

































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
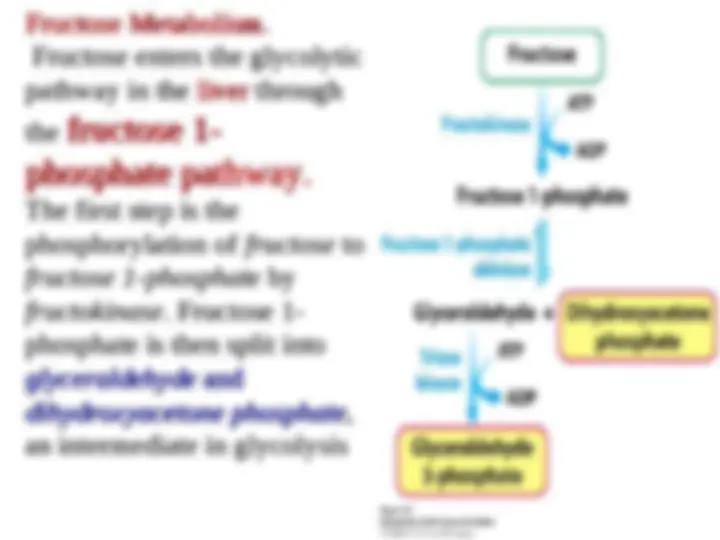
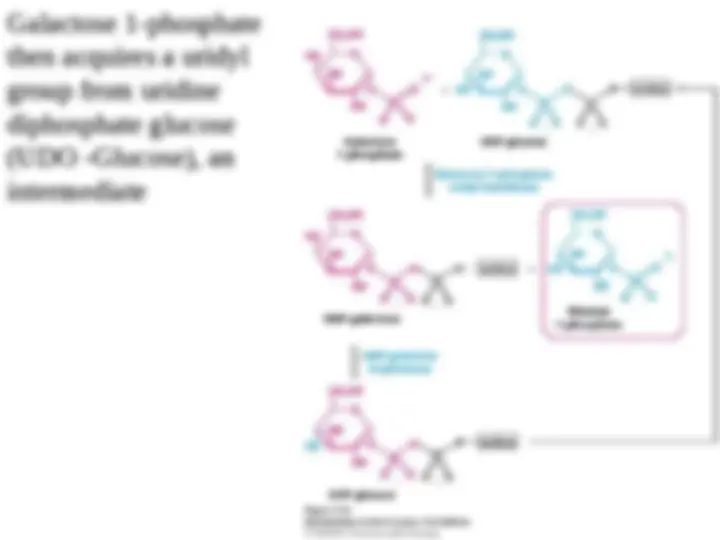
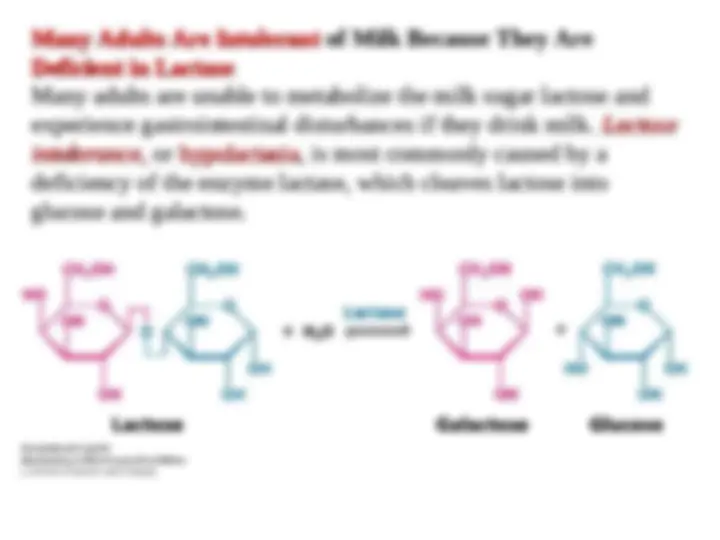
An in-depth look into the three stages of glycolysis, a process that converts glucose into pyruvate. Each stage consists of several steps, including phosphorylation, isomerization, and the formation of key intermediates. The document also discusses the role of important enzymes such as hexokinase, triose phosphate isomerase, and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase in the process.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 61

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!






















































Tymoczko • Berg • Stryer
© 2010 W. H. Freeman and Company
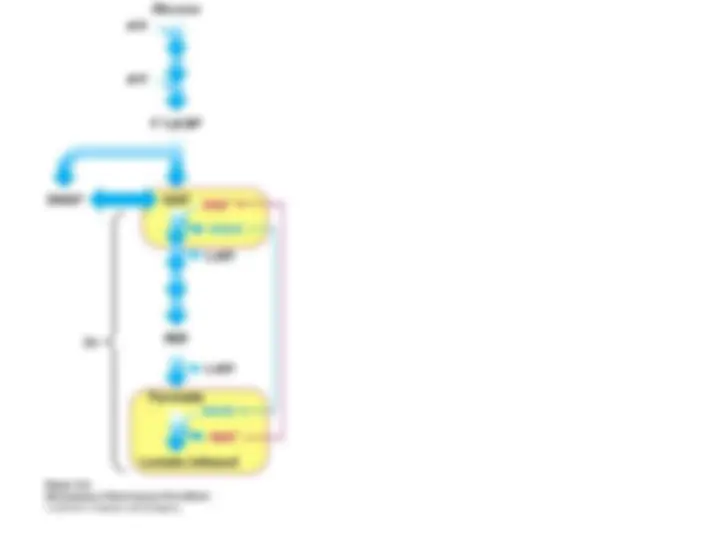
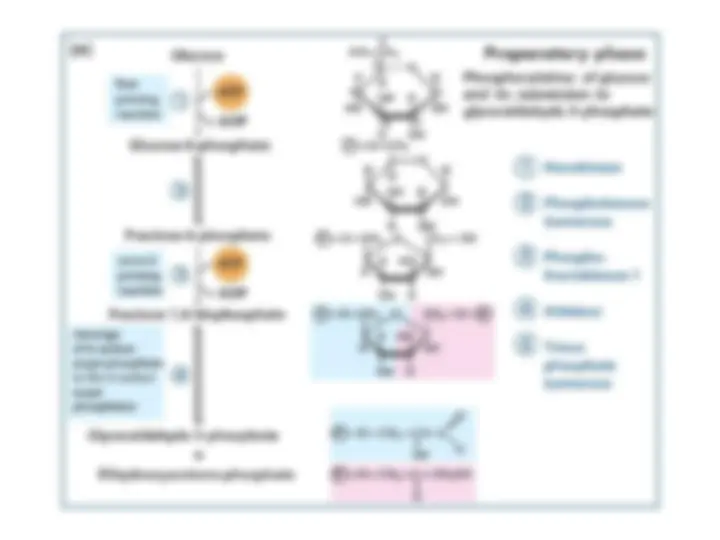
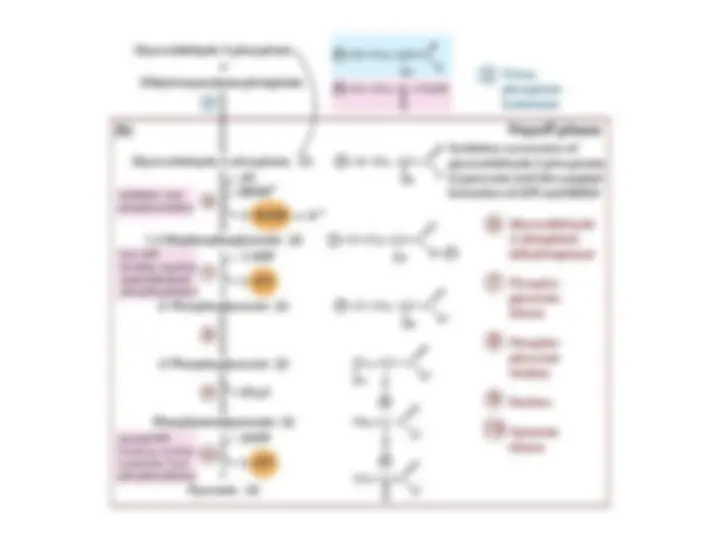
Glycolysis Is an Energy-Conversion Pathway in Many Organisms
is generated.
is generated.
Hexokinase
Hexokinase Traps Glucose in the Cell and Begins Glycolysis
Traps Glucose in the Cell and Begins Glycolysis
Glucose -
Glucose - it is phosphorylated by ATP to form glucose 6-phosphate
it is phosphorylated by ATP to form glucose 6-phosphate .
This step is notable for
This step is notable for two reasons
two reasons : (1) glucose 6-phosphate
: (1) glucose 6-phosphate
cannot diffuse through the membrane, because of its negative
cannot diffuse through the membrane, because of its negative
charges, and
charges, and
(2) the addition of the
(2) the addition of the phosphoryl group
phosphoryl group begins to
begins to destabilize
destabilize
glucose, thus
glucose, thus facilitating its further metabolism
facilitating its further metabolism .
The transfer of the phosphoryl group from
The transfer of the phosphoryl group from ATP
ATP to the
to the
hydroxyl group on carbon 6 of glucose is catalyzed by hydroxyl group on carbon 6 of glucose is catalyzed by
hexokinase
hexokinase .
.
Induced Fit
Induced Fit in
in Hexokinase
Hexokinase
. As shown in . As shown in
blue, the two lobes of hexokinase are
blue, the two lobes of hexokinase are
separated in the absence of glucose. The
separated in the absence of glucose. The
conformation of hexokinase changes
conformation of hexokinase changes
markedly on binding glucose, as shown in
markedly on binding glucose, as shown in
red. The
red. The two lobes
two lobes of the enzyme come
of the enzyme come
together and surround.
together and surround.
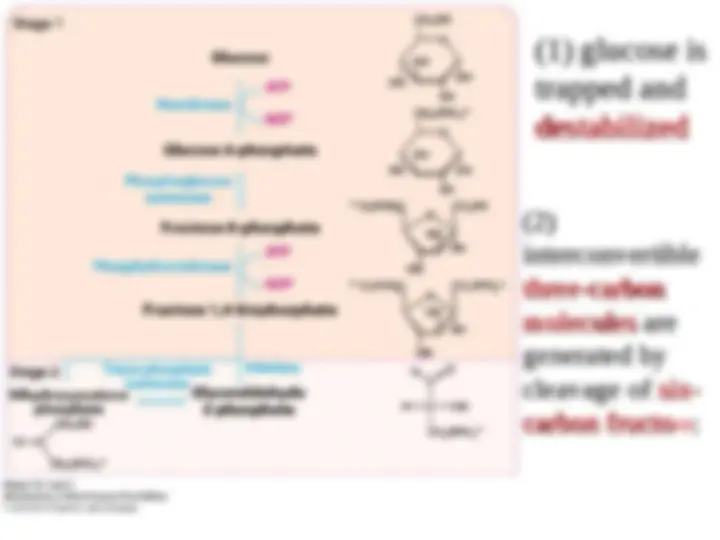
The Formation of Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate from Glucose 6-
The Formation of Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate from Glucose 6-
phosphate
phosphate
The next step in glycolysis is the
The next step in glycolysis is the isomerization of glucose 6-phosphate
isomerization of glucose 6-phosphate
to fructose 6-phosphate
to fructose 6-phosphate .
Recall that the open-chain form of glucose has an aldehyde group at
Recall that the open-chain form of glucose has an aldehyde group at
carbon 1, whereas the open-chain form of fructose has a keto group at
carbon 1, whereas the open-chain form of fructose has a keto group at
carbon 2. Thus, the
carbon 2. Thus, the isomerization of glucose 6-phosphate to fructose 6-
isomerization of glucose 6-phosphate to fructose 6-
phosphate is a
phosphate is a conversion of an aldose into a ketose
conversion of an aldose into a ketose .
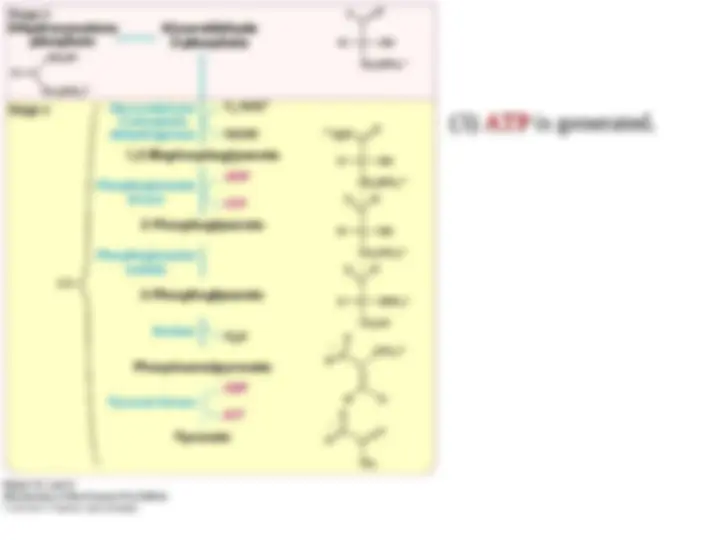
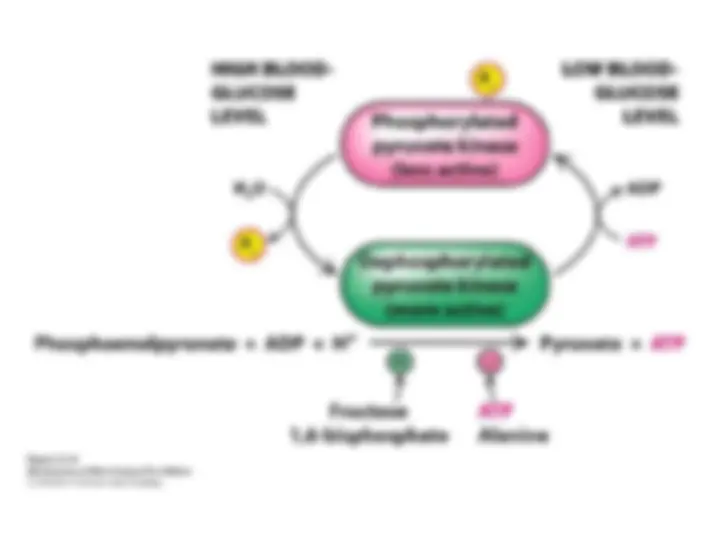
The Formation of ATP from 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate
The Formation of ATP from 1,3-Bisphosphoglycerate
The final stage in glycolysis is the generation of ATP from the
The final stage in glycolysis is the generation of ATP from the
phosphorylated three-carbon metabolites of glucose.
phosphorylated three-carbon metabolites of glucose. Phosphoglycerate
Phosphoglycerate
kinase
kinase catalyzes the
catalyzes the transfer of the phosphoryl group
transfer of the phosphoryl group from the acyl
from the acyl
phosphate of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to ADP. ATP and 3-
phosphate of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to ADP. ATP and 3-
phosphoglycerate are the products. The formation of ATP in this
phosphoglycerate are the products. The formation of ATP in this
manner is referred to as
manner is referred to as substrate-level phosphorylation
substrate-level phosphorylation because the
because the
phosphate donor,
phosphate donor, 1,3-BPG, is a substrate
1,3-BPG, is a substrate with
with high phosphoryl-transfer
high phosphoryl-transfer
potenti
potenti al.
al.
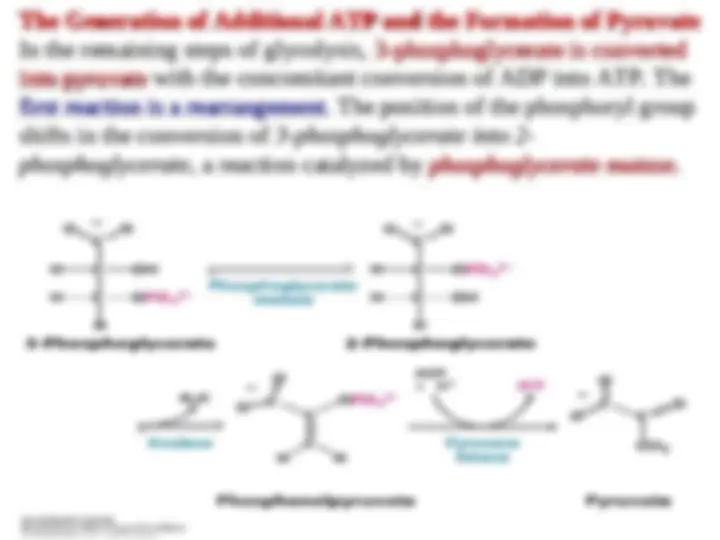
The Generation of Additional ATP and the Formation of Pyruvate
The Generation of Additional ATP and the Formation of Pyruvate
In the remaining steps of glycolysis,
In the remaining steps of glycolysis, 3-phosphoglycerate is converted
3-phosphoglycerate is converted
into pyruvate
into pyruvate with the concomitant conversion of ADP into ATP. The
with the concomitant conversion of ADP into ATP. The
first reaction is a rearrangement
first reaction is a rearrangement
. The position of the phosphoryl group . The position of the phosphoryl group
shifts in the conversion of
shifts in the conversion of 3-phosphoglycerate into 2-
3-phosphoglycerate into 2-
phosphoglycerate,
phosphoglycerate, a reaction catalyzed by
a reaction catalyzed by phosphoglycerate mutase
phosphoglycerate mutase .
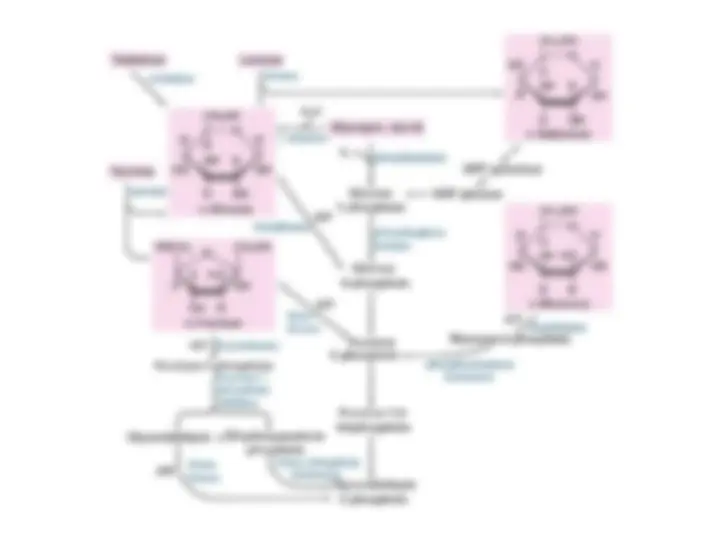
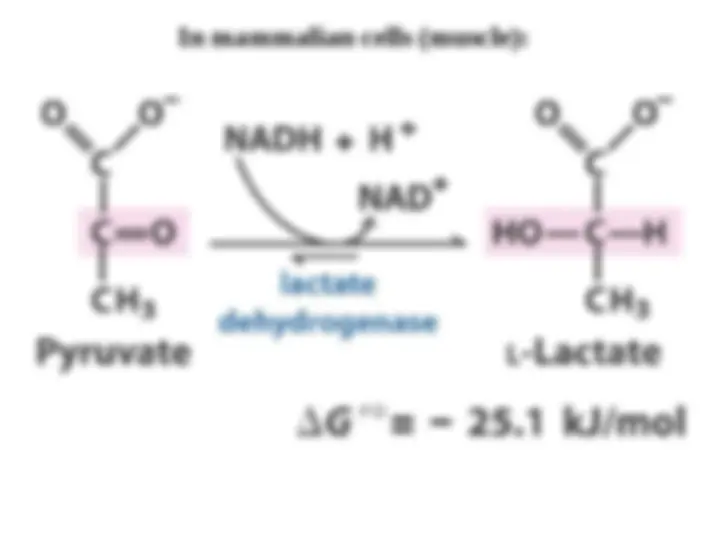
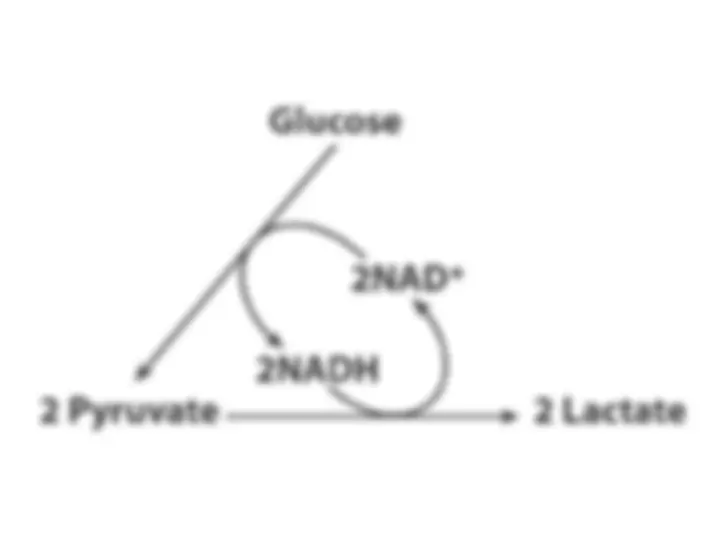
Diverse Fates
Diverse Fates of Pyruvate
of Pyruvate
. Ethanol and lactate can be formed by . Ethanol and lactate can be formed by
reactions involving NADH. Alternatively, a two-carbon unit from
reactions involving NADH. Alternatively, a two-carbon unit from
pyruvate can be coupled to coenzyme A to form
pyruvate can be coupled to coenzyme A to form acetyl CoA.
acetyl CoA.
Location of redox balance steps. The
Location of redox balance steps. The
generation and consumption of
generation and consumption of
located within the glycolytic
located within the glycolytic
pathway.
pathway.
Active Site of
Active Site of Alcohol Dehydrogenase
Alcohol Dehydrogenase
. The active site contains a . The active site contains a zinc
zinc
ion
ion bound to two cysteine residues and one histidine residue.
bound to two cysteine residues and one histidine residue. The zinc
The zinc
ion binds the
ion binds the acetaldehyde substrate through its oxygen atom
acetaldehyde substrate through its oxygen atom ,
polarizing it so that it more easily accepts a hydride
polarizing it so that it more easily accepts a hydride
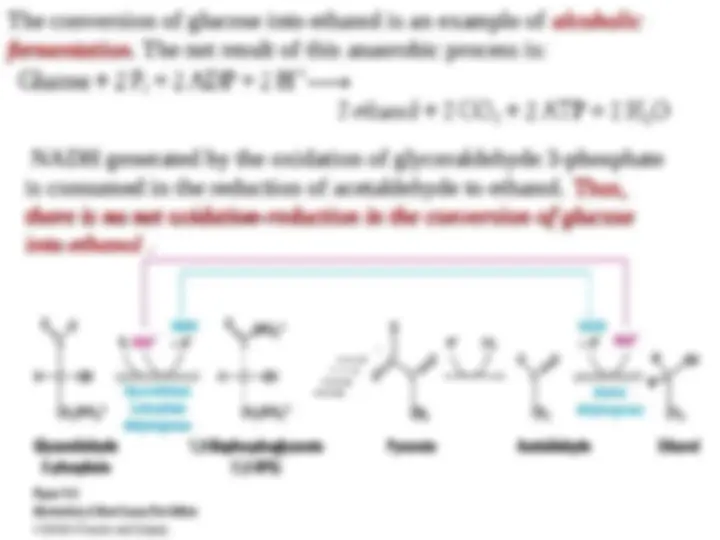
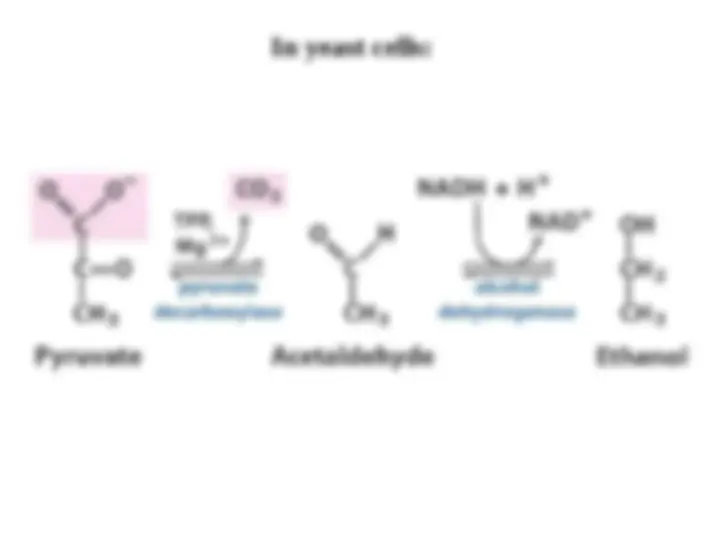
The conversion of glucose into ethanol is an example of
The conversion of glucose into ethanol is an example of alcoholic
alcoholic
fermentation
fermentation
. The net result of this anaerobic process is: . The net result of this anaerobic process is:
NADH generated by the oxidation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
NADH generated by the oxidation of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
is consumed in the reduction of acetaldehyde to ethanol.
is consumed in the reduction of acetaldehyde to ethanol. Thus,
Thus,
there is no net oxidation-reduction in the conversion of glucose
there is no net oxidation-reduction in the conversion of glucose
into ethanol
into ethanol .