
























































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
An overview of game theory, focusing on static and dynamic games, auctions, and equilibria. It covers concepts such as actions, strategies, payoffs, dominant strategies, dominated strategies, and Nash equilibria. The document also discusses the difference between pure and mixed strategies and how to find the mixed strategy. It includes examples of the prisoner's dilemma, iterated deletion of dominated strategies, and the matching pennies game.
What you will learn
Typology: Lecture notes
1 / 64

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!

























































Lecture 8
Reading: Perlo§ Chapter 13
August 2015
Game theory is the study of strategic interaction. Game theory is applicable in so many Öelds other than economics. Evolutionary biology, international relations, whether or not to open the door for the old lady behind you.
A game is a situation in which your payo§ depends not only on what you do, but what the others do. Tick-tack-toe, whether or not to under price a rival Örm, or to cut carbon emissions are all games.
An action is a move you can make at a stage in a game. Cut emissions or donít cut emissions are actions. A strategy is a plan conditional on any possible contingency. Cut emissions if everybody else cuts emissions, donít otherwise is a strategy. An equilibrium is a set of strategies such that neither player wishes to deviate.
Consider the game rock-paper-scissors. Is this a static or a dynamic game? What are the actions and the strategies in this game?
It is useful to summarize a game using normal-form representation. We show the players, their strategies and the payo§ as a combination of strategies in a payo§ matrix. It is just the summary of the game using a table.
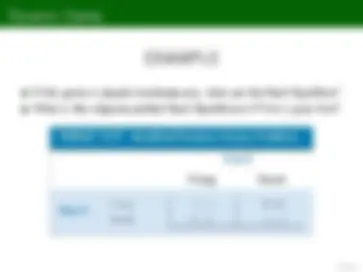
The row playerís payo§s are written Örst, and the column playerís payo§s are written second
Nick Silent Betray Tom Silent -1,-1 -12, 0 Betray 0, -12 -3, -
Sometimes players will have a dominant strategy A dominant strategy is a strategy that produces a higher payo§ than any other possible strategy. No matter what your opponent might do, you play the dominant strategy.
Do either players have a dominant strategy? Is there a dominant strategy equilibrium?
Column Left Right Row Up 2,4 10, Down 1,1 9,-
In many games, the players donít have a dominant strategy. But players might have dominated strategies. A dominated strategy is a strategy the players will never play, so we can delete them. Denying the crime is a dominated strategy in the prisonerís dilemma.
Consider the following game.
Player 2 Left Middle Right Player 1 Up 1,0 1,2 0, Down 0,3 0,1 2,
Player 2 will never play Right. Player 1 can eliminate Right from the game.
Player 2 Left Middle Player 1 Up 1,0 1, Down 0,3 0,
Player 1 will never play Down. Player 2 can eliminate down. Keep going and we are left with only fup, middleg. This is called iterated deletion of dominated strategies.
There are no dominant or dominated strategies in this game. We need to have something stronger.
Nick Right Left Stranger Right 5,5 -5, 0 Left -5,0 5, 5
We can look at best responses. A best response is a best strategy given what you think the other player will do. A dominant strategy is one that is a best response to all possible strategies.