




Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Draw complete Lewis structures for each resonance contributor of methyl isocyanate. Follow the directions given in the boxes. Restrict your drawings to all ...
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 5

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




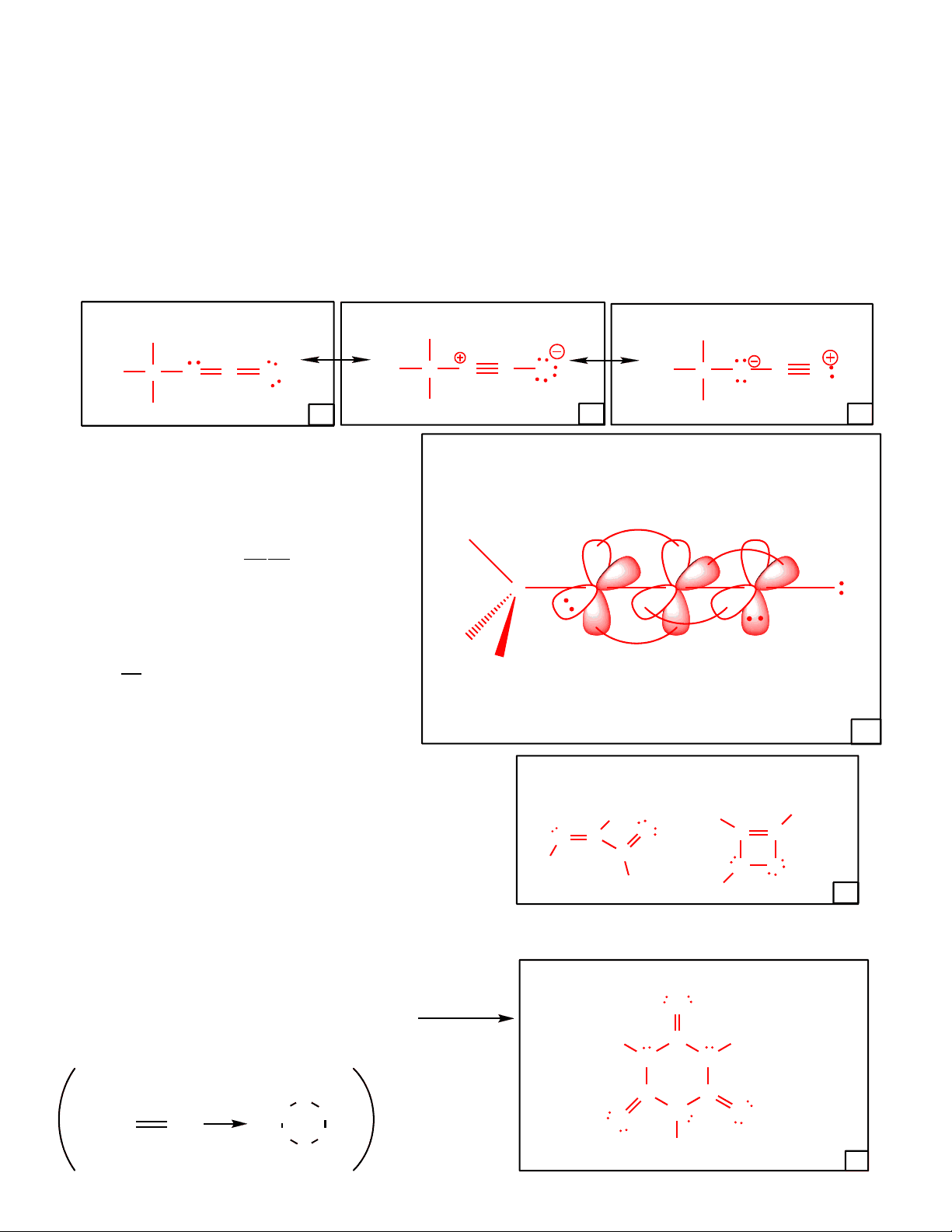
Methyl isocyanate is best represented by a group of three resonance structures. Draw complete Lewis structures for each resonance contributor of methyl isocyanate. Follow the directions given in the boxes. Restrict your drawings to all closed-shell atoms with charges of +1, 0, -1 on each atom.
Methyl isocyanate is not the only compound with a molecular formula of C 2 H 3 NO. Draw a structural isomer of methyl isocyanate that contains all closed- shell atoms and formal charges of zero on each atom.
Name _______________________ Page 1
overall dipole moment. The ring contains six atoms. Draw the structure of this product. There are no other products. For an example of the formation of a dif f erent cyclic trimer, see below.
Methyl isocyanate (connectivity: H 3 CNCO ) is a chemical used in the production of certain pesticides. It is very toxic. An accidental leak of this chemical in Bhopal, India in 1984 resulted in the deaths of 3800 people.
M ost signif icant contributor
Structural isomer of methyl isocyanate containing all closed shell atoms and zero f ormal charges.
I ntermediate contributor Least signif icant contributor
catalyst
Cyclic trimer with no molecular dipole moment.
Consider all three resonance contributors above when choosing the most reasonable hybridization for all atoms, and provide an accurate and complete three-dimensional orbital picture f or the major resonance contributor of methyl isocyanate.
As always, you should use lines, dashes, wedges, p orbitals (lone or overlapping) to show the direction of all electrons (or empty orbitals). All bond angles should reflect the appropriate geometry and hybridization chosen for your drawing. (^6)
contributor above
H 2 C H 2 C C H 2
CH 2
CH 2
H 2 C
example of cyclic trimer f ormation
H
H
H
H
C
H
H N C O
H
C
H
H N C O
H
C
H
H N C O
N H
C C
H
O
H C
N O
C
H H
H
Consider the compound shown below. Draw the other f our all closed shell resonance contributors f or this compound (formal charges on each atom between -1 and +1). Note : A linear (sp hybridized) atom cannot form in a five-membered ring!
Name _______________________ Page 2
lines, dashes and wedges to represent sigma bonds and the directionality of localized non-bonding electrons, and using overlapping p-orbitals for pi bonds, draw a representation for the three dimensional orbital structure of hydrogen cyanide (HCN; all closed shell atoms).
O N
i. draw closed shell resonance contributors here
ii. This compound can act as a base. Consider the resonance structures you drew above and what you know about basicity. Identify the most basic atom and provide the curved arrow mechanism f or the reactions predicted to occur. Draw the products.
O N
O N
H B
H
H
O
O H
3D structure of HCN
reactivity it will have with the molecule provided. Include curved arrow mechanism and products.
Lewis structure of NaH and mechanism of reaction
N aH
p roduct(s)
Draw curved arrows and product(s)
Draw curved arrows and product(s)
O N^ O N
O N^ O N
O N^ H^
O
O
O N^ B
H
H
H
Na H^ C C H
Na
Name _______________________
A pi bond is an area of high electron density. As such, it can act as a base (either Lewis or Bronsted). In the reaction below, the pi electrons from a double bond act as a Bronsted base in the first step. The second step is a Lewis acid/base reaction between the two products of step 1. Step 2 forms a charged species with an acidic proton. If this species will react with the base provided, show the mechanism, otherwise, write "no reaction" in the fourth box.
CH 3
H 3 C C
CH 2
H O
H
H
p rovide curved arrows f or the f irst step CH 3
H 3 C C
CH 3
p rovide the curved arrows f or the second step
O CH 3
O
Provide the product(s) of step 2. Also p rovide the curved arrows f or the next step, if a reaction occurs.
Reaction product(s) or "no reaction"
Lysine, shown below, is one of the essential amino acids that one must get from food (the body cannot synthesize it). It is shown in its fully protonated form as it would exist at a very acidic pH (pH<1). Titration reveals three acidic protons with pKa's of 2.2, 8.9, and 10.3.
N C C
C
O
O
C
C
C
N
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
i. Circle the most acidic proton
base
ii. Draw a complete Lewis structure of lysine (include charges and non-bonding electrons) as it would predominately exist at pH=
H O
H
As always: READ THE DIRECTIONS CAREFULLY!
H
H H
H H
H H
H H
CH 3
C
CH 3
H 3 C O
H
H
CH 3
C
CH 3
H 3 C O
H
HO CH 3
O
N C C
C
O
O
C
C
C
N
H
H
H (^) H
H
H H
H H
H H
H H
Name _______________________
Predict all of the products for each of the following spontaneous reactions. Be sure to balance your equations.
i) Draw an arrow to the most acidic proton in compound A and label it "most acidic."
i and ii) label the most acidic and second most acidic protons
Compound A
iii) In one or two sentences, explain why the most acidic proton is more acidic than the second most acidic proton in Compound A
ii) Draw an arrow to the second most acidic site in compound A and label it "second most acidic."
iii) why is it more acidic?
CH 3 Li (1 equivalent)
2-methylpropene M W = 56 g/ mol b.p. = -7 C
acetone M W = 58 g/ mol b.p. = 56.5 C
Below are two compounds, 2-methylpropene and acetone, with some physical data. Note that the boiling points are significantly different. Explain, using words and drawings, why the boiling points are different.
Below is a Lewis structure of dichloromethane. Is this molecule polar? Explain, using words and a drawing.
Cl C Cl
dichloromethane
Is dichloromethane polar?
Most Acidic
Second Most Acidic
Sulfur, a third row element, is bigger than oxygen. This has two consequences. It forms a bond with lower covalency with hydrogen and the resulting anion (conjugate base) can more easily stabilize the negative charge.
Li
2-methylpropene has only London dispersion forces, while acetone also has stronger dipole-dipole interactions.
Cl
Cl H
Yes, the carbon is sp 3 hybridized, so dichloromethane is tetrahedral. Thus, the bond C-Cl bond dipoles add to give an overall molecular dipole moment.