




Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Instructions for conducting lab experiments on series and parallel circuits, resistances, and ohm's law. Students are asked to make measurements using a multimeter and record potential differences and resistances. The document also includes instructions for calculating resistance and creating graphs.
Typology: Lab Reports
1 / 6

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




General Physics 2 Lab 6: Circuits Siena College
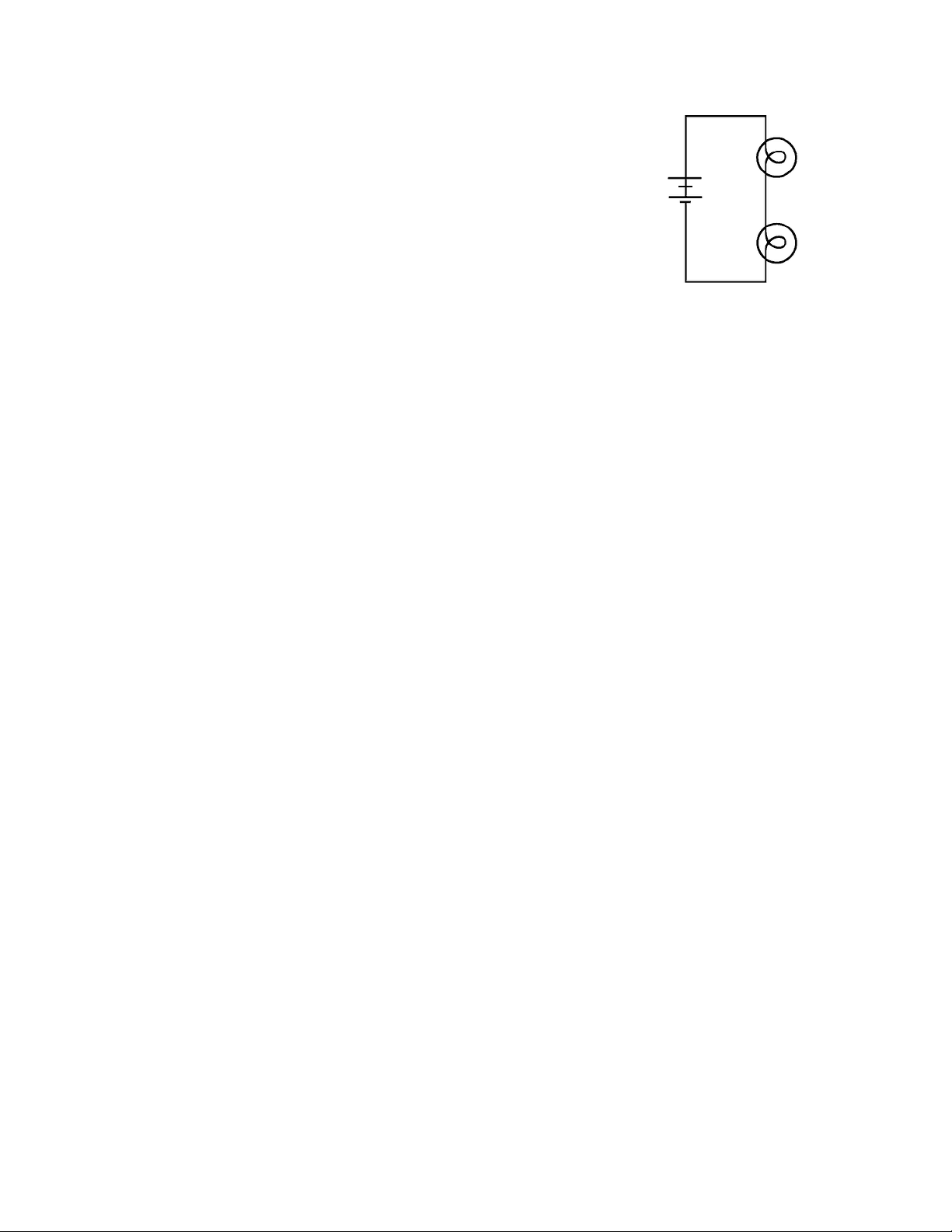
Connect the circuit shown in the figure at the right, which consists of two batteries connected to two bulbs in series.
Predict how the potential difference across the battery will compare with the potential difference across the series combination of bulbs.
Using your multimeter to measure potential differences, make the following measurements:
Potential difference across batteries: __________
Potential difference across both bulbs: __________
How do the two potential differences compare? Did your observations agree with your prediction?
Assuming two bulbs are identical, predict how the potential difference across each bulb will compare to the potential difference across the battery.
Measure the potential difference across each bulb:
Potential difference across bulb 1: __________
Potential difference across bulb 2: __________
Did your measurements agree with your predictions? Discuss any discrepancies.
Formulate a rule for how potential differences across individual bulbs in a series connection combine to give the total potential difference across the series combination of the bulbs. How is this related to the potential difference across the battery?
Connect the circuit shown in the figure above, which consists of two batteries connected to two bulbs in parallel.
Predict how the potential difference across the battery will compare with the potential difference across the parallel combination of bulbs.
Using your multimeter to measure potential differences, make the following measurements:
Potential difference across batteries: __________
Potential difference across both bulbs: __________
How do the two potential differences compare? Did your observations agree with your prediction?
Predict how the potential difference across each bulb will compare to the potential difference across the battery.
Measure the potential difference across each bulb:
Potential difference across bulb 1: __________
Potential difference across bulb 2: __________
Did your measurements agree with your predictions? Discuss any discrepancies.
Formulate a rule for how potential differences across the different branches of a parallel circuit. How are these related to the potential difference across the battery?
The figure to the right shows the circuit that will be used in this part of
voltage, to the circuit and R is either a light bulb or a resistor.
The emf source we are using is called a DC power supply. Your instructor will explain how to use this device to power the circuit in the figure.
Make sure your power supply is off. Then connect one of the brown, cylindrical resistors in the circuit. The resistor should have four colored bands painted on it in this order: red, red, brown, gold. Turn both current knobs all the way down and turn both voltage knobs all the way up. Set the AMPS button for the LO setting (button depressed) and set the display switch to read AMPS.
Turn your power supply on. Using the fine current adjustment knob, increase the current, i , from 0 to 0.080 amps in ten (10) steps. Record the current, i , and voltage, V , at each step.
Voltage (V) Current (A)
Now enter the readings in an Excel spreadsheet. On the spreadsheet calculate the resistance of the bulb, R = V / i , for each data point. Produce a plot of the voltage versus current, V vs. i , and resistance versus current, R vs. i.
Provide a sketch of these graphs below for the resistor. Be sure to label the axes. Indicate the values of the highest and lowest values of resistance calculated.
Turn the current knobs all the way down. Substitute a light bulb in place of the resistor in the circuit. Using both the coarse and fine adjustment current knobs, increase the current through the light bulb to a maximum of 0.30 amps in steps 10 steps of 0.03 amps each. Do not increase the current beyond 0.30 amps or the light bulb will blow.
Sketch your graphs for the light bulb below:
If a graph of V vs. i is a straight line, what quantity does the slope of the line represent?
Did either of the graphs of V vs. i result in a straight line? If so, which one?
Did either the light bulb or the resistor obey Ohm’s law? If so, which one(s) and why?
What is the resistance of your resistor?
R = _________
Voltage (V) Current (A)