Download Gluconeogenesis - Biochemistry | BIO 3390 and more Study notes Biochemistry in PDF only on Docsity!
Biochemistry: A Short CourseBiochemistry: A Short Course
First Edition First Edition
Biochemistry: A Short Course Biochemistry: A Short Course
First Edition First Edition
Tymoczko • Berg • Stryer Tymoczko • Berg • Stryer
© 2010 W. H. Freeman and Company
CHAPTER 16 CHAPTER 16
Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis
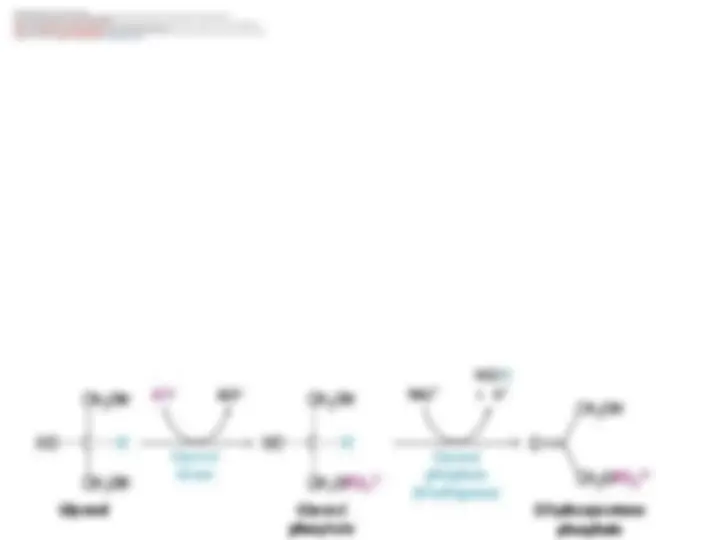
Glucose Can Be Synthesized from Noncarbohydrate PrecursorsGlucose Can Be Synthesized from Noncarbohydrate Precursors synthesis of glucose fromsynthesis of glucose from noncarbohydrate precursorsnoncarbohydrate precursors , a process called, a process called gluconeogenesisgluconeogenesis .. This metabolic pathwayThis metabolic pathway The daily glucose requirement of the brain in a human being -120 g,The daily glucose requirement of the brain in a human being -120 g, is importantis important because thebecause the brain depends on glucosebrain depends on glucose as its primary fuel andas its primary fuel and red bloodred blood cellscells use only glucose as a fueluse only glucose as a fuel.. The amount of glucose present in body fluids -20 g, and that readily available fromThe amount of glucose present in body fluids -20 g, and that readily available from During a longer period ofDuring a longer period of starvationstarvation, glucose must be formed from, glucose must be formed from noncarbohydrate sourcesnoncarbohydrate sources glycogen, a storageglycogen, a storage form of glucose. direct glucose reserves are sufficient to meet glucose needs for about aform of glucose. direct glucose reserves are sufficient to meet glucose needs for about a day.day.
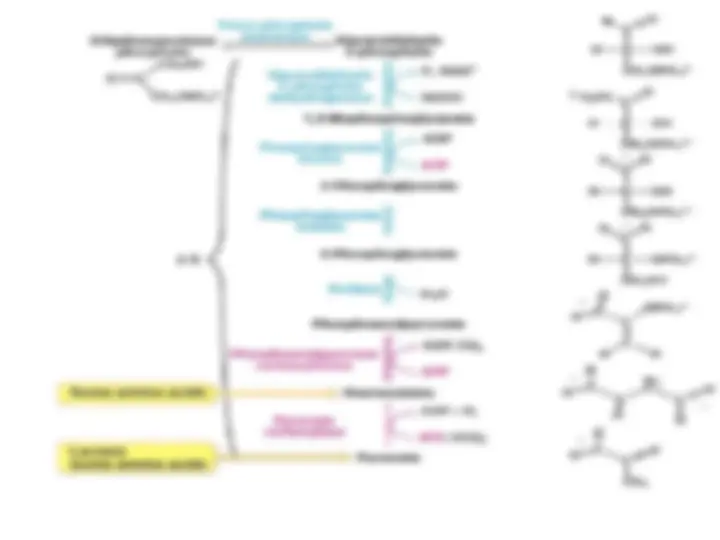
Pathway of Gluconeogenesis. The distinctive reactions and enzymes of this pathway are shownPathway of Gluconeogenesis. The distinctive reactions and enzymes of this pathway are shown
in red. The other reactions are common to glycolysis.in red. The other reactions are common to glycolysis.^ The enzymes for gluconeogenesis areThe enzymes for gluconeogenesis are
located in the cytosol,located in the cytosol, except for pyruvate carboxylase (in the mitochondria)except for pyruvate carboxylase (in the mitochondria)
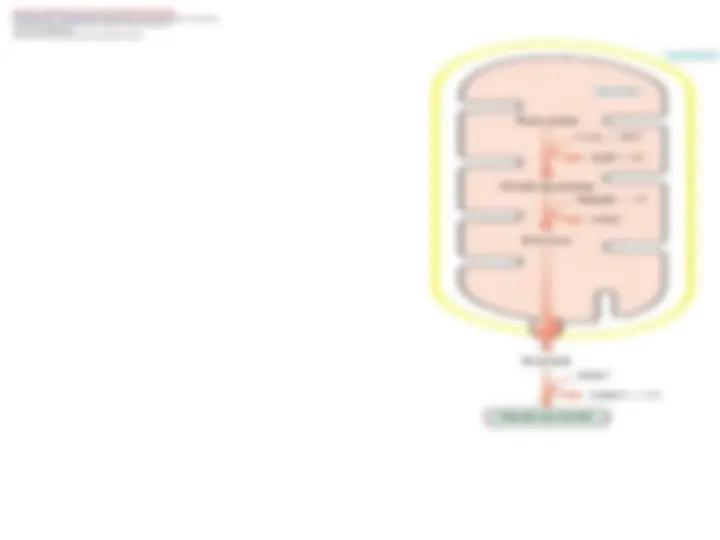
The majorThe major site of gluconeogenesissite of gluconeogenesis isis thethe liverliver , with a small amount also taking place in the, with a small amount also taking place in the kidneykidney. Little gluconeogenesis takes place in the. Little gluconeogenesis takes place in the brainbrain, skeletal, skeletal musclemuscle, or, or heart muscleheart muscle. Rather,. Rather, gluconeogenesis in the liver and kidney helps to maintain the glucose level in the blood so that brain and muscle can extract sufficient glucosegluconeogenesis in the liver and kidney helps to maintain the glucose level in the blood so that brain and muscle can extract sufficient glucose from it to meet their metabolic demandsfrom it to meet their metabolic demands ..
The Conversion of Pyruvate into Phosphoenolpyruvate Begins with the Formation of OxaloacetateThe Conversion of Pyruvate into Phosphoenolpyruvate Begins with the Formation of Oxaloacetate
TheThe first stepfirst step inin gluconeogenesis igluconeogenesis is thes the carboxylation of pyruvatecarboxylation of pyruvate toto form oxaloacetateform oxaloacetate at the expense of a molecule of ATP.at the expense of a molecule of ATP.
this reactions take place inside the mitochondria. this reactions take place inside the mitochondria. reaction reaction isis catalyzedcatalyzed byby pyruvate pyruvate carboxylasecarboxylase ..
Oxaloacetate Is Shuttled into the Cytosol and Converted into PhosphoenolpyruvateOxaloacetate Is Shuttled into the Cytosol and Converted into Phosphoenolpyruvate
Pyruvate carboxylase is a mitochondrial enzyme,Pyruvate carboxylase is a mitochondrial enzyme, Oxaloacetate- is reduced to malate inside the mitochondrion for transport to the cytosol.Oxaloacetate- is reduced to malate inside the mitochondrion for transport to the cytosol. whereas the other enzymes of gluconeogenesis are cytoplasmic.whereas the other enzymes of gluconeogenesis are cytoplasmic.
enzyme- malate dehydrogenase.enzyme- malate dehydrogenase.
When malate has been transported across the mitochondrial membraneWhen malate has been transported across the mitochondrial membrane
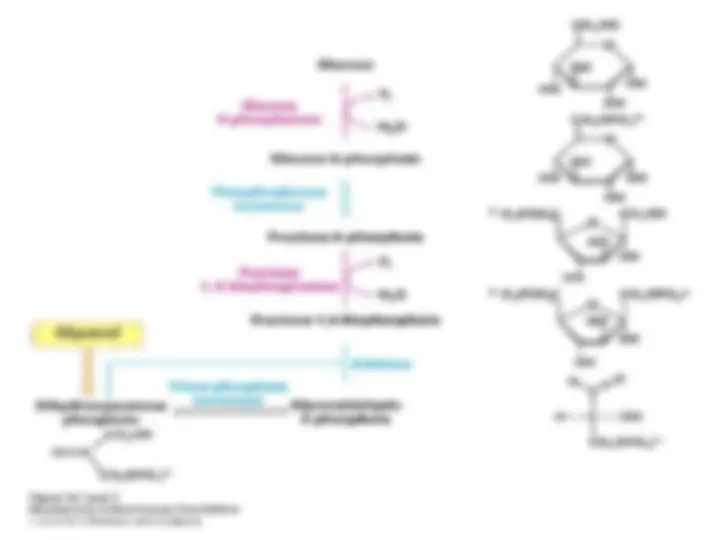
The Generation of Free Glucose Is an Important Control PointThe Generation of Free Glucose Is an Important Control Point
The fructose 6-phosphate generated by fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase is readily converted into glucose 6-phosphate. In most tissues, gluconeogenesis ends here. Free glucose is not generated; rather, the glucose 6-phosphate is processed in some other fashion, notably to form glycogen.The fructose 6-phosphate generated by fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase is readily converted into glucose 6-phosphate. In most tissues, gluconeogenesis ends here. Free glucose is not generated; rather, the glucose 6-phosphate is processed in some other fashion, notably to form glycogen. One advantage to ending gluconeogenesis at glucose 6-phosphateOne advantage to ending gluconeogenesis at glucose 6-phosphate is that,is that,
unlike free glucose,unlike free glucose,^ the molecule cannot diffuse out of the cell.the molecule cannot diffuse out of the cell.
This final step in the generation of glucose does not take place in the cytosolThis final step in the generation of glucose does not take place in the cytosol then shuttled back to the cytosol by a pair of transportersthen shuttled back to the cytosol by a pair of transporters. The glucose transporter in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane is like those found in the plasma membrane. It is striking that five proteins are needed to transform cytosolic glucose 6-phosphate into glucose.. The glucose transporter in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane is like those found in the plasma membrane. It is striking that five proteins are needed to transform cytosolic glucose 6-phosphate into glucose.. Rather, glucose 6-phosphate. Rather, glucose 6-phosphate is transported into the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum,is transported into the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum, where it is hydrolyzed to glucose by glucose 6-phosphatase, which is bound to the membrane. An associated Cawhere it is hydrolyzed to glucose by glucose 6-phosphatase, which is bound to the membrane. An associated Ca 2+2+-binding stabilizing protein is essential for phosphatase activity.-binding stabilizing protein is essential for phosphatase activity. Glucose and PGlucose and Pii areare
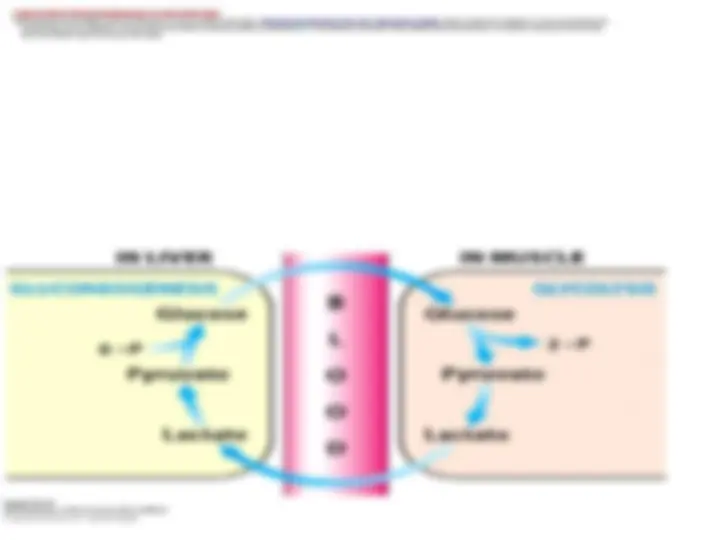
Lactate and Alanine Formed by Contracting Muscle Are Used by Other OrgansLactate and Alanine Formed by Contracting Muscle Are Used by Other Organs
Lactate produced by active skeletal muscle and erythrocytes is a source of energy for other organs.Lactate produced by active skeletal muscle and erythrocytes is a source of energy for other organs. Erythrocytes lack mitochondria and can never oxidize glucose completelyErythrocytes lack mitochondria and can never oxidize glucose completely. lactate is a dead end in metabolism. It must be converted back into. lactate is a dead end in metabolism. It must be converted back into
pyruvate before it can be metabolized. The only purpose of the reduction of pyruvate to lactate is to regeneratepyruvate before it can be metabolized. The only purpose of the reduction of pyruvate to lactate is to regenerate NADNAD++^ so that glycolysis can proceed in active skeletal muscle and erythrocytes.so that glycolysis can proceed in active skeletal muscle and erythrocytes. The formation of lactate buys time and shiftsThe formation of lactate buys time and shifts
part of the metabolic burden from muscle to other organspart of the metabolic burden from muscle to other organs ..
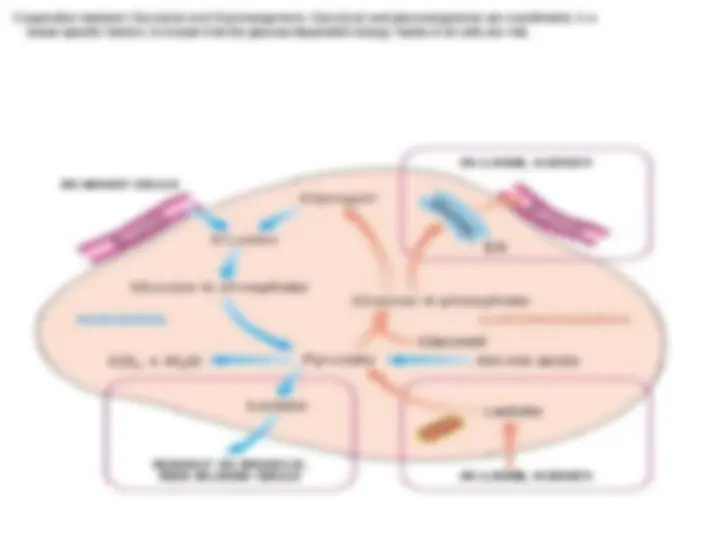
Cooperation between Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis. Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis are coordinated, in aCooperation between Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis. Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis are coordinated, in a tissue-specific fashion, to ensure that the glucose-dependent energy needs of all cells are met.tissue-specific fashion, to ensure that the glucose-dependent energy needs of all cells are met.