

















Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
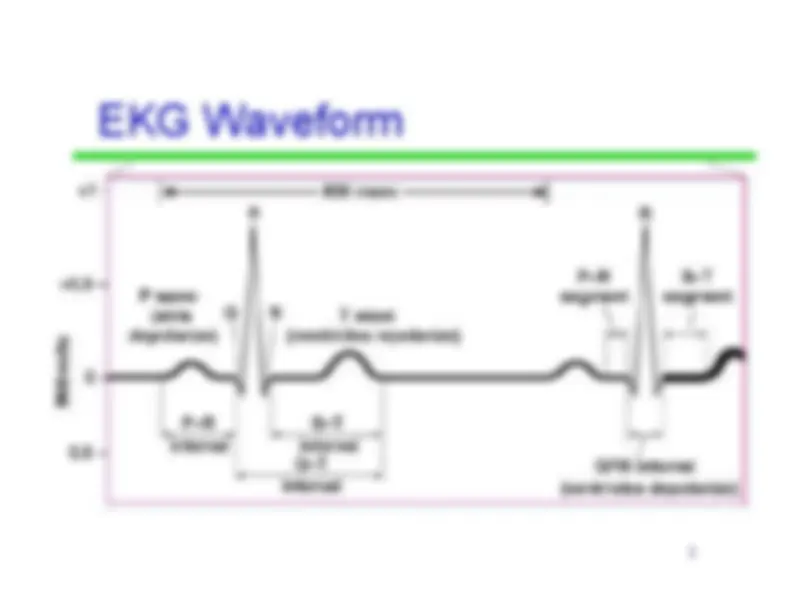
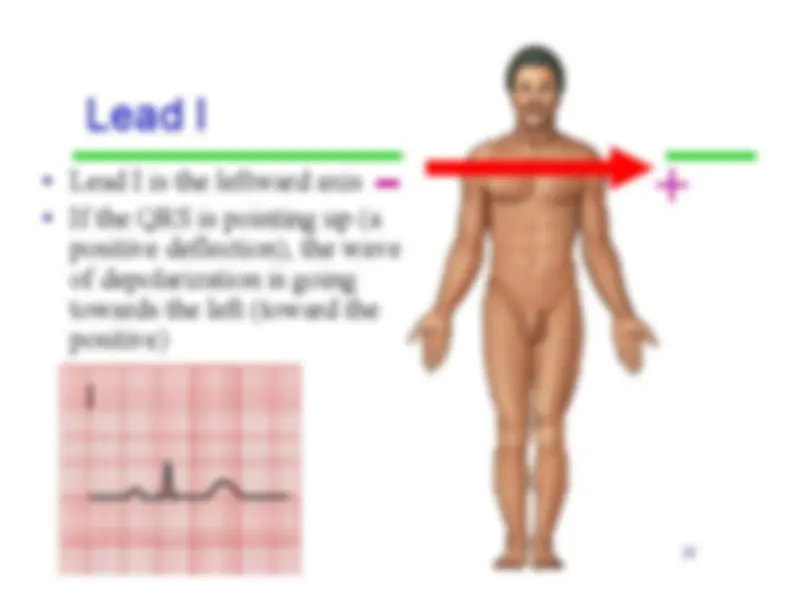
An in-depth analysis of various components of an ekg waveform, including the p wave, pr segment, pr interval, qrs complex, st segment, t wave, and qt interval. It also covers terminology related to heart rate and axis determination. Students of healthcare-related fields will find this document useful for understanding the electrical activity of the heart.
Typology: Papers
1 / 45

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!






































Portland Community College
BI 232
Reference: Dubin, Dale. Rapid Interpretation of EKG’s
th^. 6edition.
Tampa: Cover Publishing Company, 2000.
1 second
Measured from the end of the P wave to thebeginning of the QRS complex • This pause is caused by the slowdepolarization within the AV node.
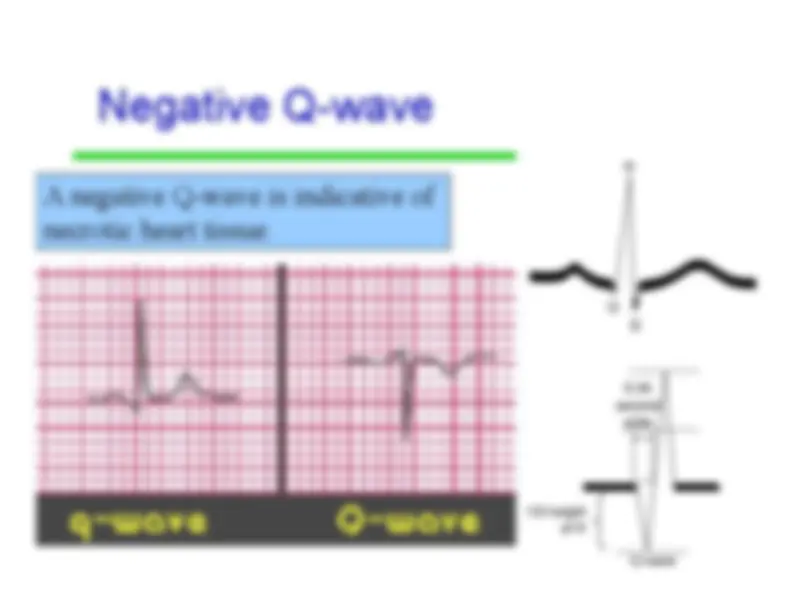
-^ Indicates ventricular depolarization, throughthe Bundle Branches and Purkinje fibers.(Starts the contraction of the ventricles) •^ Normally not longer than .10 seconds induration
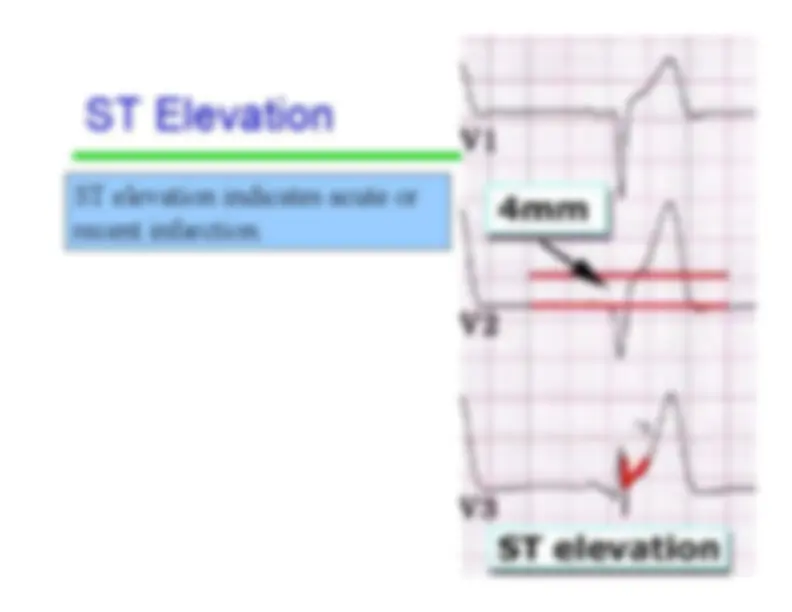
Indicates early ventricular repolarization;the plateau phase • Represents the ventricles in an activecontraction state but with no electricalactivity occurring. • The S-T segment is measured from the endof the QRS complex to the beginning of theT-wave
QRS complex occurs with each
large box
, then the R-R interval will be 0.
second, and the rate of the rhythm is
beats/minute
(i.e., 5 beats occur each second
X 60 seconds/minute = 300/minute).
, rate =
300 (
300 ÷ 1)
-^ R-R interval is 2 large boxes
, rate =
150 (
300 ÷ 2)
-^ R-R interval is 3 large boxes
, rate =
100
(300 ÷ 3)
-^ R-R interval is 4 large boxes
, rate =
75
(300 ÷ 4)
-^ R-R interval is 5 large boxes
, rate =
60
(300 ÷ 5)
-^ R-R interval is 6 large boxes
, rate =
50
(300 ÷ 6)
-^ If the R-R interval is between boxes, you just estimate or divide1500 by the number of small boxes per R-R interval.
-^ Find an R wave on a thick line, then start counting Start here: It is on a thick line
The next R wave is 2.5 large boxes away
2 boxes=150 and 3 boxes = 100So 2.5 boxes is about 120 beats/minute
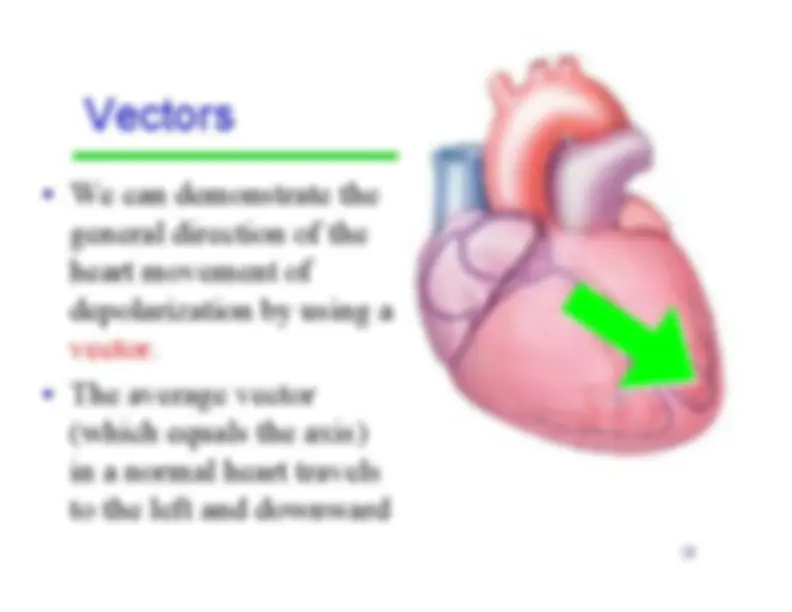
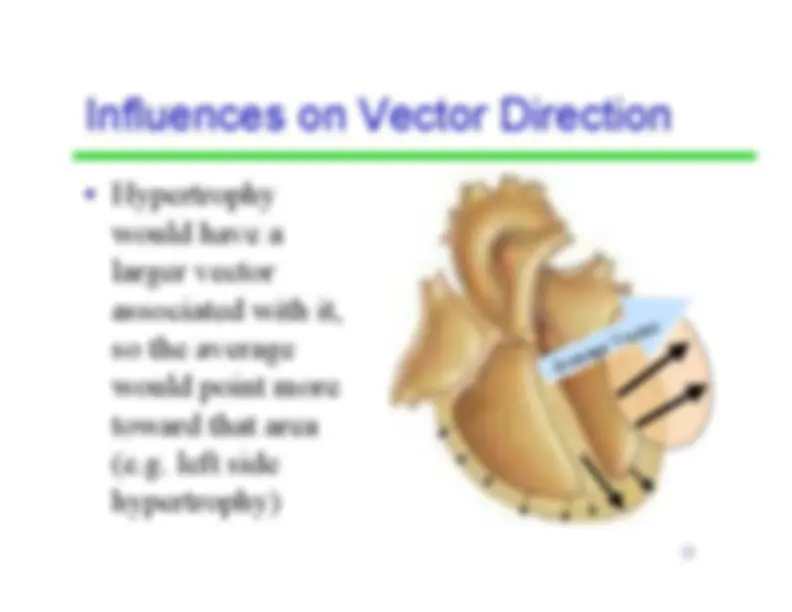
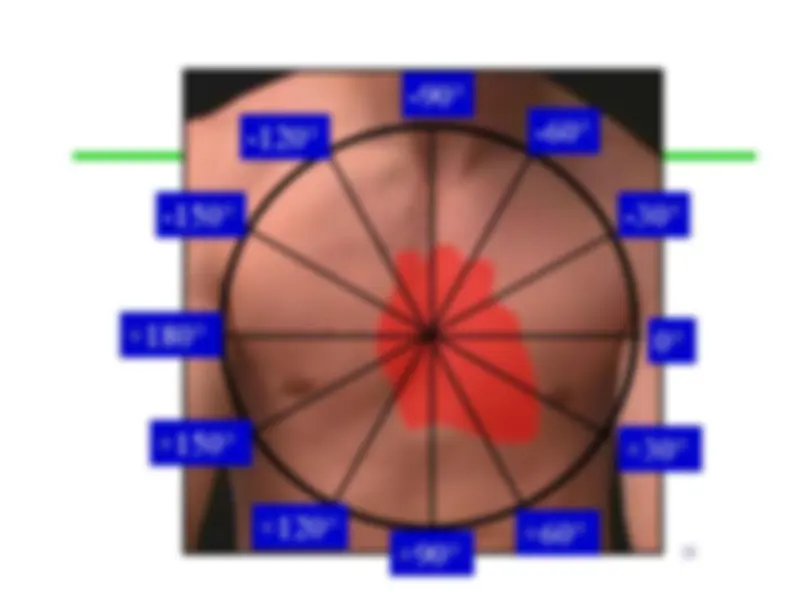
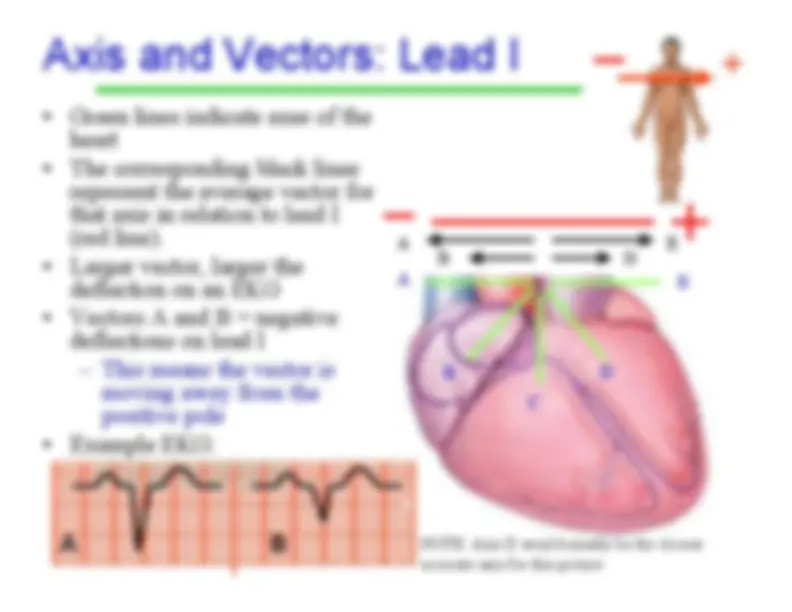
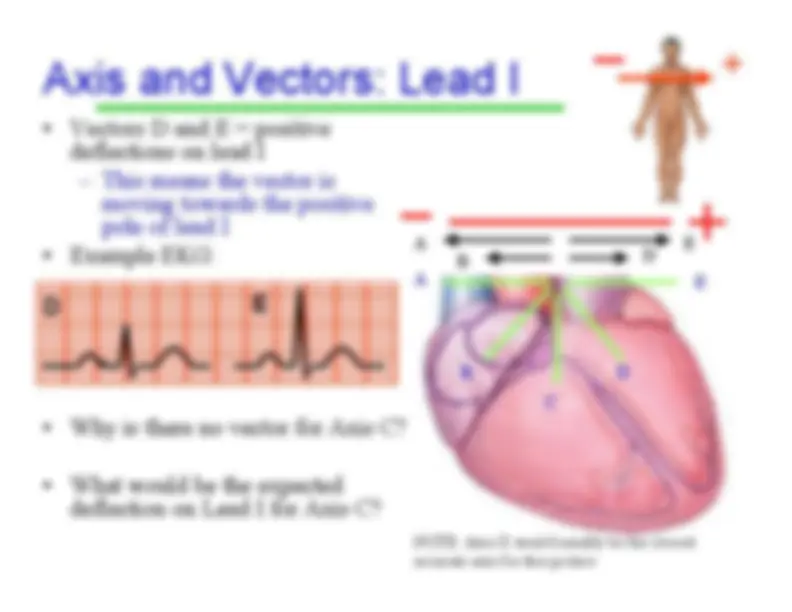
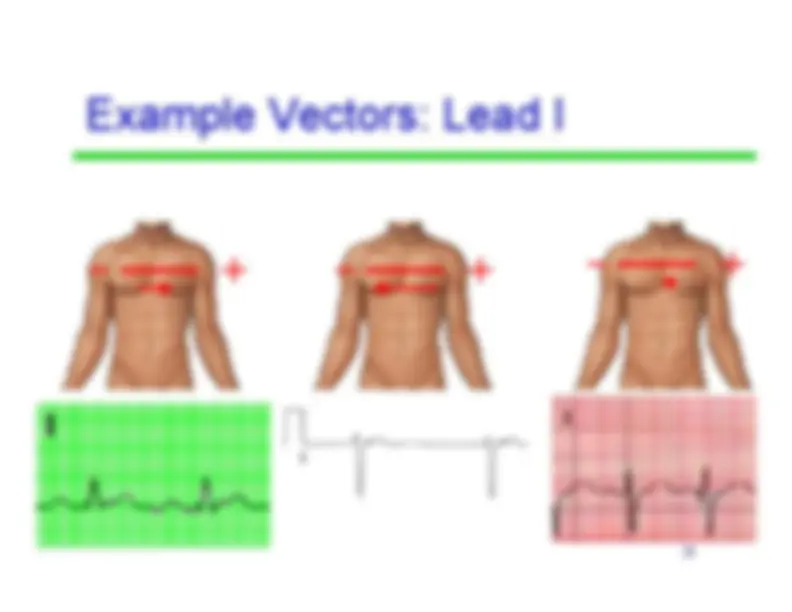
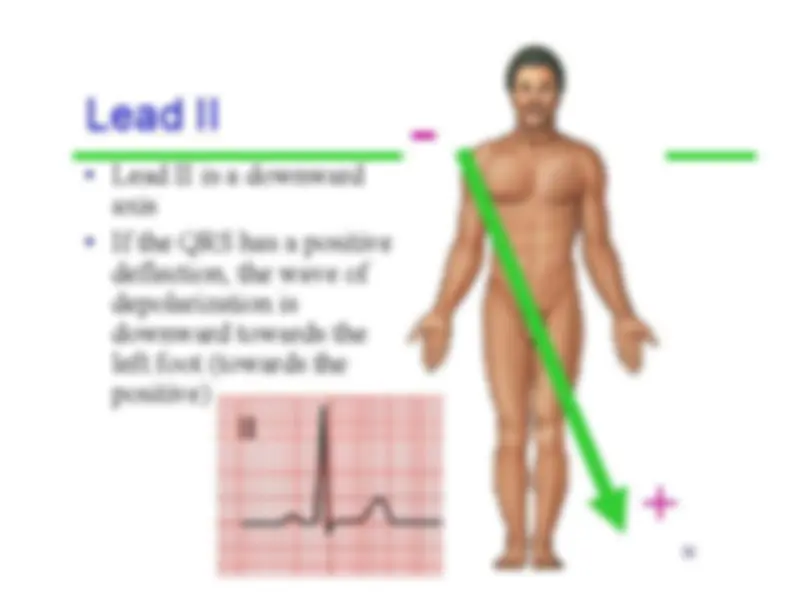
refers to the average direction ofthe movement ofdepolarization, whichspreads throughoutthe heart to stimulatethe myocardium tocontract.
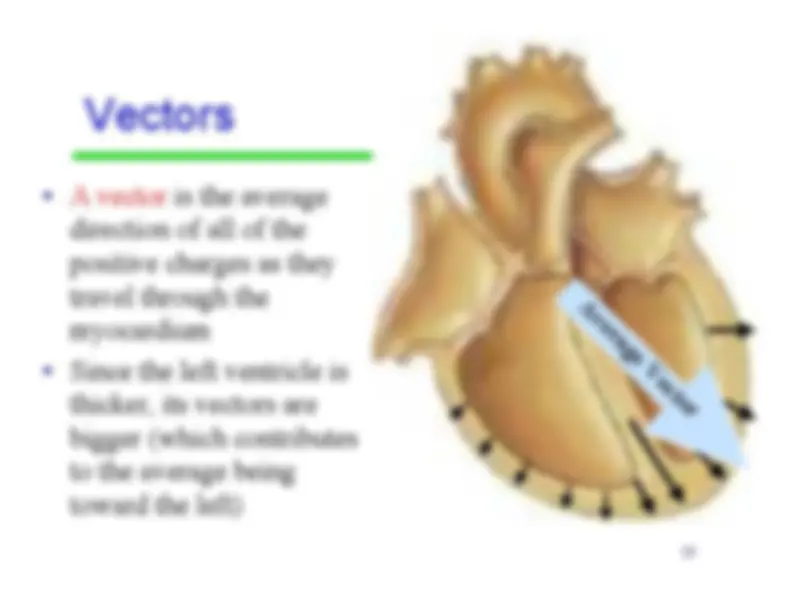
-^ A vector
is the average direction of all of thepositive charges as theytravel through themyocardium • Since the left ventricle isthicker, its vectors arebigger (which contributesto the average beingtoward the left)
Average Vector
Average Vector