


























Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
Material Type: Exam; Class: Special Topics Industrial Engr; Subject: Industrial Engineering; University: University of Texas - El Paso; Term: Unknown 2006;
Typology: Exams
1 / 59

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!




















































1.1 Conducting the LCA 1.2 Goal & Scope Definition: ISO 14040 1.3 Goal & Scope Definition: Using GABI
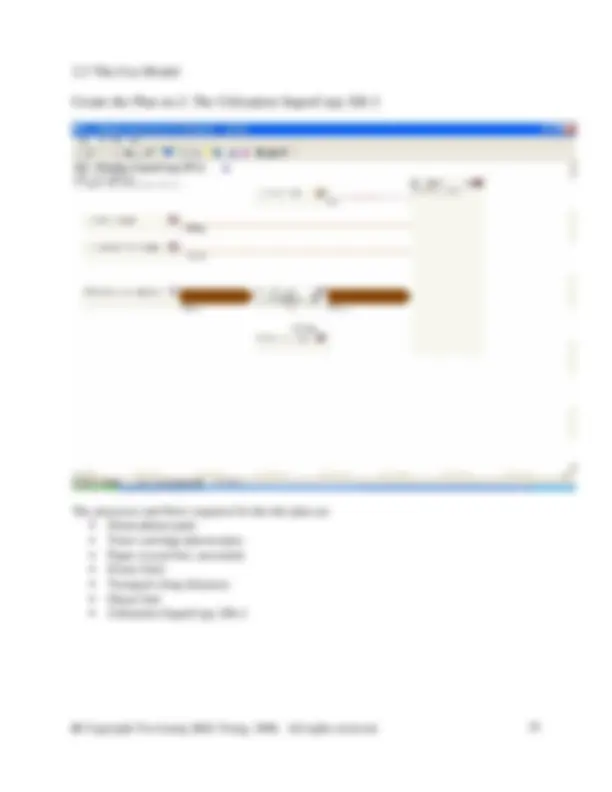
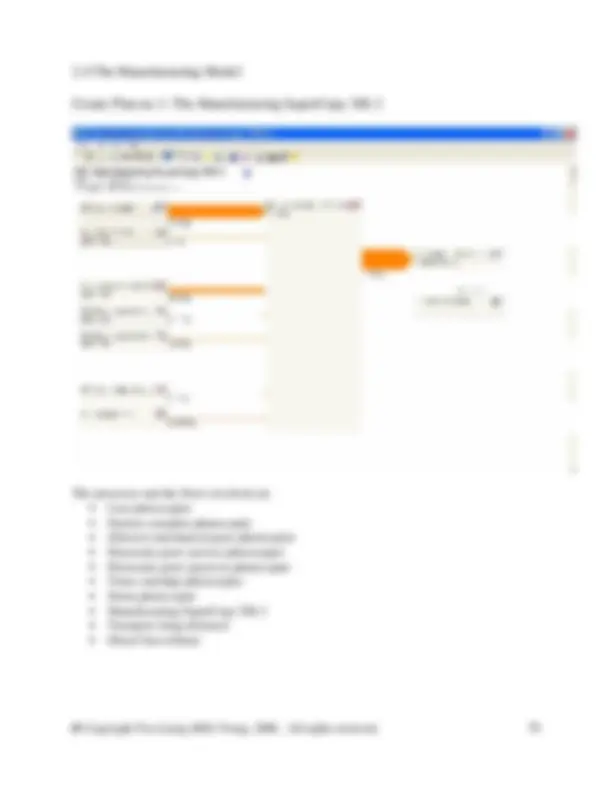
2.1 The Final Model. 2.2 The Recycling Model 2.3 The Use Model 2.4 The Manufacturing Models
3.1 Screening A Balance Result 3.1.1 Mass Balance View 3.1.2 Energy View 3.2 Dominance Analysis 3.3 Characterization, Normalization and Evaluation 3.3.1 Characterization 3.3.2 Normalization 3.3.3 Evaluation
4.1 Parameter Variation. 4.2 Scenario Analysis 4.3 Monte Carlo Analysis
Start
Modeling the System “Photocopier” Single Score Evaluation (GaBi Software)
Data collection (GaBi Software) Dominance Analysis (GaBi Software)
Modeling the Product System Screening the balanceresults (GaBi Software)
First Goal and Scope (GaBi software) Calculating the balances (GaBi Software)
End
The Goal definition shall unambiguously state:
Linking the goal and scope definitions : The process of defining the scope of a study must always be directly related to the goal: The scope should be defined well enough to ensure that the breadth and depth of a study are compatible with and sufficient to address the stated goal. Scope definition is an iterative process (elements of the initially defined scope have to be reviewed and in practice often be revised). If the scope needs to be revised, ensure the definition is still directly linked to the goal. If not the goal definition must be revised. Elements of scope definition according to ISO :
The processes involved in this plan are
MANUFACTURING SUPERCOPY XR- UTILIZATION SUPERCOPY XR- END OF LIFE SUPERCOPY XR- DISPOSAL TONER DISPOSAL AND RECYCLING PRINTED PAPER DISPOSAL DRUM
Starting with No. 6 “ DISPOSAL DRUM ”
To build the Disposal drum Recycling process plan we require:
The required process and the flows can be dragged and dropped on to the plan. If any process or flow is missing then we have to create according to the data available.
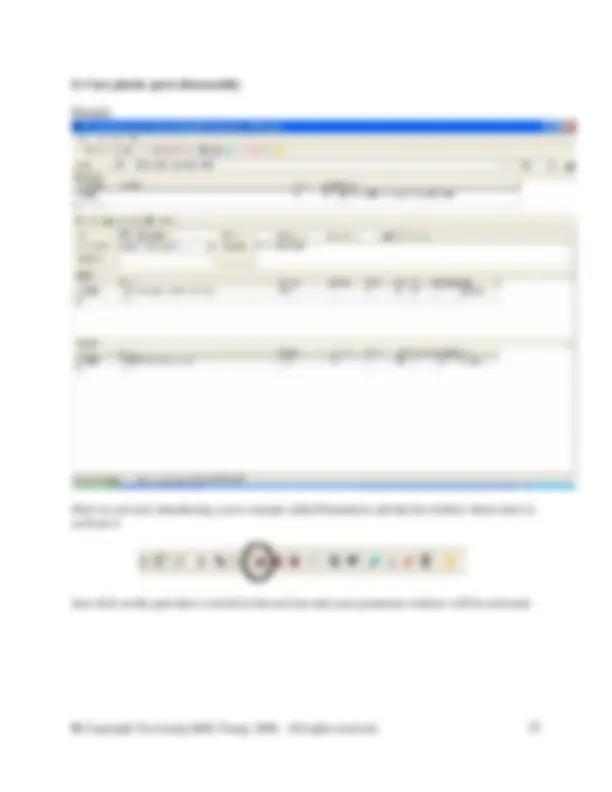
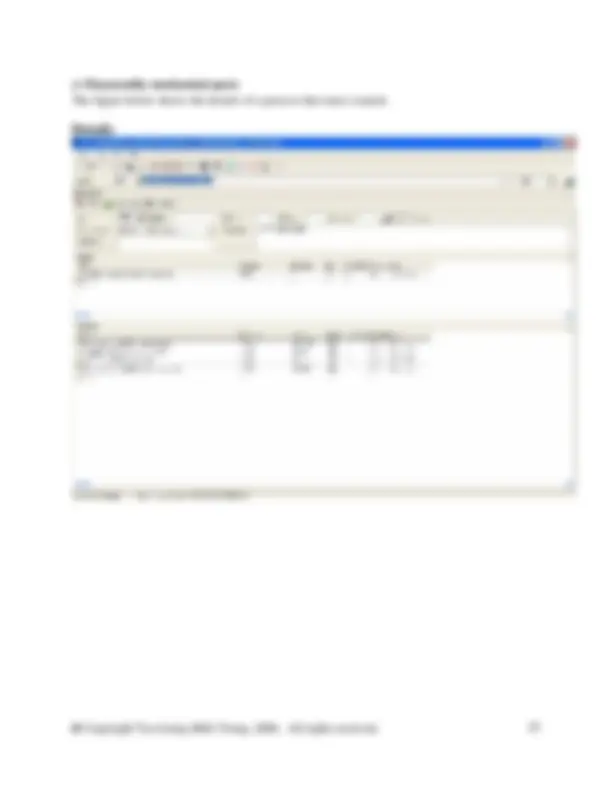
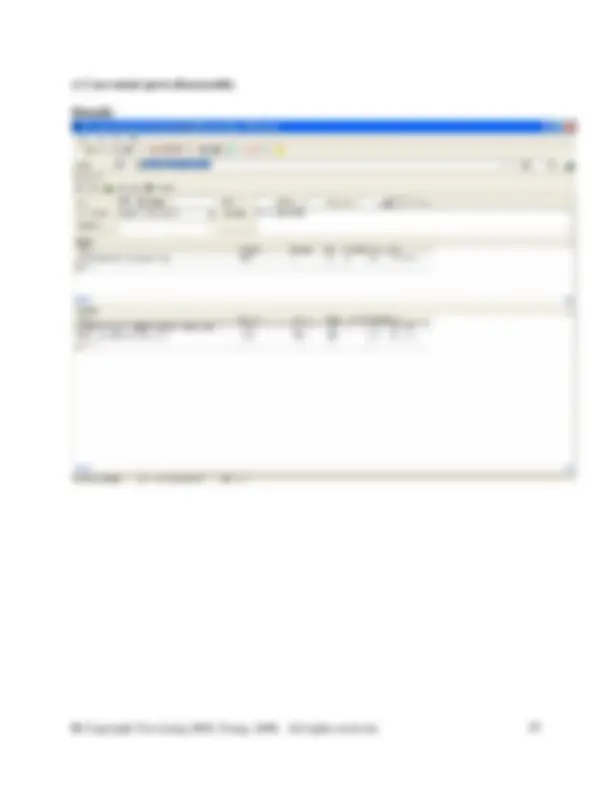
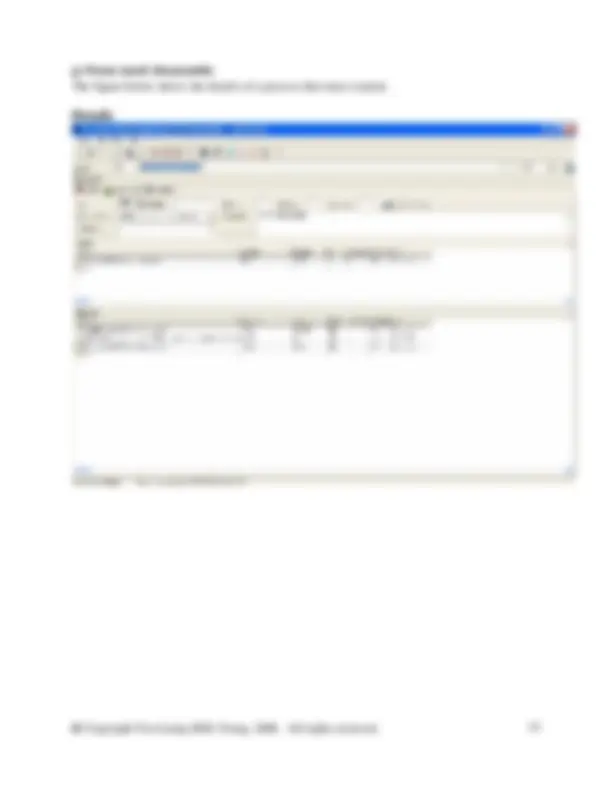
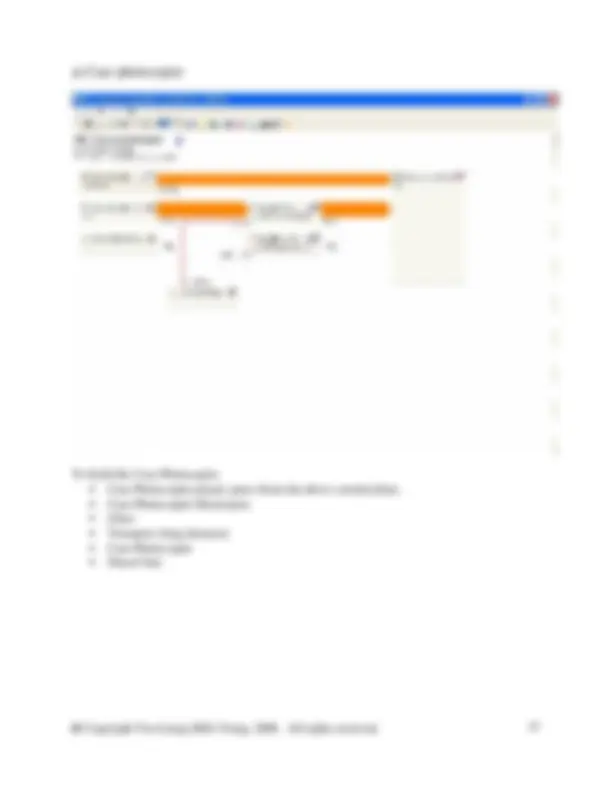
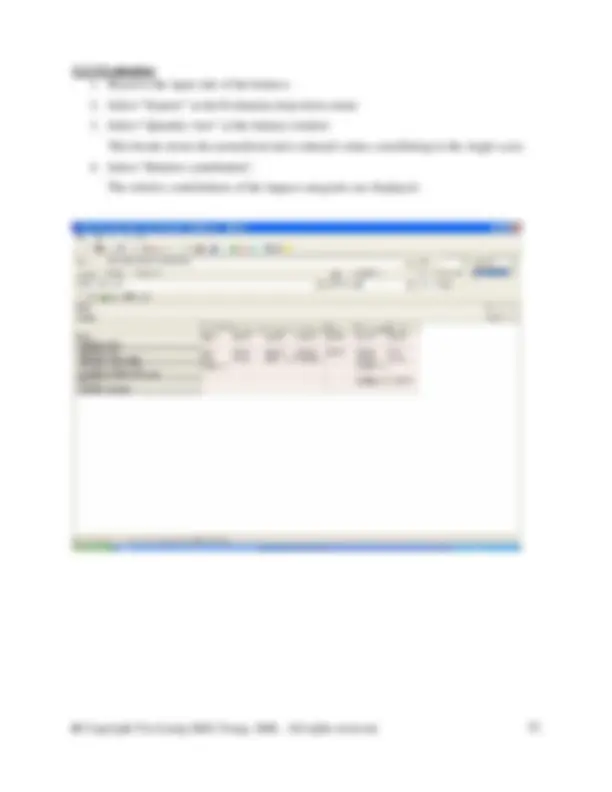
The figure below shows the details of a process that must created.
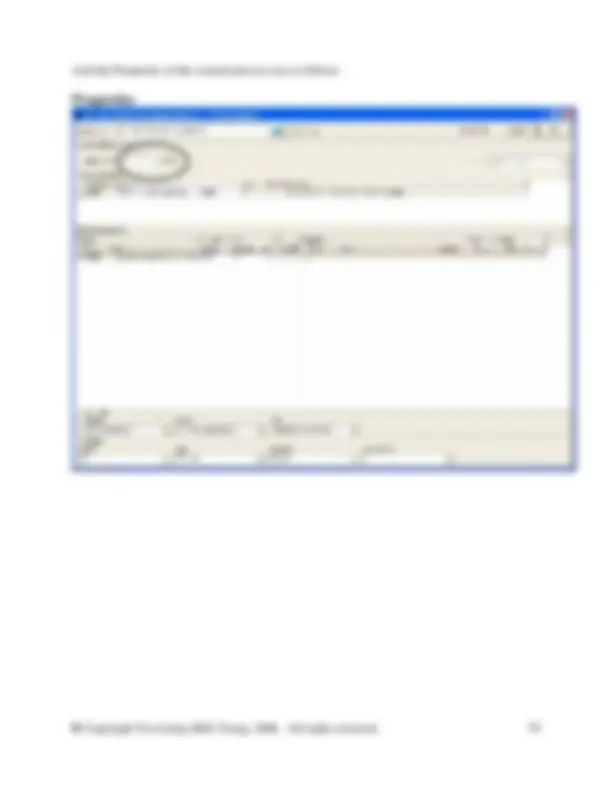
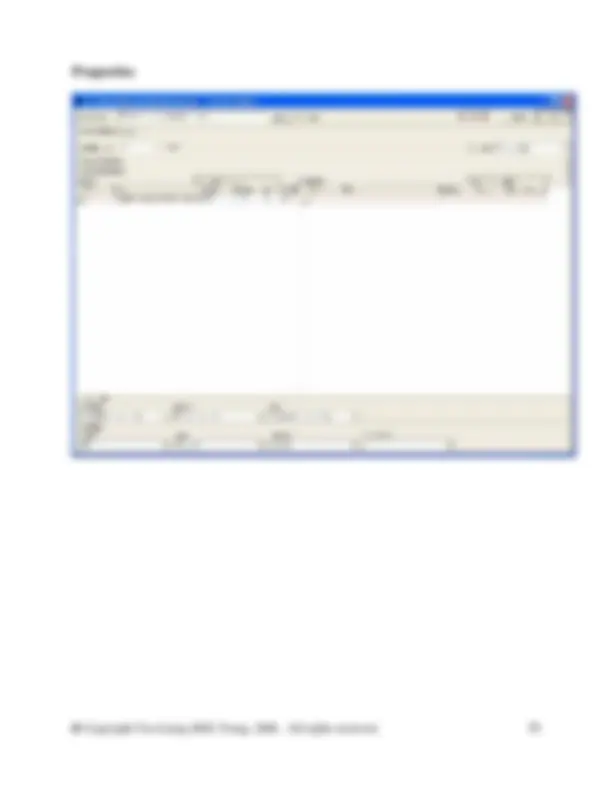
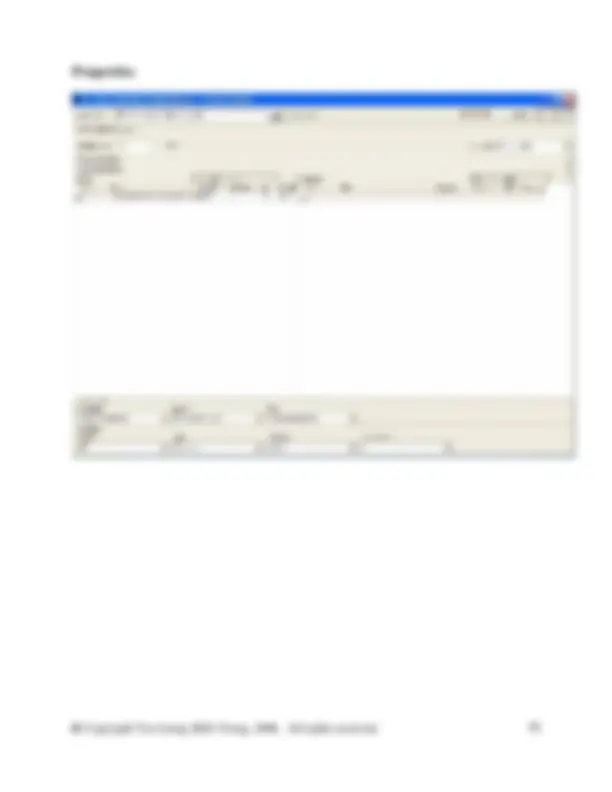
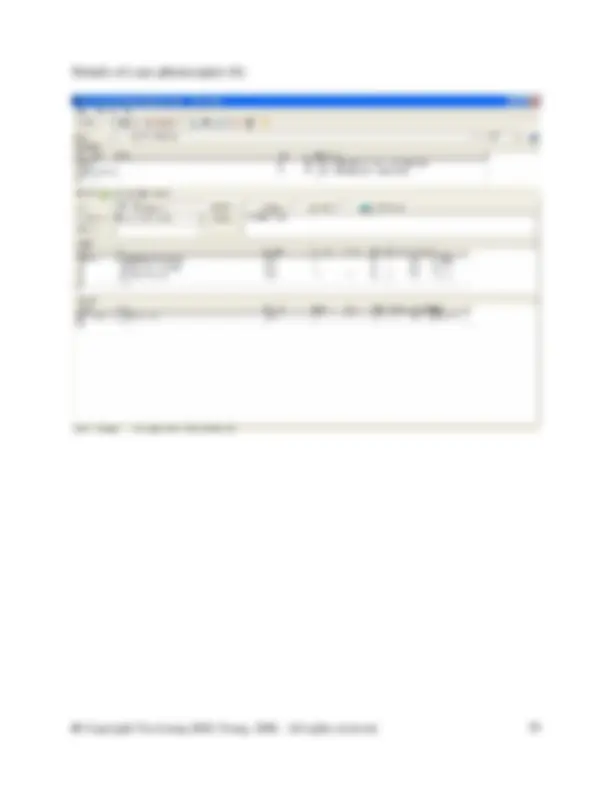
In the database manager, in category waste for recovery, right click on the right side of the DB Manager to create a new unit process. Fill in the information as shown in the screen shot above. You will need to create a new flow here called Steel scrap (St). To do so switch to the DB Manager and crate it in the flow hierarchy in the waste for recovery category. Right click and select new from the menu. Complete the new flow as shown in the figure below. Then close the new flow and switch back to your unit process to enter the new flow.
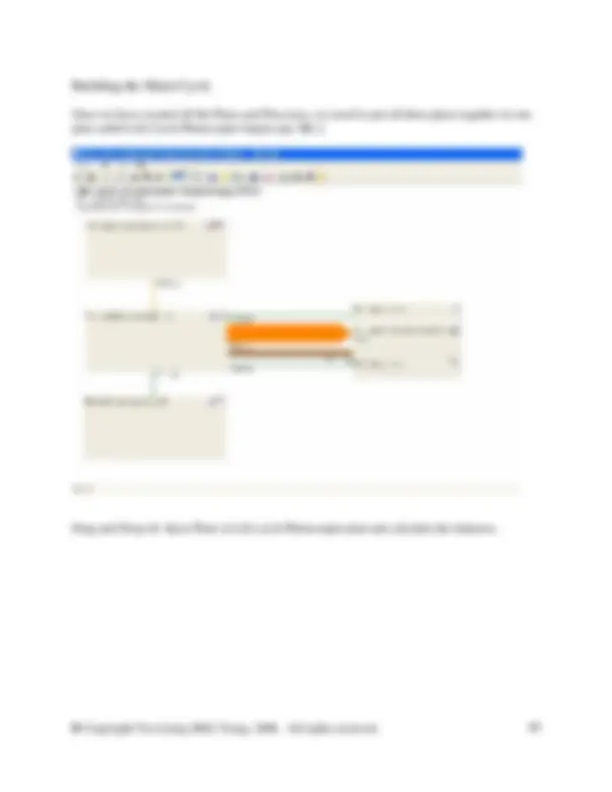
Complete the plan by connecting the unit processes and fixing the Drum disassembly process to one. Fixing a processes can be done be double clicking on the process itself, and entering a “1” in the Scaling Factor box and ticking the checkbox marked Fixed.
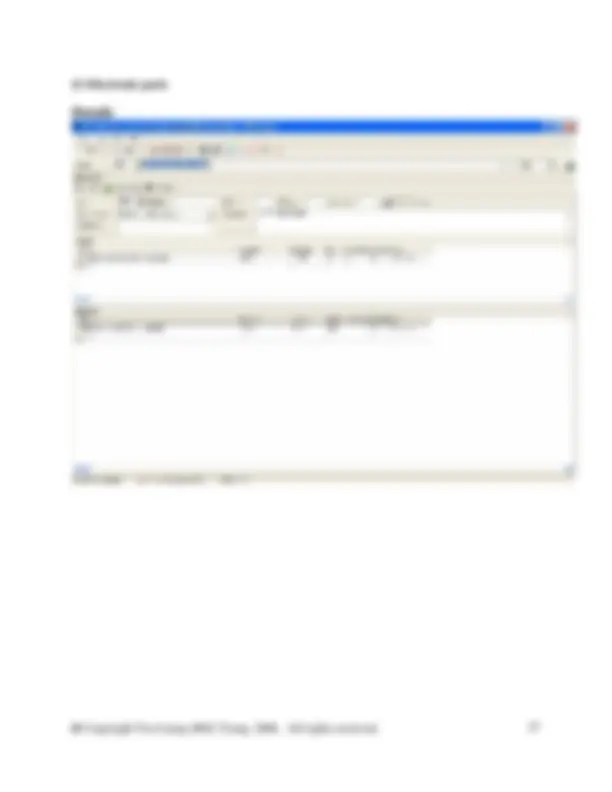
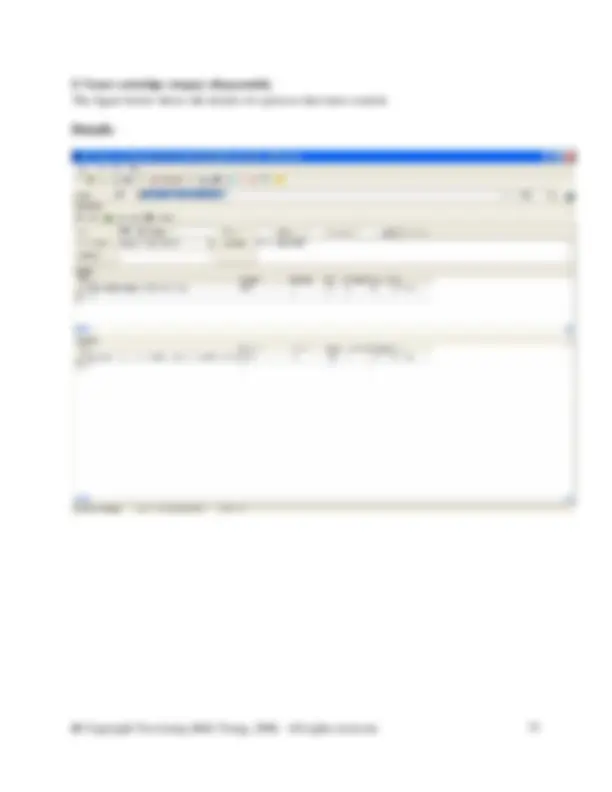
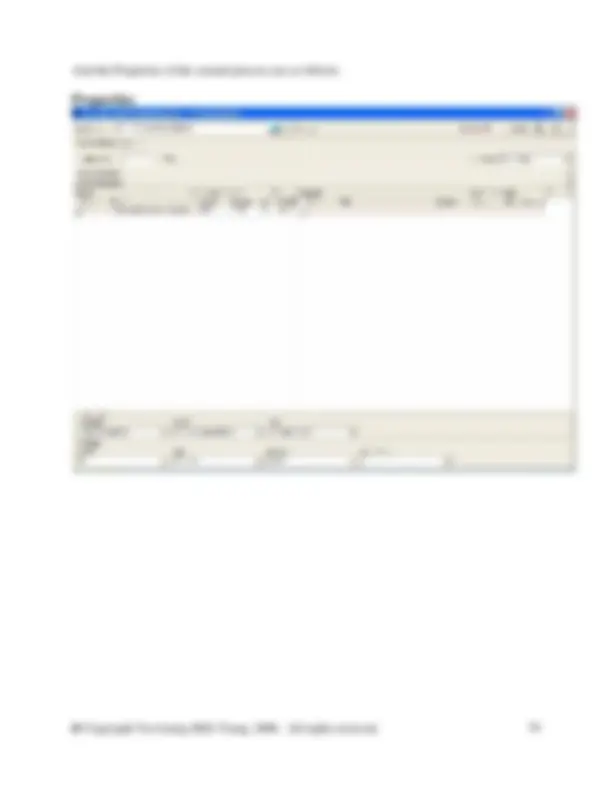
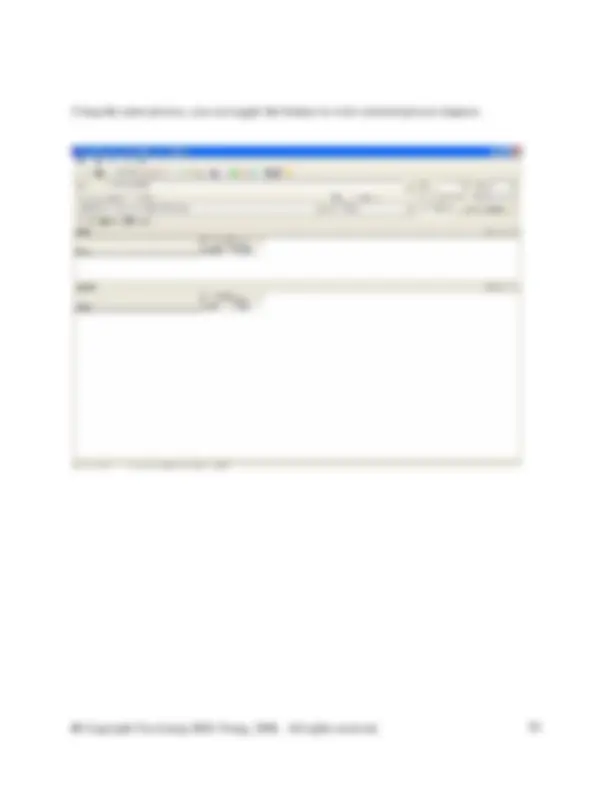
As mentioned above create a new flow called Water (feed water) in water of the flow hierarchy
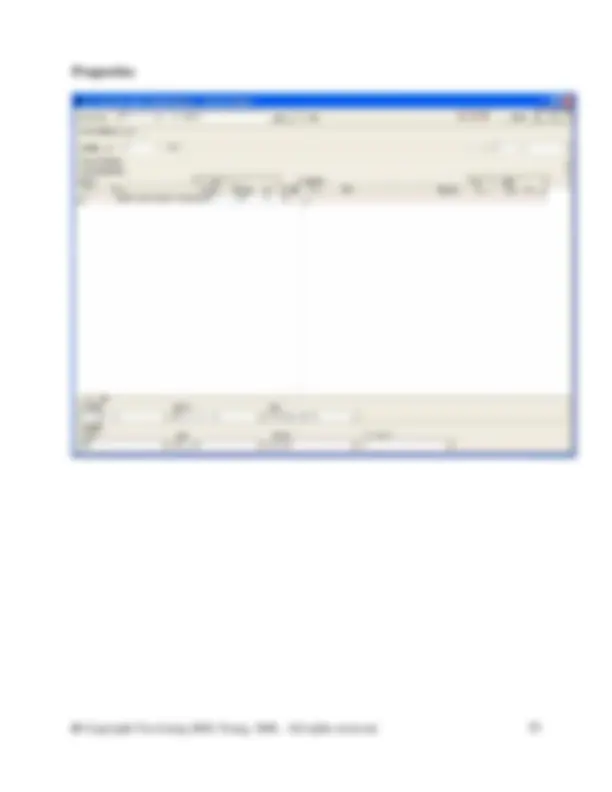
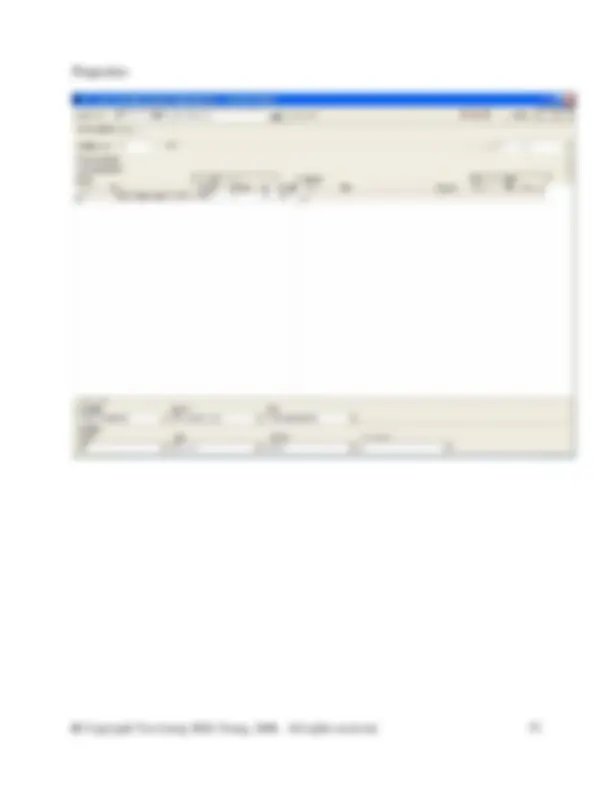
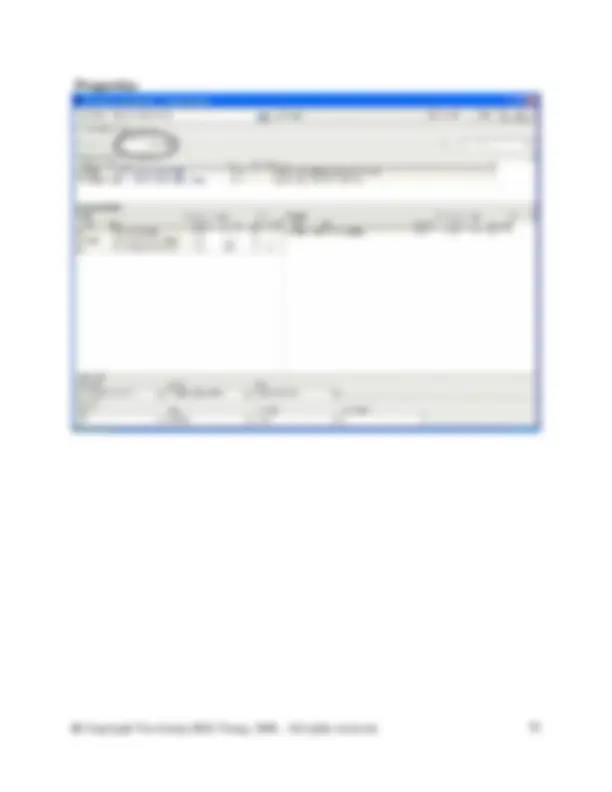
And the Properties of the Waste paper recycling are as follows:
The processes we require for Disposal toner are as follows Toner cartridge disassembly Diesel fuel Transport (long distance) Waste incineration plant Gas and steam power plant
The processes we require End of Life SuperCopy XR- for are as follows
Now we are going to create processes for all listed below
a) Drawer disassembly