




Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Material Type: Notes; Class: Pathophysiology; Subject: Biology; University: Missouri Western State University; Term: Unknown 1989;
Typology: Study notes
1 / 7

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




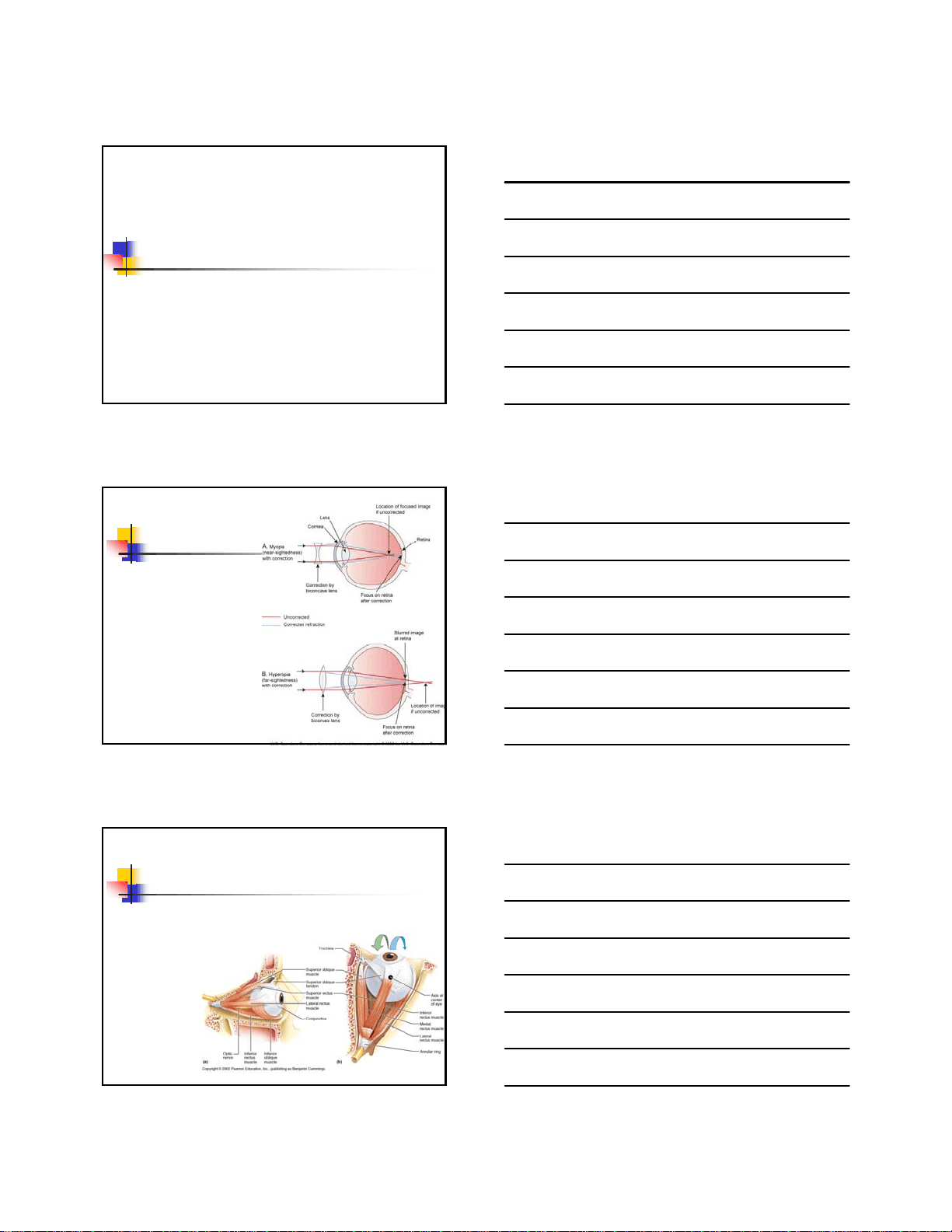
Refraction Defects are typically caused by irregularities in corneal curvature, focusing power of the lens or length of the eyeball Myopia Hyperopia Presbyopia Astigmatism
Movement Defects Strabismus Nystagmus
Allergens and irritating chemicals Staphylococcus aureus causes pinkeye Chlamydia trachomatis andgonorrhea are STD’s that may infect newborns; gonorrhea may be self-inoculated in adults
Abrasions can cause visual loss by damaging the cornea Penetration injuries can cause damage to the internal structures of the eye, allow loss of vitreous humor or allow entrance by microorganisms
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a common cause of visual loss in older persons
Cause seems to be a combination of genetic factors and environmental exposure to UV and drugs
Degeneration occurs at the fovea centralis in the macula lutea, with its high concentration of cones Vision become blurred Loss of depth perception
Conduction deafness Wax accumulation or object in canal Scar tissue or adhesions of eardrum or ossicles Sensorineural deafness Infection Head trauma Ototoxic drugs Sudden loud noise or prolonged exposure to loud noises Presbycusis Congenital deafness
Otitis media Build up of exudate in the cavity impedes movement of eardrum and ossicles Auditory tube usually obstructed by inflammation preventing drainage Increasing pressure may cause rupture of eardrum Prolonged infection can cause scar tissue and adhesions leading to permanent conductive hearing loss May lead to mastoiditis Enlarged adenoids may compress tube
Excess endolymph develops intermittently Attacks may last minutes to hours Causes vertigo, tinnitus and unilateral hearing loss, May result in loss of balance, falls, nausea and vomiting, inability to focus and nystagmus