




Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
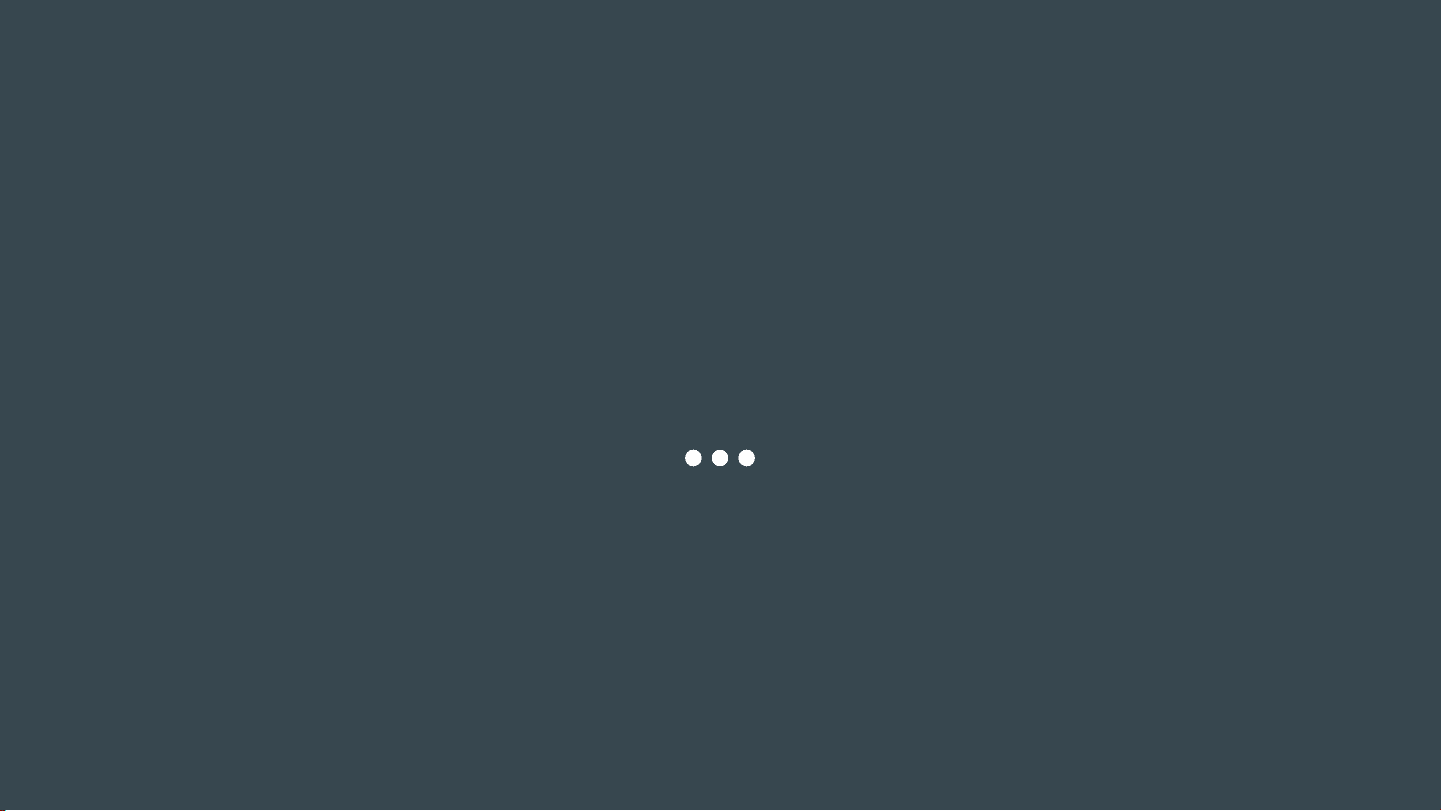
2 types of fermentation. ○ lactic acid. ○ alcoholic ... Lactic Acid Fermentation ... 2 NADH. ○ 2 net ATP. ○ Without O2, the 2 NADH convert back to NAD+.
Typology: Study notes
1 / 9

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!






what you and cheese have in common
● Glycolysis is anaerobic ○ If O2 is present, pyruvic acid goes to mitochondria for aerobic respiration ○ If no O2 is available, fermentation occurs
● Glycolysis produces: ○ 2 pyruvic acids ○ 2 NADH ○ 2 net ATP ● Without O2, the 2 NADH convert back to NAD+ ● NAD+ allows glycolysis to continue ● Electrons released from NADH convert pyruvic acid into lactic acid
● For every glucose broken, you get, ○ 2 net ATP (from glycolysis) ○ 2 lactic acids (from fermentation) ● Lactic acid creates burn in muscles after long use ○ When O2 is added back to the cell, lactic acid breaks down into pyruvic acid ○ When O2 is present, fermentation stops, and respiration continues
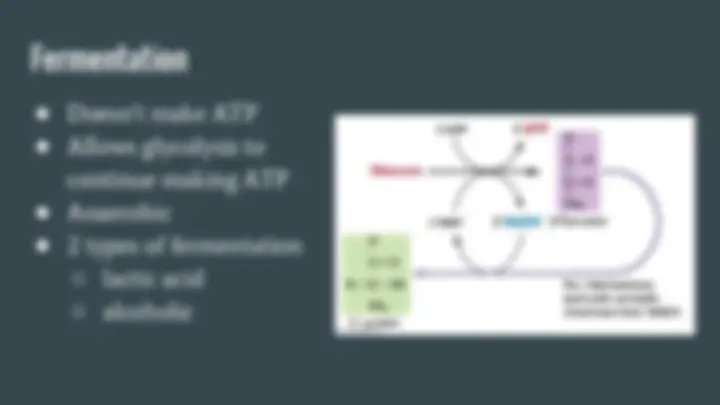
● Similar process to lactic acid fermentation ● Instead of creating lactic acid, the products are ○ ethyl alcohol ○ CO ● HUMANS DO NOT DO THIS!!!
● Formula: pyruvic acid + NADH -> alcohol + CO2 + NAD+ ● Occurs in organisms like yeast ● We use yeast to make: ○ bread (holes in bread are from CO2) ○ alcohols