

















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An overview of site-directed mutagenesis and recombinant dna technology, including the identification and isolation of desired dna segments, the use of restriction endonucleases and dna ligase, and the introduction of recombinant dna into host cells. The document also discusses the requirements for dna cloning and the use of plasmids as vectors.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 27

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




















CHEM-
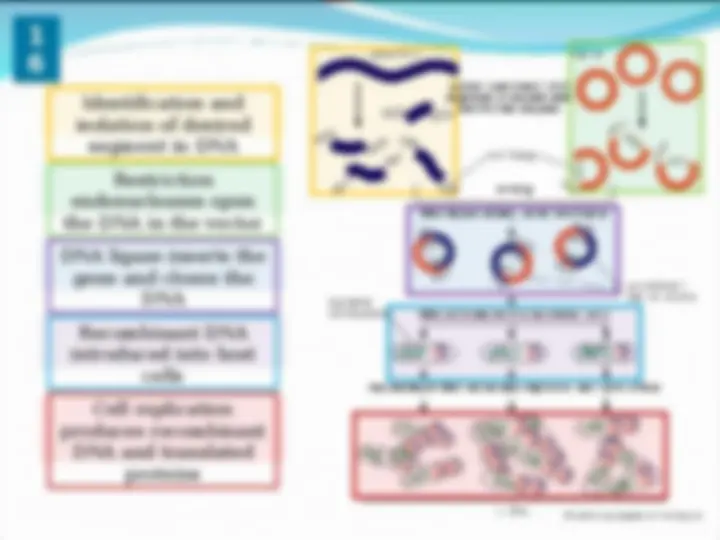
Identification and
isolation of desired
segment in DNA
Restriction
endonucleases open
the DNA in the vector
DNA ligase inserts the
gene and closes the
DNA
Recombinant DNA
introduced into host
cells
Cell replication
produces recombinant
DNA and translated
proteins
beginning and end of the gene of interest.
nucleases to create a compatible opening.
ligase.
(transformation).
proteins for further studies and use.
Identification and
isolation of desired
segment in DNA
Restriction
endonucleases open
the DNA in the vector
DNA ligase inserts the
gene and closes the
DNA
Recombinant DNA
introduced into host
cells
Cell replication
produces recombinant
DNA and translated
proteins
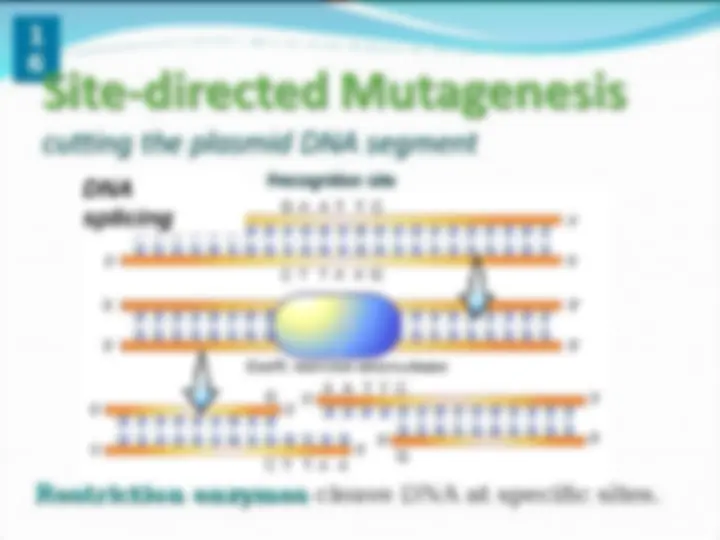
DNA splicing
Restriction endonucleases are enzymes that
have become exceptional tools for cutting DNA
at specific nucleotide sequences.
These enzymes are able to cut both strands of
DNA at specific palindrome sequence across the
double helix.
where
R = A or G and
Y = C or T
BamHI BstYI EndonucleasesEndonucleases:
Palindrome Palindrome
Sequences Sequences
Restriction enzymes Restriction enzymes cleave DNA at specific sites.
splicing
Recognition site Recognition site
Use of nucleases to cleave
DNA at specific recognition
sites
An artificial self-
replicating circular
DNA vector
Contains a selectable
marker for
ampicilin ampicilin
resistance resistance.
Contains a
polycloning site for
gene insertion
Identification and
isolation of desired
segment in DNA
Restriction
endonucleases open
the DNA in the vector
DNA ligase inserts the
gene and closes the
DNA
Recombinant DNA
introduced into host
cells
Cell replication
produces recombinant
DNA and translated
proteins
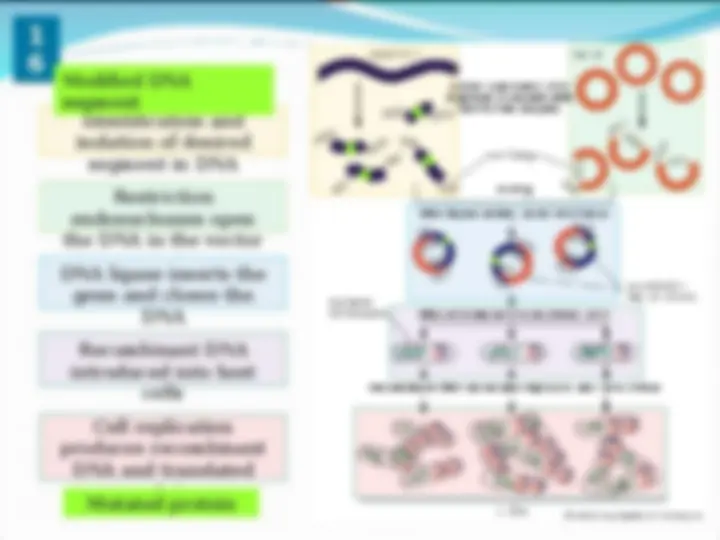
Modified DNA
segment
Mutated protein
Once the gene for
human insulin was
identified, the
segment that codes
for insulin was cut
from the chromosome
and recombined with
a cut circular DNA
plasmid.
The plasmid is
inserted into a
suitable bacterium
and production starts
as the gene is
Recombinant DNA Technology Recombinant DNA Technology
Antibiotic Resistance Antibiotic Resistance
It is not possible to have
100% of the bacteria
containing the recombinant
DNA.
In order to avoid competition
a specific antibiotic is used.
The recombinant DNA
besides having the desired
gene, it has a gene that
makes the bacteria
resistant to a specific
antibiotic.
Only colonies having the recombinant DNA
survive and reproduce.