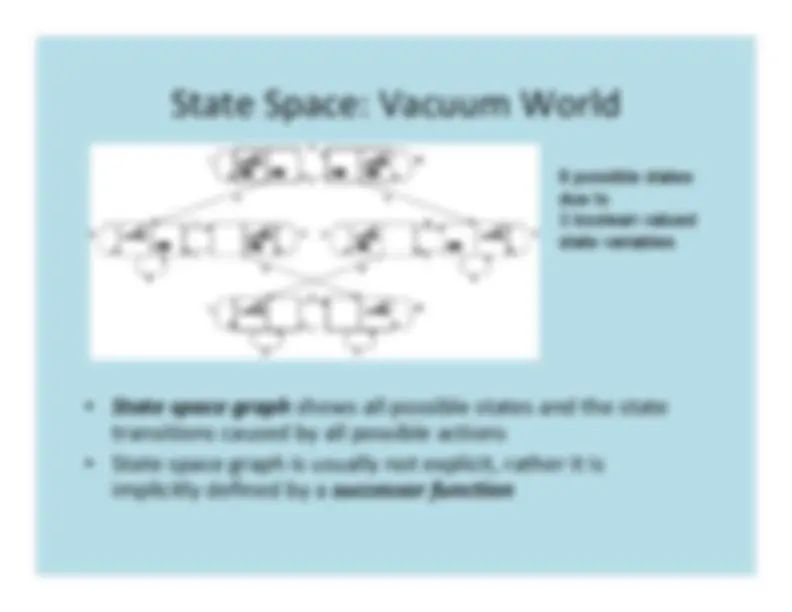
Vacuum world has two cells (left and right),which can be dirty or clean.The vacuum robot which can do any of the following:
The goal is to have both cells clean.
State
space
graph
shows
all
possible
states
and
the
state
transitions
caused
by
all
possible
actions
State
space
graph
is
usually
not
explicit,
rather
it
is
implicitly
defined
by
a
successor
function
8 possible statesdue to3 boolean valuedstate variables
successor
function
maps
a
state
and
action
to
a
new
state
<state,
action>
Æ
state
It
may
be
explicit
(i.e.
a
lookup
table)
or
implicit
(defined
as
a
function)
states? locations
of
tiles
actions? move
blank
left,
right,
up,
down
goal
test? goal
state
(see
figure)
path
cost?
1
per
move
The
successor
function
is
best
defined
by
a
function
a
table
would
be
excessively
large
How
many
possible
states
are
there
for
this
problem?
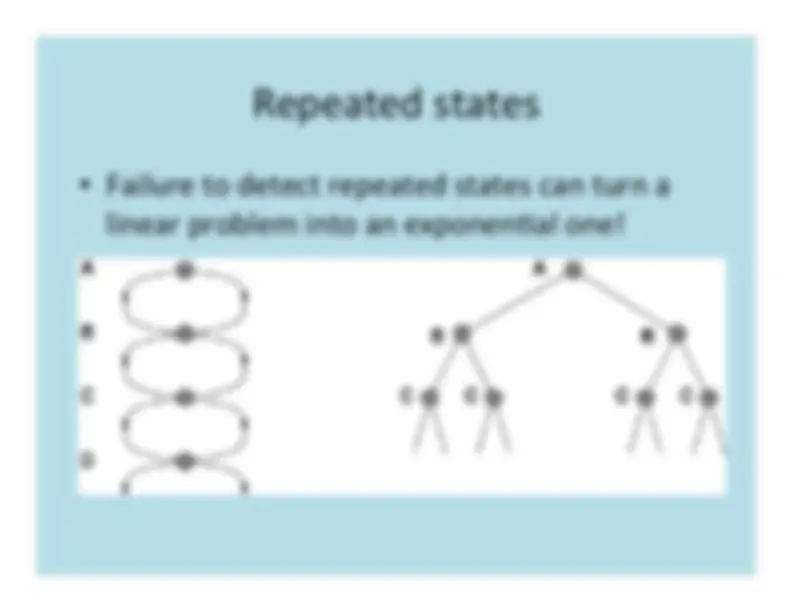
explore
the
state
space
by
generating
successors
of
already
explored
states
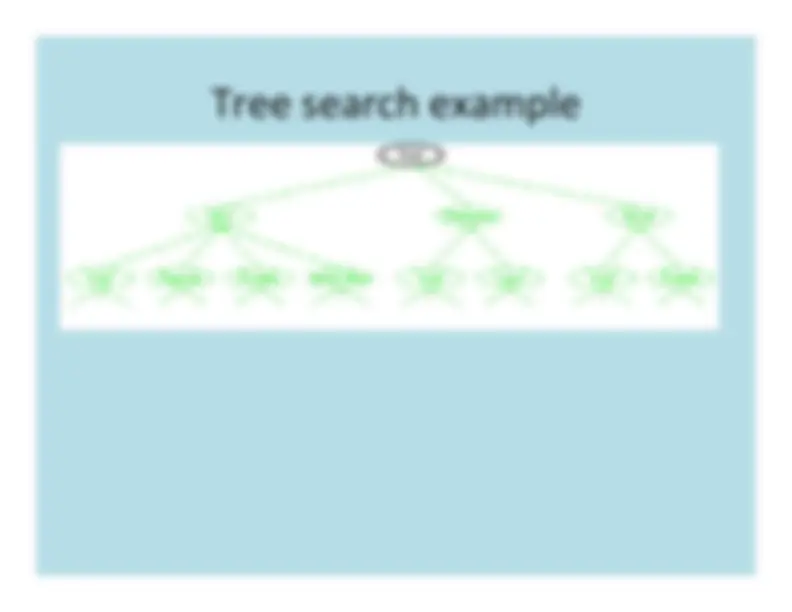
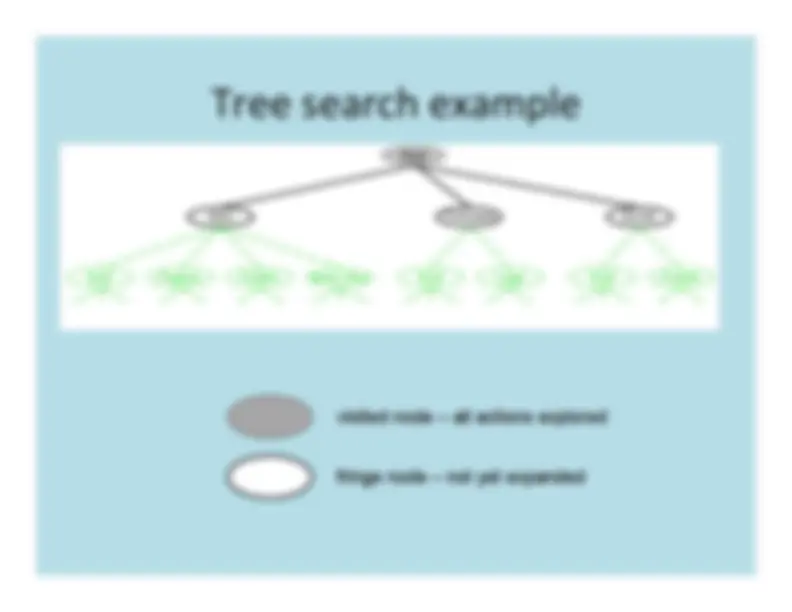
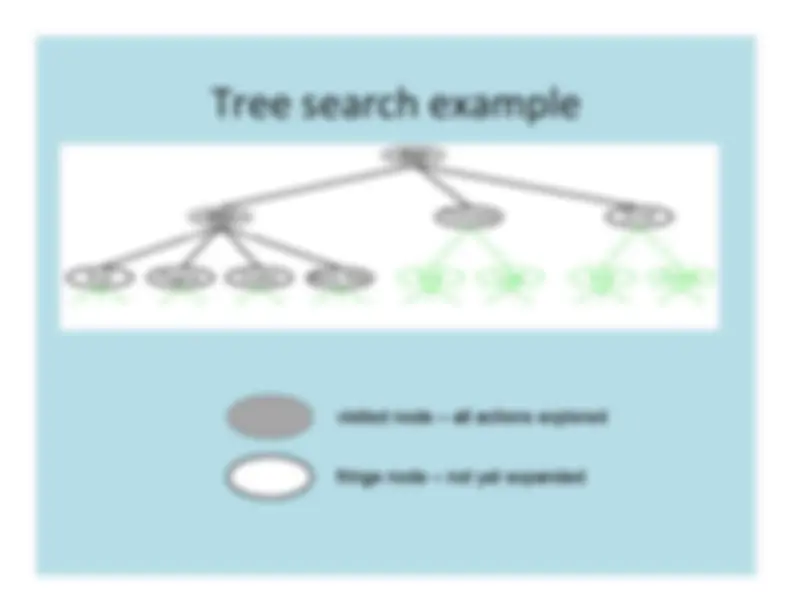
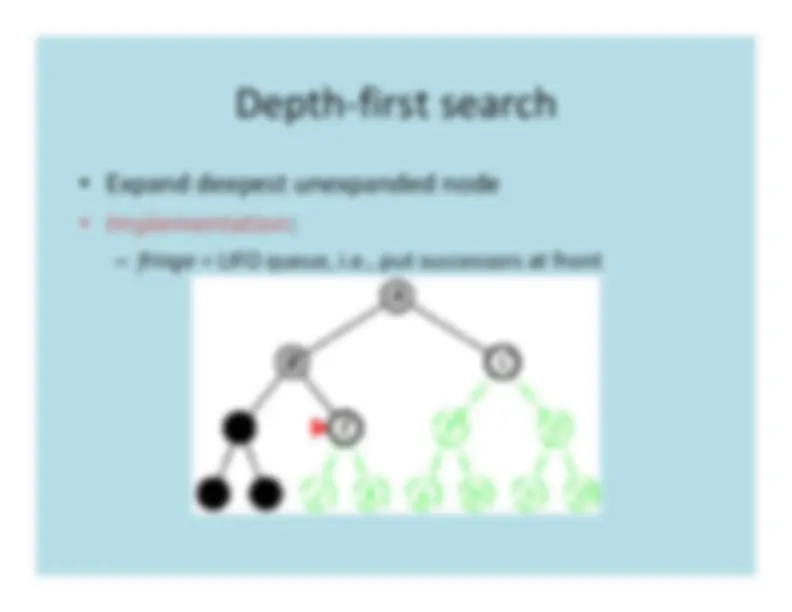
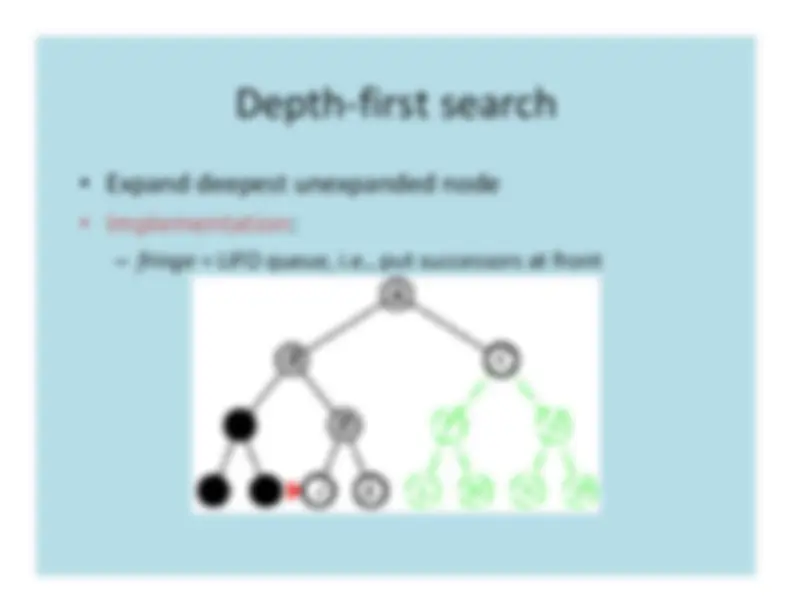
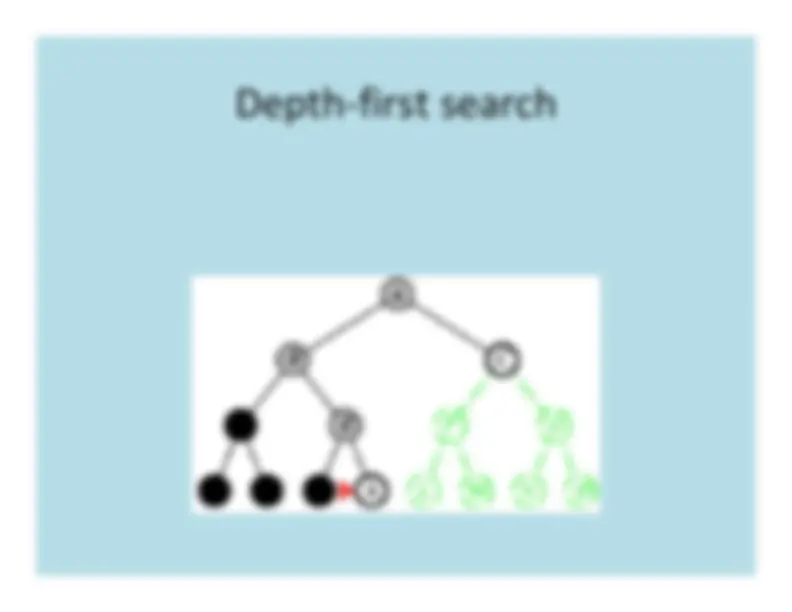
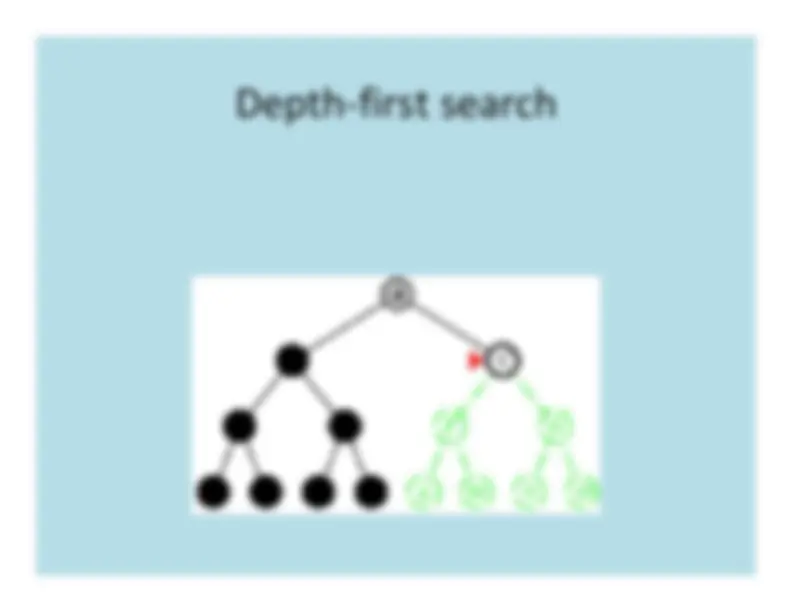
The strategy for selecting the next nodeto expand determines the type of search
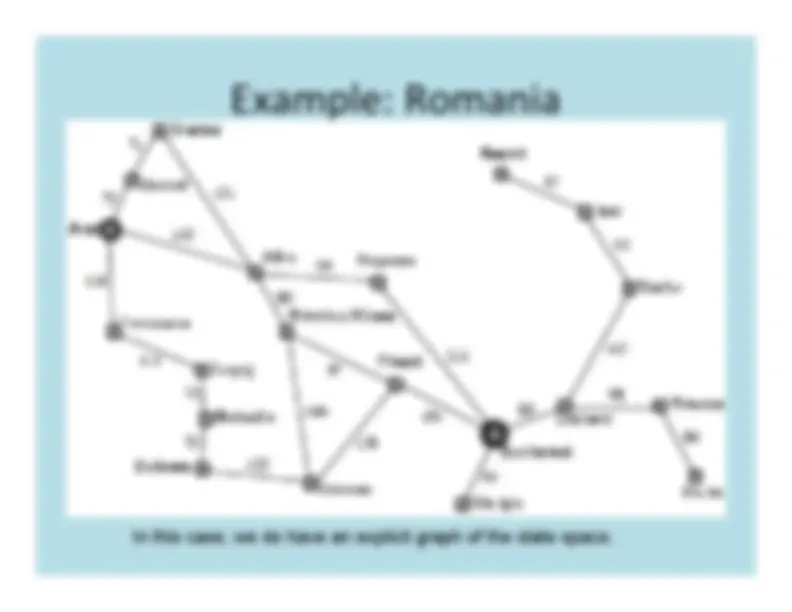
In this case, we do have an explicit graph of the state space.