










Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
The Low Self-Control Theory, which explains the stability and versatility of crime through the concepts of unobserved heterogeneity and state dependence. The theory posits that individuals with low self-control are more likely to commit crimes due to their impulsive nature and inability to delay gratification. The document also discusses the assumptions of control theories and three empirical facts that other criminological theories cannot explain.
Typology: Slides
1 / 21

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!














Crime and the Life Course
SOC 401
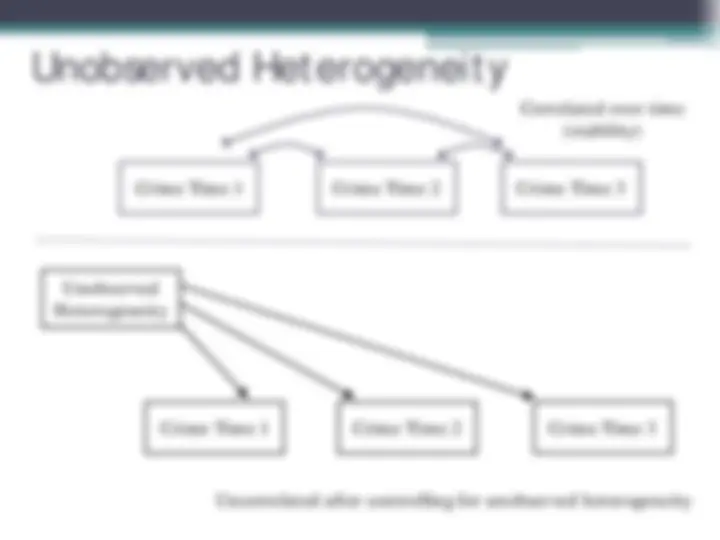
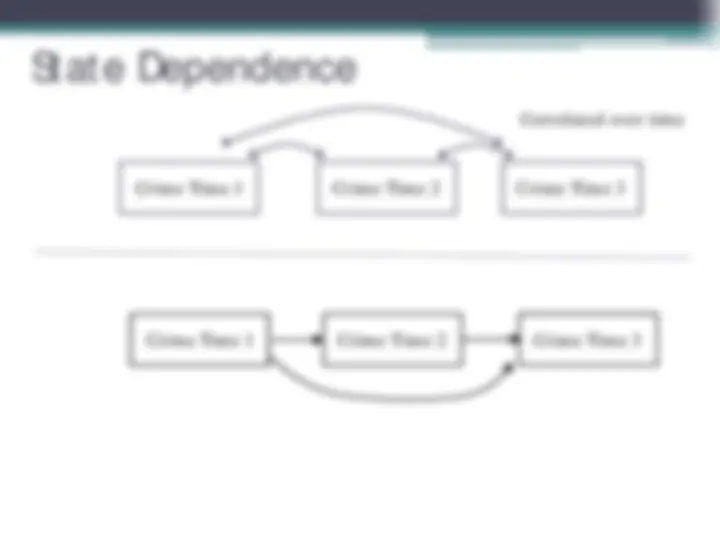
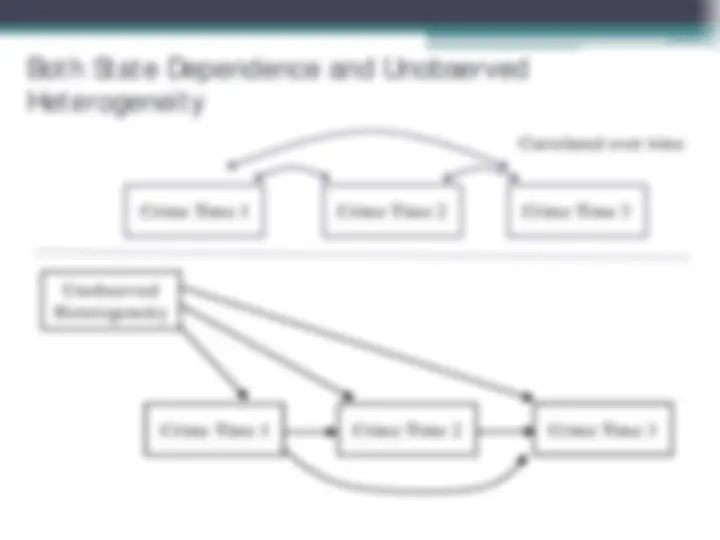
Crime Time 1 Crime Time 2 Crime Time 3
Crime Time 1 Crime Time 2 Crime Time 3
Correlated over time
Crime Time 1 Crime Time 2 Crime Time 3
Crime Time 1 Crime Time 2
Unobserved Heterogeneity
Crime Time 3
Correlated over time
▫ Crime is not learned ▫ Explain conformity, not crime
A General Theory of Crime: Low Self
Control Theory
Identifying the Concept of Low Self Control
H&G: Look at modal characteristics of crime and infer modal characteristics of criminals:
Characteristics of Crimes Characteristics of Criminals Exciting & risky Seek excitement and risk Immediately pleasurable Seek immediate pleasure No delayed gratification Cannot delay gratification No manual or academic skill Lack manual or academic skill Entails suffering of others Indifferent to suffering of others Self-centered Tend to be self-centered Impulsive Tend to be impulsive Low tolerance for frustration Have a low tolerance for frustration
Adds up to low self-control: A stable trait like personality. Doesn’t change throughout the life course (Note: example of unobserved heterogeneity.)
Low Self Control and Stability of Crime
Low Self Control & Age Distribution
Origins of Low Self Control
Delinquent Peers and Delinquency
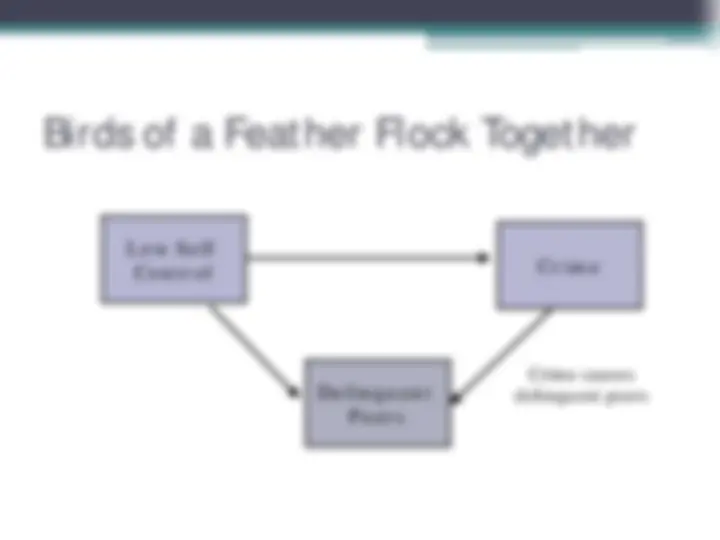
Correlation between delinquent peers and delinquent behavior is not causal ▫ Spurious: Low self-control causes delinquency and delinquent peer association ▫ Reverse causal order (selection effect): “Birds of a feather flock together” ▫ Measurement artifact (asking respondent about delinquent peers tells us about his/her own delinquency)
Low Self Control
Delinquent Peers
Crime
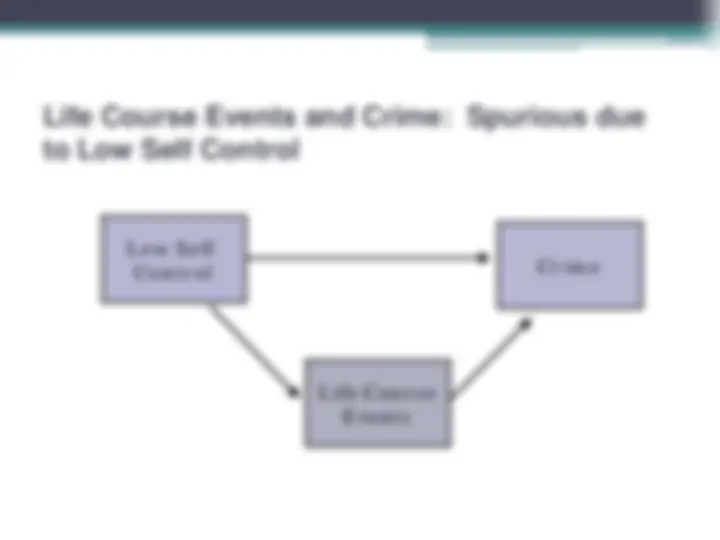
Life Course Transitions and Crime
Low Self Control
Life Course Events
Crime