









Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
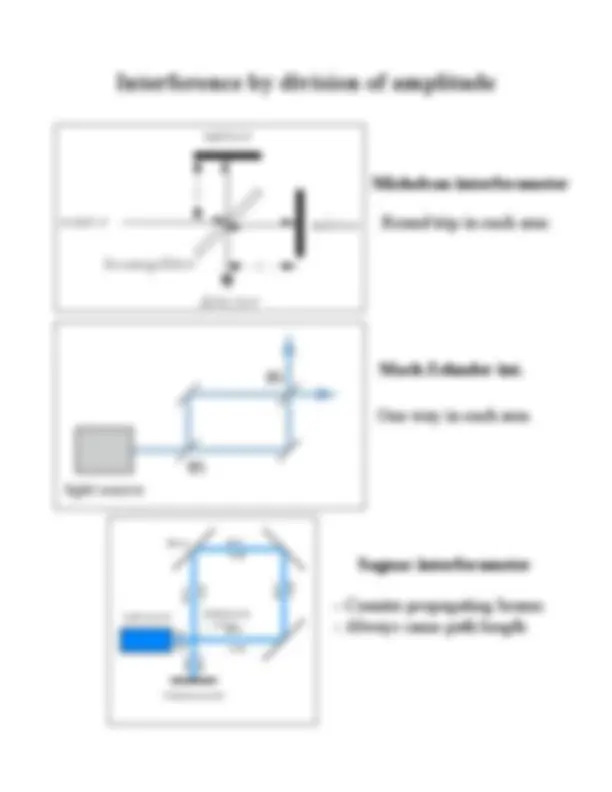
Interferometry, specifically the division of wavefront and amplitude. Topics include temporal coherence, time and spatial domain interferometry, and various interferometer types such as lloyd's mirror, michelson interferometer, and sagnac interferometer. Applications include measuring optical surface quality and characterizing nonlinear self-focusing effects.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 14

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!









\\ Gt\J ~ 6 2
II - Interferonletry by division of amplitude / Notion of temporal coherence
.--- ----;--;:>
:-[1 --r~ , t n-J \ '1~!-~-" '~:-4-~i)L. u, / N,~ <,,, ·i r, ~ f'",J ,.-t~~~ CD
CD ~~~~> ,.. ,,- 4 ~C4/t- ~ A,- ~- ')~4'-u~-t-~ ~~~k
U.",o- 2 ;, 'kj>,-",L,J 1,/--* '''~CM t,· ~L i,A'f--"': ~ NA· '-'""~ <::::
y qvvVLa 2 .,k~s _ r~~ r/~ J.._lt.. ""-"'-f'"f"<'r" ( s~-'" F,? :s, 5 r:~ ') ( s L.,., .J.:.~?)
\v' £. " .... 6 C(:: 0 [? rj ] T (^) P t- _ 'I t I ~.L'? / -- L "" - () ---~ It-'--L:--K' c\ce') t ' I)d",v-<~ ~ GeL cl t· rL iV'l L<-k I 8v.-f-!) f fee ""'-5 t 1,,, t::L S<~ :
Nc. ,rL,..;:c~ I l~ L, "1 Q.l<'te;nJ ?"k"", ''\II ik L'""'IJ('u «"',
h y" t-J :: 2 ~ c> (L J - L 1 )
JE,I;/ I~z)
2 ~ T I fT~ {.dJ /j '
T ('>vl- :::: I I (,. 0 I -I- 0? C. c':> IJ Cf )
lIlT (^) I
J.2 I - 0 SI 2 ' (I Z.
~J- J'- ~-- ~~~--0r-~-~c~ __'Sr:~-J2:c-'~(' 1
klc- t-)~ (&'"vt~cJ: U -- L ·,:~C l (~
f~ lA-JR Cj Y.; T^ I^ tf^ ')^ _ 1=
~..- ~ f; := 0 ~
, -----;,^ fj)!;; "-^.^ tv,"^ ~~^ x.~.^ J^ cf^ f'~r~^ ;
[ t, cr ()' ,) .. /j 'f (y, ) J« 2 TI
2'-1 bV.l- 2 <c::: ZIT
2
Ij-'--=: c{
cJ W'('-d 1" ~ jU f~d?-
~--.- ~ L c
-II \h.X JJ-I<-dL-:v.- ;tI'J-~f~-(' ~ ~{ '6,-(17"-) bC4..c t S dY'-(' cP_
1(' '- "») (^) 'z:l )
'/1 I
~
-'~'~'-""""":'<:'----~"h ~,.. £: "- c ~ I..J
t" elJ T
t- l
d!.,L,
1 tj C( bL'~---~-;l (L l
(
---~----- IF (^) • , 2 f-^ t; L, (^7) 'r- 'jo..J '., .... ,Zf:.ol l (^) c:: / .. (^) J~ - )
Interference by division of wavefront
Figure 3.3 Fowles
Lloyd’s mirror
Fresnel’s mirrors
Fresnel’s biprism
Add 10 μm delay on one beam
Spatial fringes taken with a CCD I(x,y)
Add 10 μm delay on one beam
The beams can’t interfere anymore, as the delay is larger than the temporal coherence of the laser
Delay = 0
Time-domain interferometry
Spatial domain interferometry
laser
laser
θ
Photodiode Measure I at given time delay t
Record I(x,y)
Interferometric autocorrelator Devices for measuring the intensity or field autocorrelation function of light, mostly used for determining the duration of ultrashort pulses
Wavelength
Space
Aberration-free
BS^ MR R=90%
2D Imaging Spectrometer CCD
50 fs / 1 mJ
BS R=90%
Sapphire plate
λ
r
Femtosecond laser pulse 50 fs
With nonlinear effect
Characterization of nonlinear self-focusing effect (Here at Mines. With Pr. Chip Durfee)
Spatio-spectral phase ϕ(r,λ)
Spatio-temporal laser intensity I(r,t) after nonlinear propagation