



















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
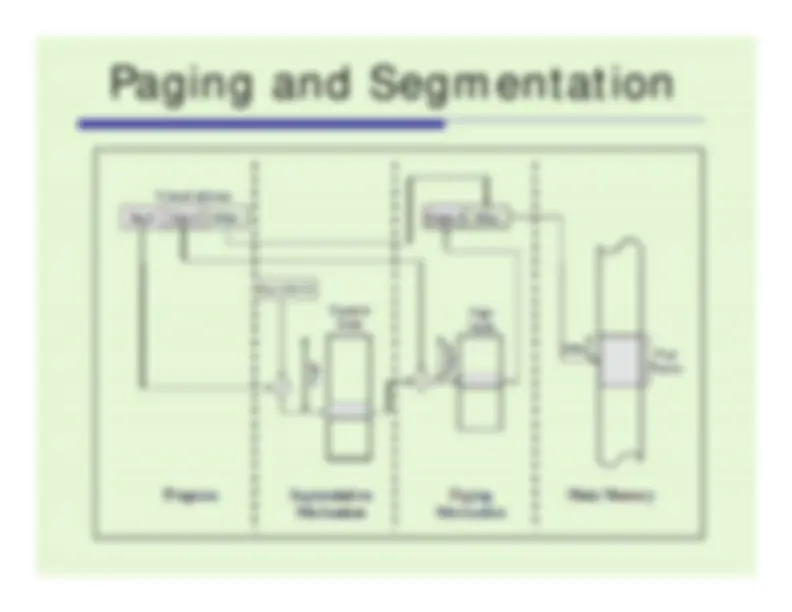
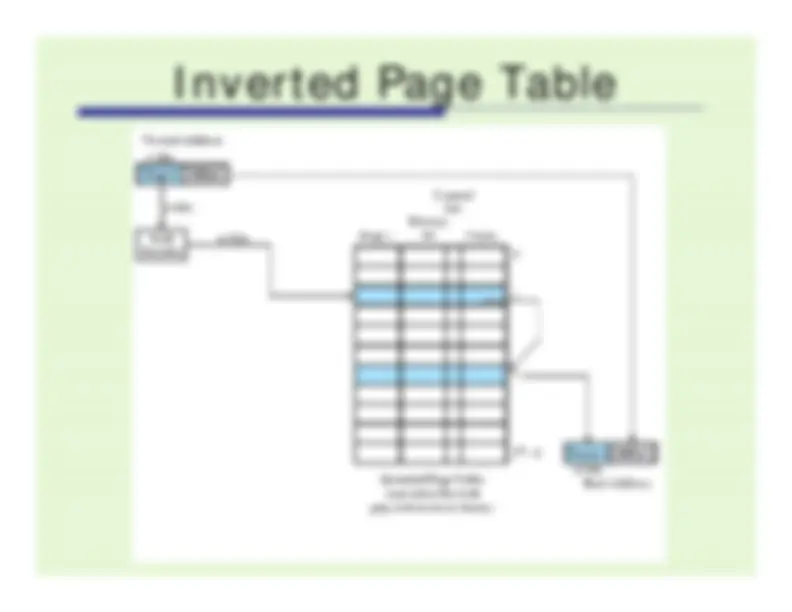
An in-depth exploration of paging and segmentation concepts in operating systems. It covers the basics of paging, including page and frame sizes, page table data structures, and page fault handling. Segmentation is also discussed, including the advantages of segmentation and the logical address to physical address translation process.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 37

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!






























titi
i^
t^
ll^
l fi
d
i^
h
k
no external
internal only in last page of a process
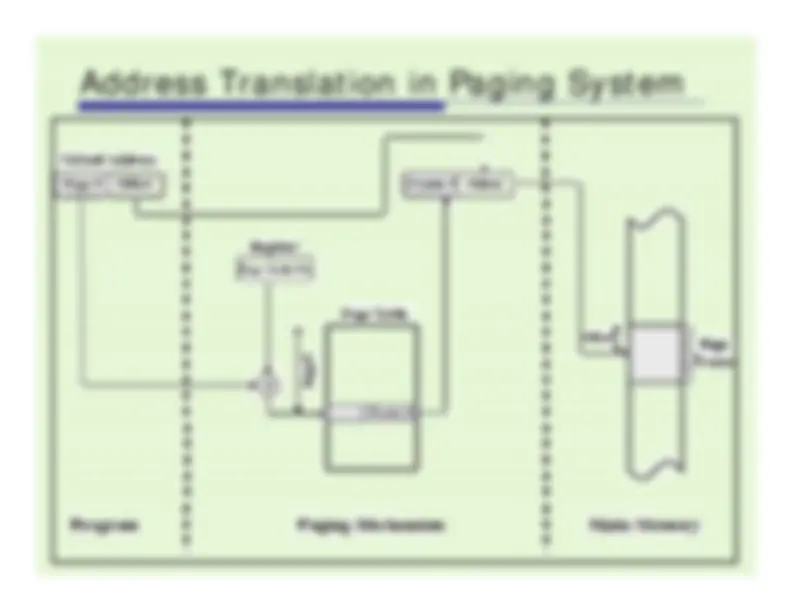
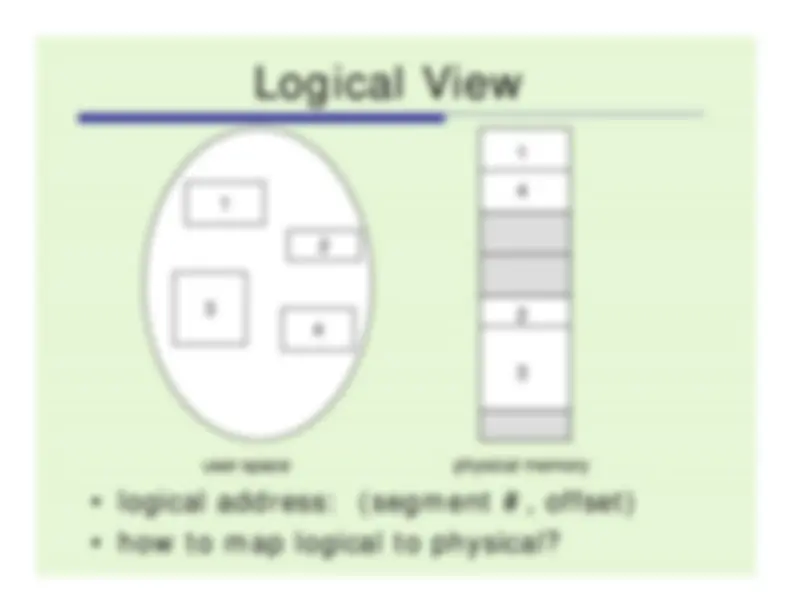
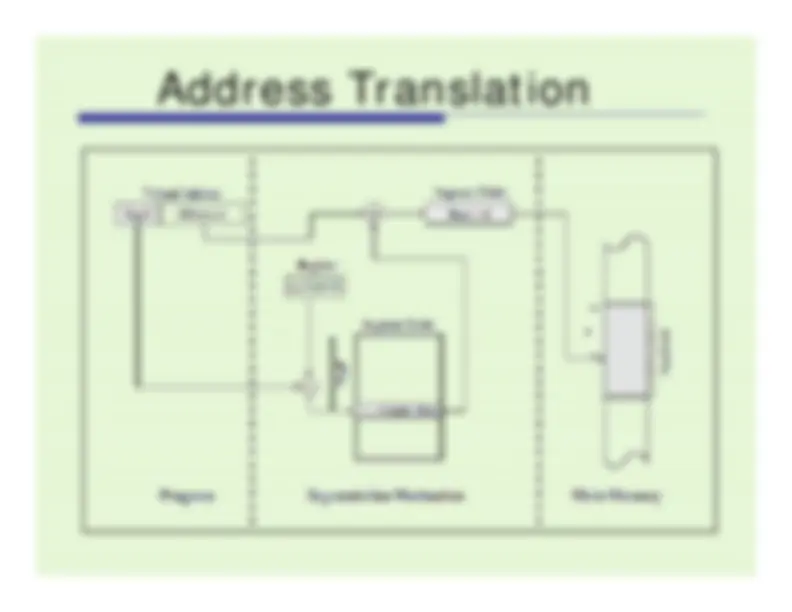
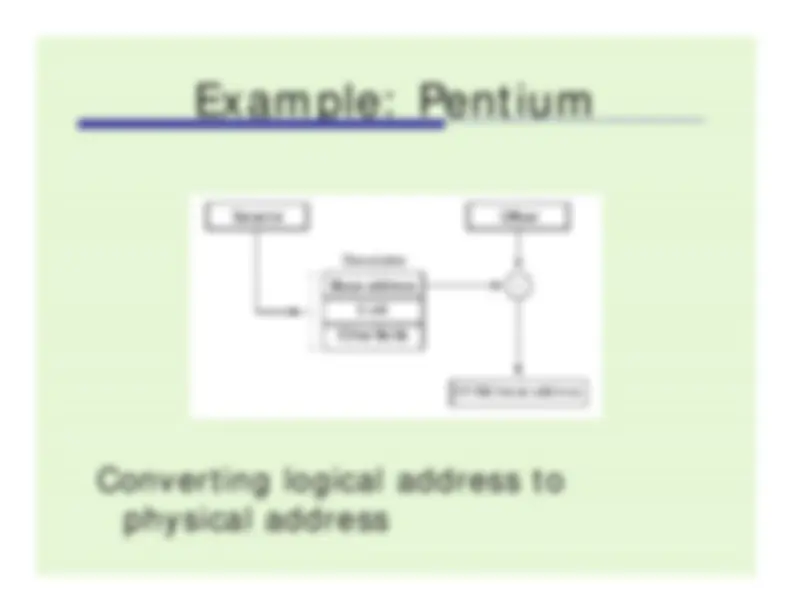
Address Translation in Paging System
never changes during execution
associative memory: fast!
f^
t i
d
i kl
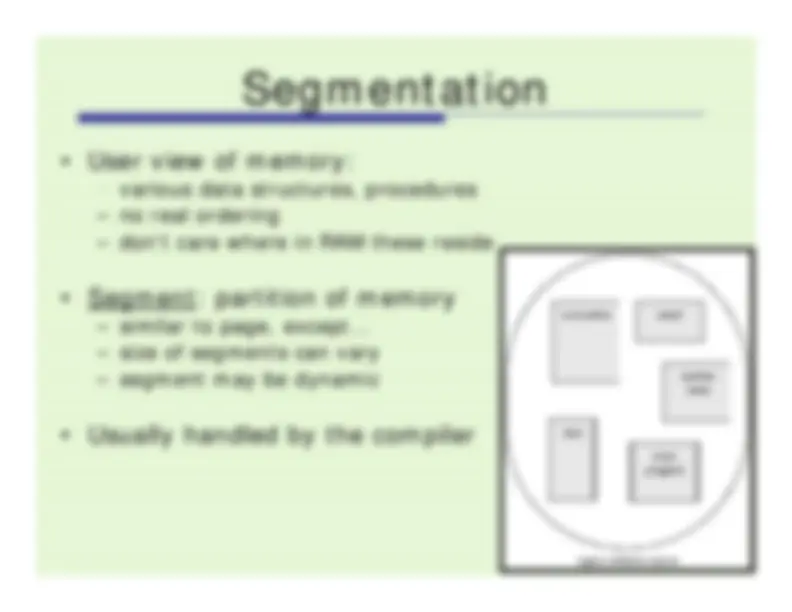
procedures
various data structures, procedures
f
rarely know size a priori
no need to relink/reload entire set
gives starting physical address of segment
compare offset (rightmost
m
bits) to length
if >, invalid address!
physical address = base + offsetphysical address
base + offset
e.g.: address 4848
in binary: 0001 | 001011110000
(logical address)
in binary: 0001 | 001011110000
(logical address)
compare offset with length in entry 1 of segment table;then add offset to base from entry 1 of segment table
then add offset to base from entry 1 of segment table