



Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
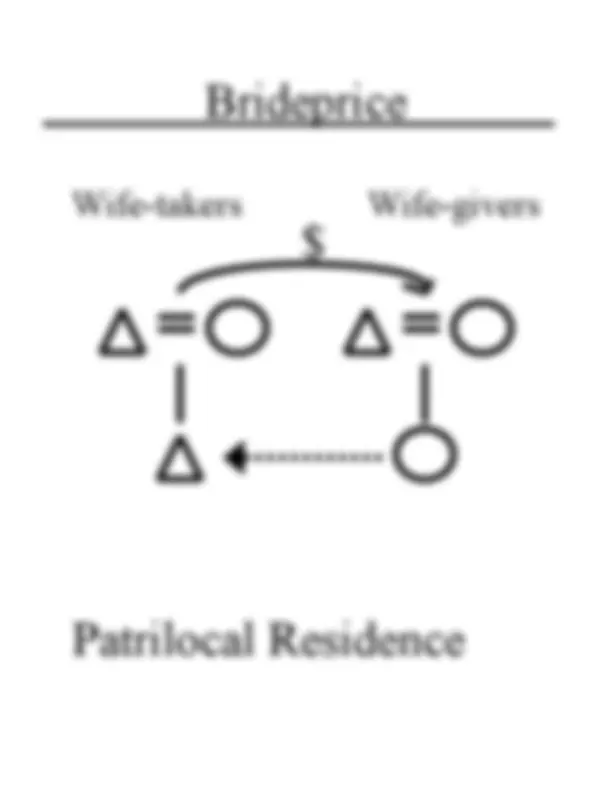
An insight into various family structures and inheritance practices discussed in a sociocultural anthropology lecture held in spring 2004. Topics include nuclear family, stem family, joint family, compound joint family, partible inheritance, per stirpes vs. Per capita division, ancestral estate, indirect dowry, wife-takers and wife-givers, and patrilocal residence. The lecture notes also cover the concepts of brideprice and balanced exchange.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 10

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!







ANT 101: Introduction to Sociocultural AnthropologySpring 2004, M,W,F 8:30 — 9:20, Chambers 2084 Prof. Eriberto P. Lozada Jr.Office: Carnegie 01 T, Th 10:00 – 11:15 am or by appointmentOffice Hours: M, W, F 10:30 – 11:30 am Telephone: 704-894-2035 (^) Web: http://www.davidson.edu/personal/erlozadaEmail: erlozada@davidson.edu Lecture Notes, 4 February 2004 Corporate Lineages, Descent, and Family Life
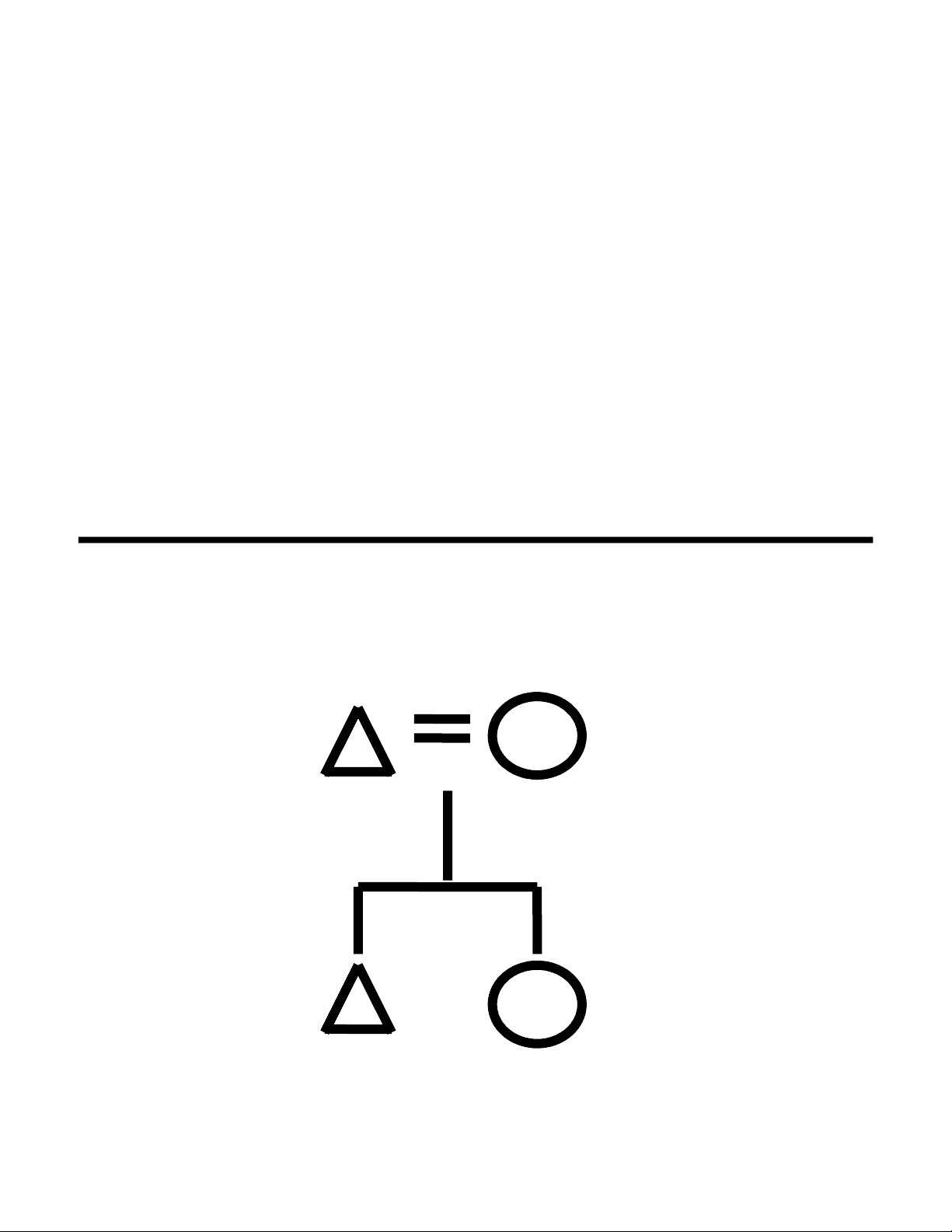
marries out
3 generation stem in patriline
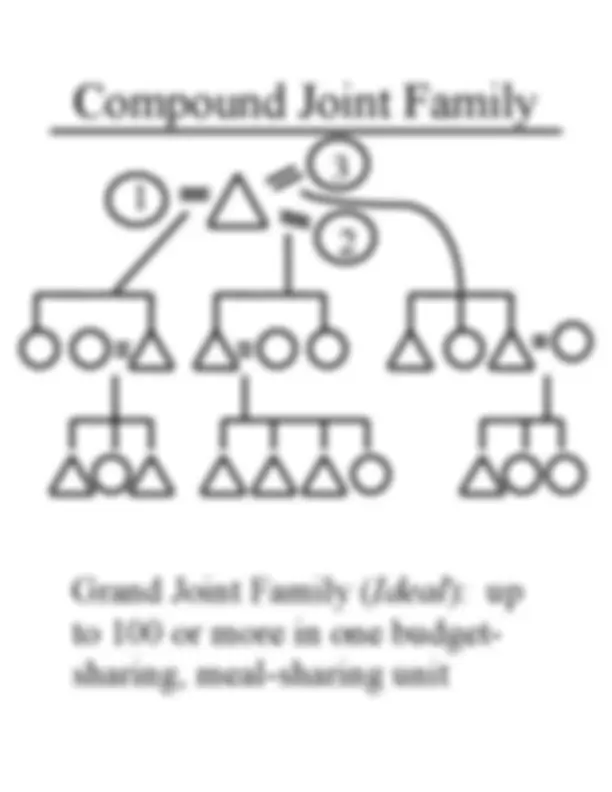
Grand Joint Family ( Ideal ): up to 100 or more in one budget- sharing, meal-sharing unit
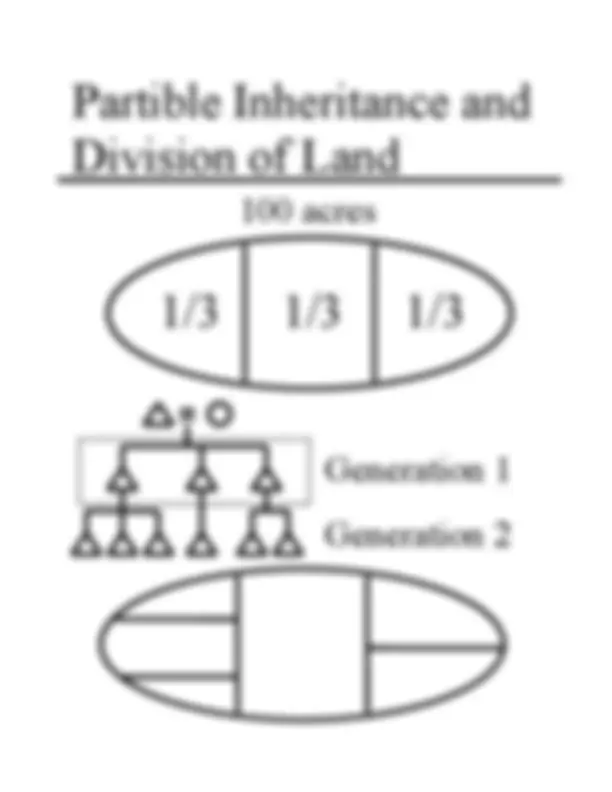
Generation 1
Generation 2
100 acres
Personal property of legitimate heirs; divided each generation by partible inheritance.
Inalienable estate managed by descendants; profits divided per stirpes. Land itself is not divided.
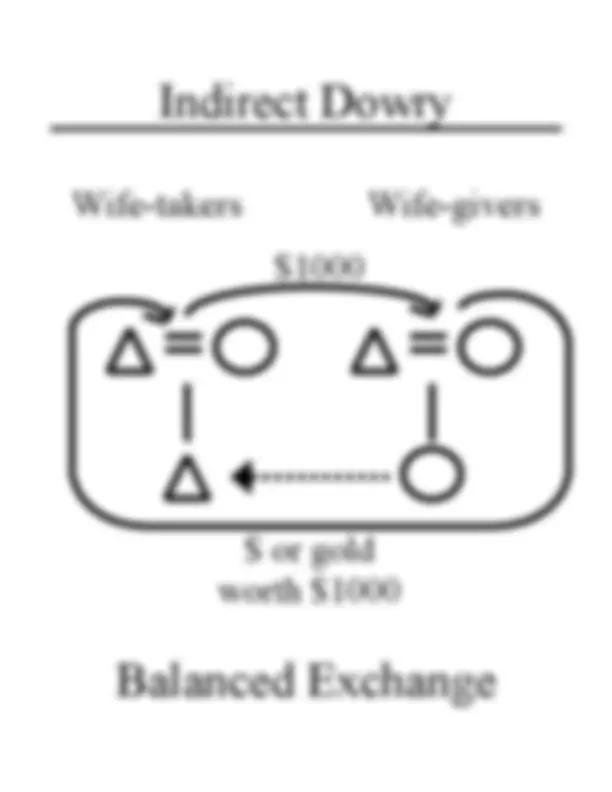
Wife-takers Wife-givers
$ or gold worth $
Wife-takers Wife-givers