





































Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan


Prepare for your exams
Study with the several resources on Docsity

Earn points to download
Earn points by helping other students or get them with a premium plan
Community
Ask the community for help and clear up your study doubts
Discover the best universities in your country according to Docsity users
Free resources
Download our free guides on studying techniques, anxiety management strategies, and thesis advice from Docsity tutors
The organization of a pipelined datapath in computer architecture, including the roles of each stage (if, id, ex, mem, wb) and the usage of registers and control signals. It also discusses data hazards and forwarding techniques to mitigate their effects.
Typology: Assignments
1 / 44

This page cannot be seen from the preview
Don't miss anything!





































Instructi on fetch Re g ALU Data Access Reg Instructi on fetch Re g ALU Data Access Reg Instructi on fetch Re g ALU Data Access Reg
lw $1, 100($0)
lw $2, 100($0)
lw $3, 100($0)
Prog. Exec. Order
Instructi on fetch Reg ALU Data Access Reg Instructi on fetch Re g ALU Data Access Reg R e ALU Data Access Reg g
Instruct ion fetch
lw $1, 100($0)
lw $2, 100($0)
lw $3, 100($0)
Prog. Exec. Order
(^) What makes it easy? (^) all MIPS instructions are the same length (fetch) (^) just a few instruction formats ( rs, rt fields are invariant) (^) memory operands appear only in loads and stores
(^) What makes it hard? (^) structural hazards: suppose we had only one memory (^) control hazards: need to worry about branch instructions (^) data hazards: an instruction depends on a previous instruction
(^) We’ll talk about data hazard and forwarding, stalls and branch hazards
(^) We’ll talk about exception handling
Pipelining
(^) 5 -> 2
(^) 4 -> 1
A Pipelined Datapath
Five-stage Pipeline
Five-stage Pipeline
Five-stage Pipeline
CC2, CC3 and CC4 respectively
Five-stage Pipeline Registers
Allows the ID stage to decode instruction 1, while IF stage fetches instruction 2
ID/EX Latch: Stores the sign-extended immediate value and values fetched from register rs and rt Allows EX stage to utilize stored values, while the ID stage decodes Inst. 2 and the IF stage fetches register for instruction 3 EX/MEM Latch: Stores the branch target address, the ALU result, ALU output bit and value in the rt register Allows MEM stage to use stored values, while EX and ID stage execute the following instructions MEM/WB Latch: Stores ALU result and Data read from memory Allows WB stage to use stored data, while data memory fetches data for the following Instruction
Announcement
Review (1)
(^) Instruction fetch (IF) (^) Instruction decode and register fetch (ID) (^) Execute (EX) (^) Memory access (MEM) (^) Write back (WB)
Hardware Usage
IM Reg ALU DM Reg
IM Reg ALU DM Reg
CC 1 CC 2 CC 3 CC 4 CC 5 CC 6 CC 7
Time (in clock cycles)
lw $ 2 , 200 ($ 0 )
lw $ 3 , 300 ($ 0 )
Program execution order (in instructions) lw $1, 100($0) IM Reg ALU DM Reg
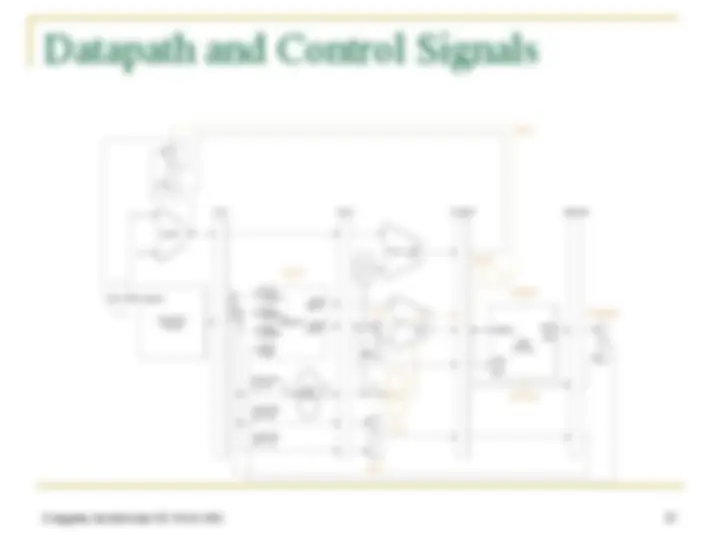
Pipelined Datapath
In mstreumcotioryn
Address
4
32
0
Add (^) resultAdd left 2Shift
Instruction
IF/ID EX/MEM MEM/WB
M u x
0 1
Add
PC
0
Address
Write data
M u x
Registers 1
data 1Read data 2Read
Read register 1 Read register 2
(^16) Sign extend
Write register Write data
Read data memoryData 1
resultALU M u x
ALUZero
ID/EX