









Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
This lecture from new mexico tech's cs/it 111 course introduces the concept of number systems, focusing on binary, octal, and hexadecimal. The categories of numbers, positional notation, conversion between bases, and the relationship between these number systems. It also explains how to perform arithmetic in other bases and the concept of 'power of 2' number systems.
Typology: Papers
1 / 14

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!









L E C T U R E 7 New Mexico Tech: CS/IT 111
Categories of numbers
Positional notation
Conversion to and from base-
Binary, octal, and hexadecimal relationship
“Power of 2” bases and computing
Number
Natural numbers
Negative numbers
Integers
Rational numbers
How many ones are there in 1337?
Ù
Ù
Ù
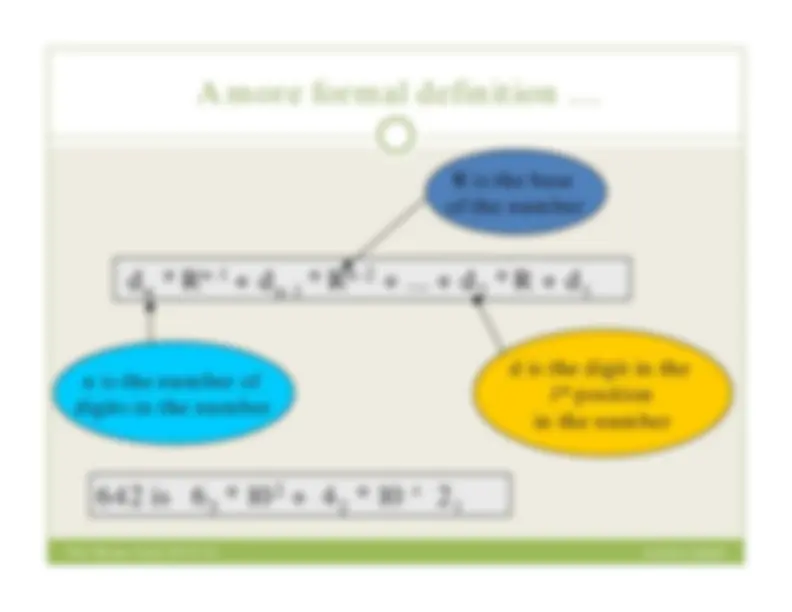
The base of a number determines the number of digits in the system and the value of the digitpositions.
Digits are represented by distinct symbols fordecimal values 10 and above
A B C D E F 10 11 12 13 14 15
Numbers are written using positional notation
In polynomial form:
3
2
1
0 Ù
1 * 10 3 = 1 * 1000 = 1000
3 * 10 2 = 3 * 100 = 300
3 * 10 1 = 3 * 10 = 30
7 * 10 0 = 7 * 1 = 7 1337 This number is in base 10 The power indicates the position of the number
We’ve seen 1337 in base 10, what about another base?
1337 12 is equivalent to 2275 10 1 * 12 3 = 1 * 1728 = 1728
3 * 12 2 = 3 * 144 = 432
3 * 12 1 = 3 * 12 = 108
7 * 12 0 = 7 * 1 = 7 2275
02/02/
There’s nothing to be afraid of!
Ù
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 1
1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 2 2 0 2 1 0 1 0 1 1 1
1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
02/02/ Binary New Mexico Tech: CS/IT 111 Octal Hex Dec 0000 0 0 0 0001 1 1 1 0010 2 2 2 0011 3 3 3 0100 4 4 4 0101 5 5 5 0110 6 6 6 0111 7 7 7 1000 10 8 8 1001 11 9 9 1010 12 A 10 1011 13 B 11 1100 14 C 12 1101 15 D 13 1110 16 E 14 1111 17 F 15 A group of 4 binary digits can be converted into a single hexadecimal digit: So: 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 2 is ABC 16 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 A B C
An algorithm …
Ù
Ù
What is 1988 10 in octal?
What is 3567 10 in hexadecimal?