





















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
IP Multimedia Subsystem, IMS Registration, High Level IMS, Implicit Registration, Implicit Registration Set, Session Initiation, Private User Identity are the topics professor discussed in class.
Typology: Slides
1 / 31

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!
























Docsity.com
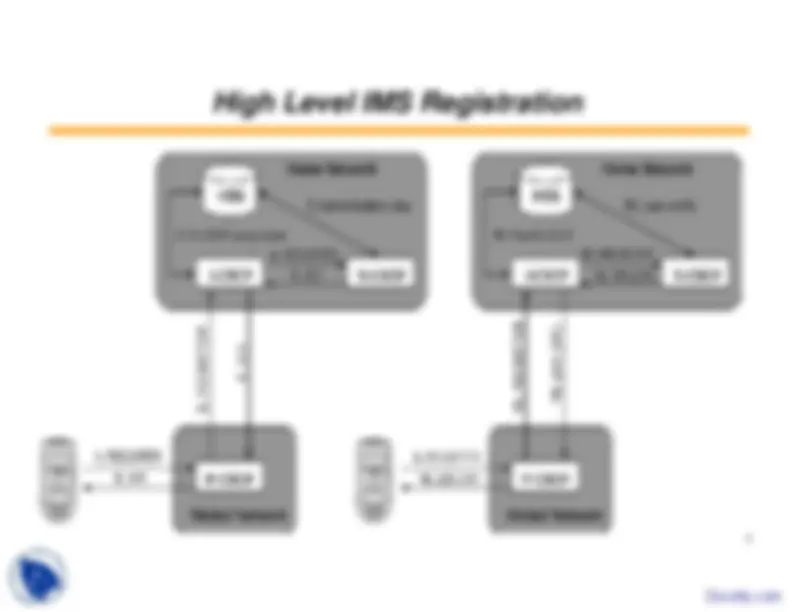
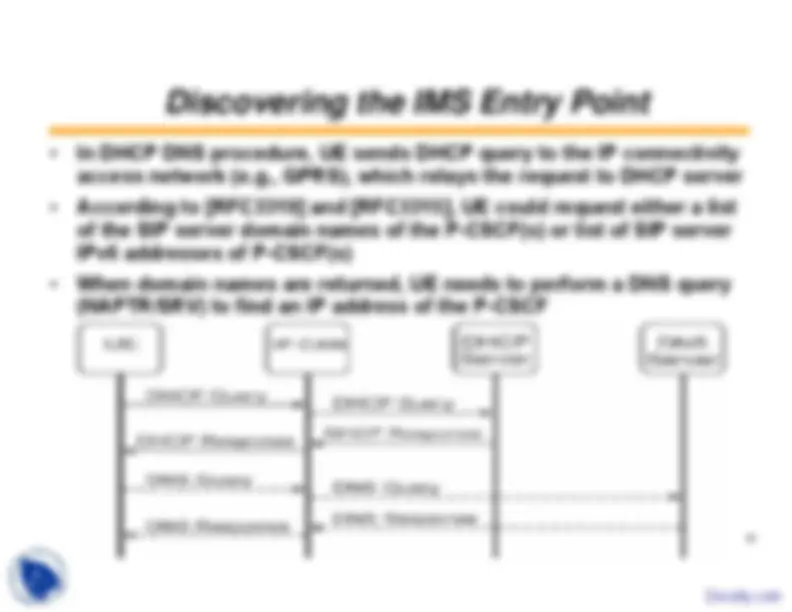
The UE must obtain an IP connectivity bearer
The UE discover an IMS entry point (i.e., the P-CSCF) - For example, in case of GPRS access the UE performs the GPRSattach procedure and activates a Packet Data Protocol (PDP)context for SIP signalling
How the network challenges the UE
How the UE responds to the challenge and completes theregistration
Docsity.com
Docsity.com
Docsity.com
Docsity.com
For example, a user has four public user identities that aregrouped in two implicit registration sets
When Joe sends a REGISTER request containingjoe.smith@brandnewcar.com as an identity to be registered - The S-CSCF downloads the service profiles that are associatedwith the public user identities belonging to the implicit registrationset (service profile 1)
Docsity.com
Docsity.com
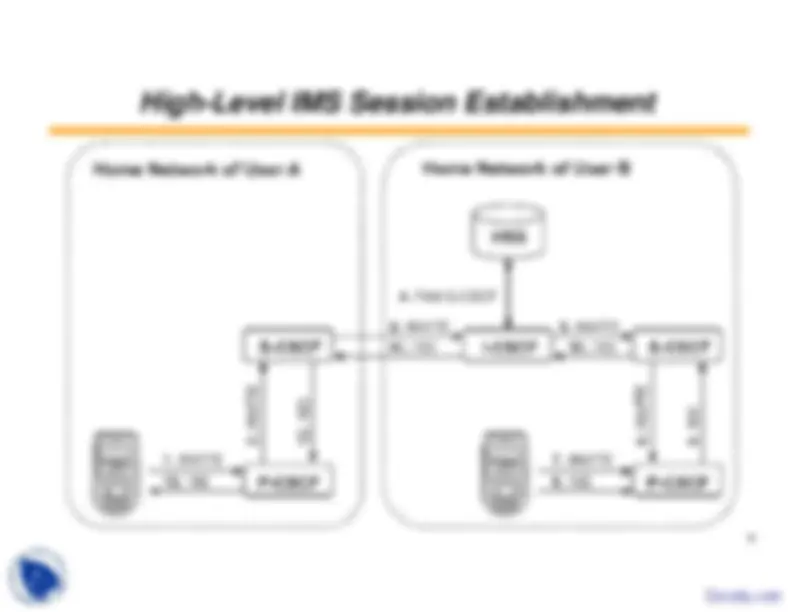
interactions with ASs
delivers the request to the P-CSCF over the Mw reference point
183 Session Progress – which traverses back to UE A followingthe route that was created on the way from UE A
both sets of UE complete session establishment
able to start the actual application Docsity.com
S-CSCF will need to obtain and store the private user identity onregistration and on unregistered termination
It will not be used for routing of SIP messages - It will be permanently allocated to a user - It is securely stored in IMS Service Identity Module (ISIM)application - It will be valid for the duration of the user’s subscription within thehome network - It will not be possible for the UE to modify the private user identity - HSS will need to store the private user identity - Private user identity will optionally be present in charging recordsbased on network policies Docsity.com
They are the identities used for requesting communication withother users
Public identities can be published (e.g., in phone books, Webpages, business cards) - To be reachable from the CS side, the public user identity mustconform to telecom numbering (e.g., þ358501234567) - To communicate with Internet clients, the public user identity mustconform to Internet naming (e.g., joe.doe@example.com)
The public user identity/identities will take the form of either a SIPUniform Resource Identifier (URI) or a telephone Uniform ResourceLocator (tel URL) format Docsity.com
Derivation of public and private user identities
Relationship between these identities - Identification of network entities Docsity.com
ISIM is an application residing onthe Universal Integrated CircuitCard (UICC)
The UICC is physically securedevice that can be inserted andremoved from UE - The ISIM itself stores IMS-specificsubscriber data - Stored data can be divided into sixgroups - Most of the data are needed whena user performs an IMSregistration [3GPP TS 31.103] Docsity.com
Docsity.com
Docsity.com