









Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
30 slides covering biology lab 6
Typology: Slides
1 / 16

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!










Stamen and Carpel
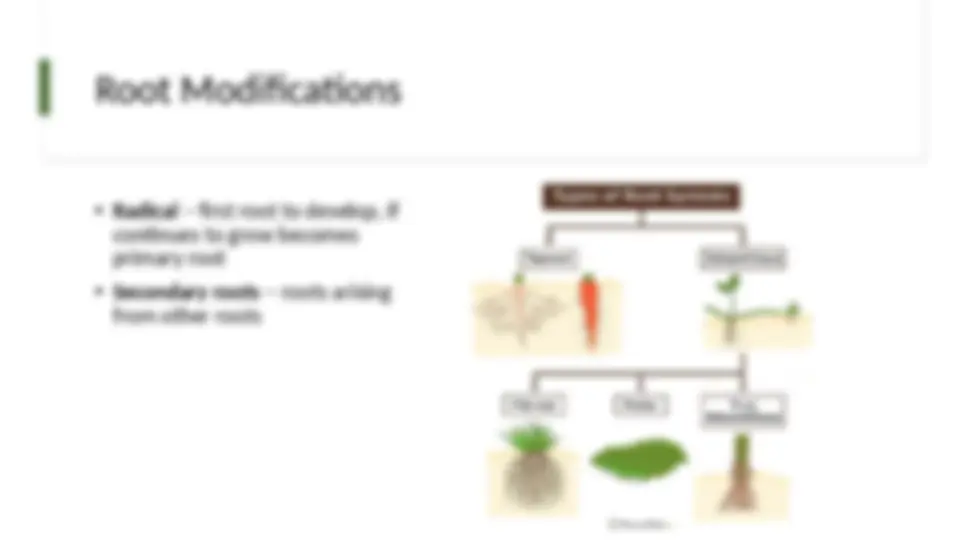
Monocots: monophyletic, stem is atactostele not eustele, parallel venation Eudicots: paraphyletic, tricolpate pollen grains
shoot with some stem and roots, majority fleshy storage leaves shoot with lots of stem tissue and small leaves stem that is horizontal under or on the ground with scaly leaves flattened photosynthetic stem
Thorn : sharp pointed stem or shoot Spine : which is a sharp-pointed leaf or leaf part Prickle: a sharp-pointed epidermal structure found anywhere on the plant